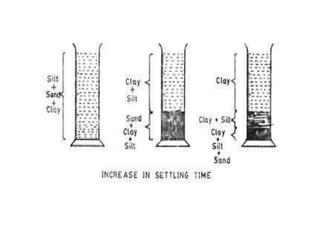
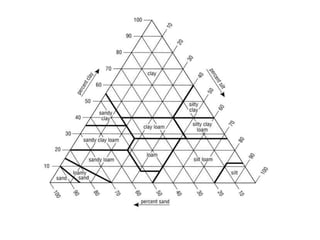
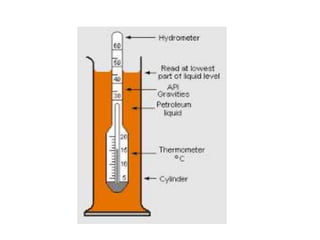
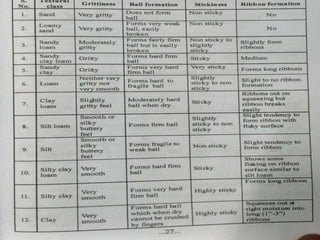
This document defines soil texture and describes several systems used for soil particle classification. It explains that soil texture refers to the proportions of sand, silt, and clay in a soil sample. Several methods are presented for determining soil texture through mechanical analysis and measurement of particle sizes, including the pipette method, hydrometer method, and feel method. The influence of different soil textures on properties like water retention, aeration, and crop growth are also discussed.