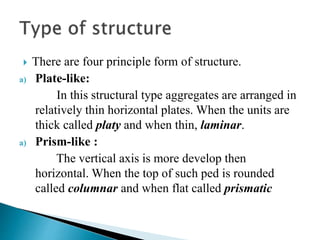
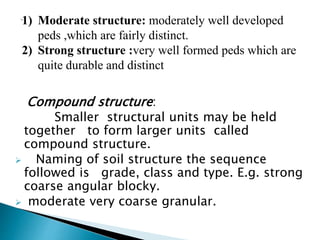
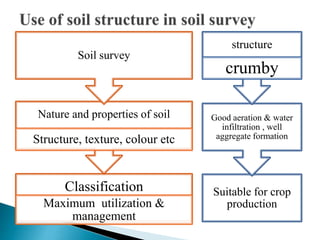
Soil structure refers to the arrangement of soil particles into aggregates. There are four principal types of soil structure: platy, prismatic, blocky, and spheroidal. Within each type are size classes from very fine to very coarse. Structure grade indicates the distinctness of aggregates and is classified as structureless, weak, moderate, or strong. Compound structure occurs when smaller units combine into larger ones. Proper soil structure promotes good aeration, water infiltration, and aggregate formation beneficial for crop production.