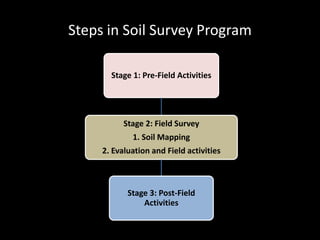
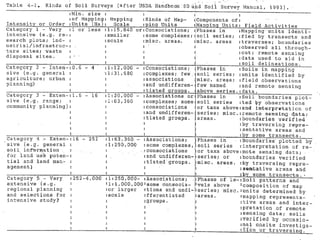
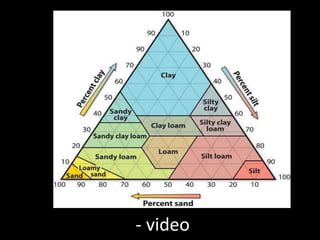
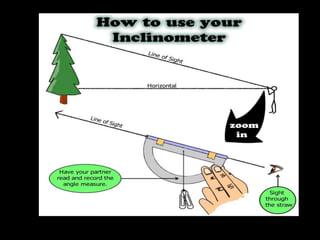
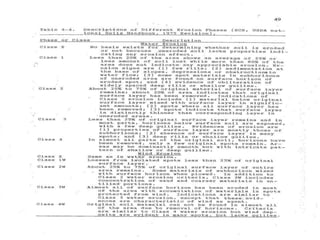
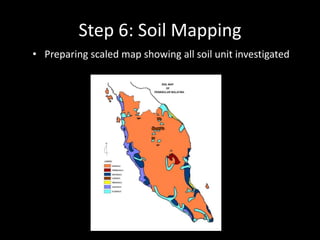
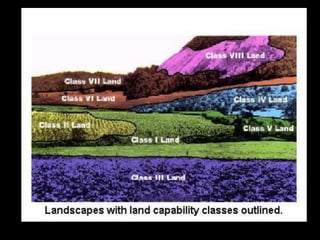
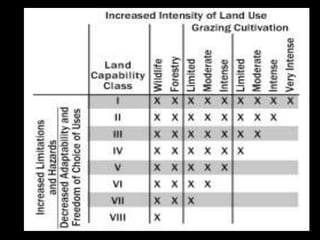
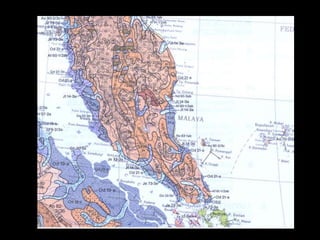
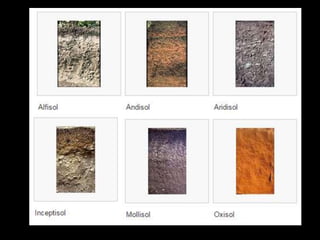
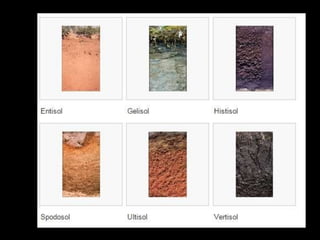
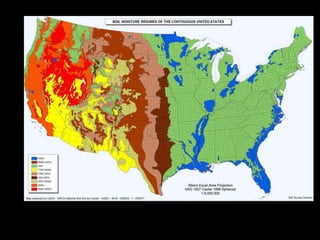
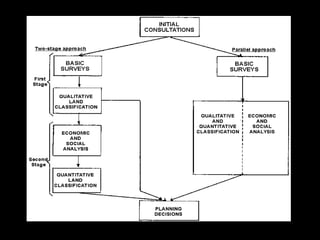
Chapter 4 covers soil survey methodologies, classifications, and land evaluations. It outlines the steps of soil survey, including pre-field, field, and post-field activities, and discusses soil classification systems like FAO/UNESCO and USDA. Additionally, it highlights the importance of land evaluation in assessing property value, considering both physical and socio-economic factors.