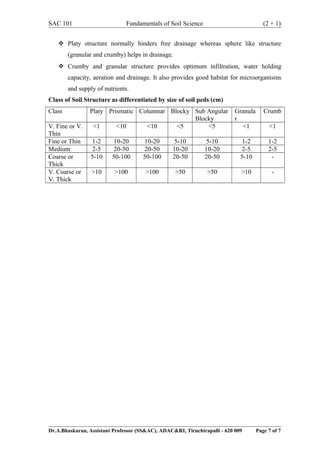
This document discusses soil structure, including its definition, significance, formation, classification, and factors affecting it. Soil structure refers to the arrangement and grouping of individual soil particles. It is significant as it influences properties like water movement, aeration, and porosity. Soil structure is formed through the binding and cementing of primary particles into aggregates or secondary particles. Aggregates are classified based on their type (shape), class (size), and grade (distinctness). Factors like climate, organic matter, and tillage influence the development of soil structure.