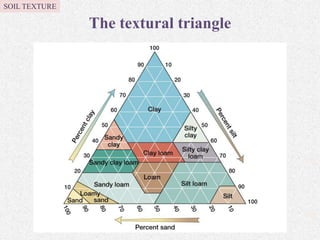
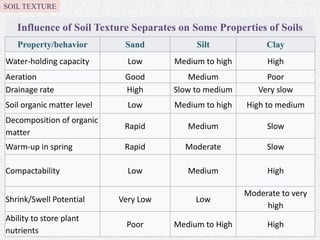
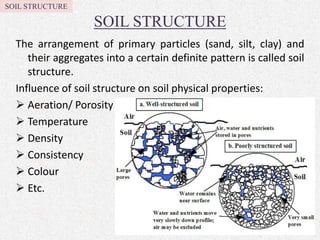
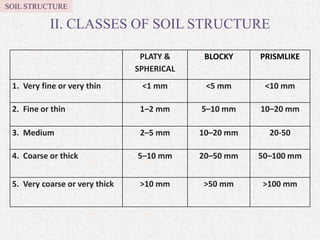
Soil texture refers to the relative percentages of sand, silt, and clay in soil. Texture influences various soil properties like water holding capacity, aeration, drainage, and nutrient storage. The arrangement of soil particles into aggregates is called soil structure, which also impacts properties such as porosity, density, and consistency. Common soil structures include platy, prismatic, blocky, granular, and crumb structures. Factors like organic matter, tillage practices, climate, and soil fauna influence aggregate formation and stability. Ideal soil structure, such as moderate or crumb structure, supports plant growth through improved drainage, aeration, and habitat for microbes.