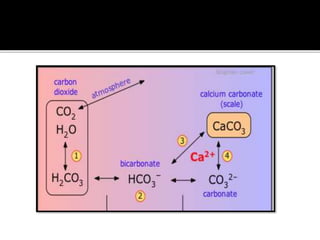
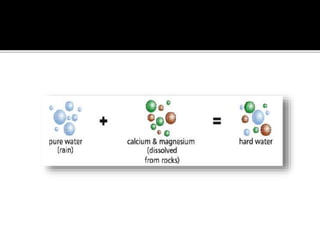
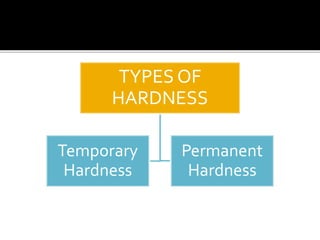
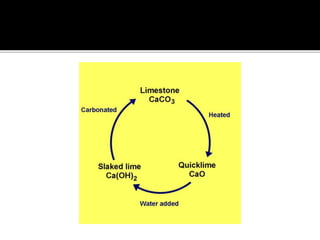
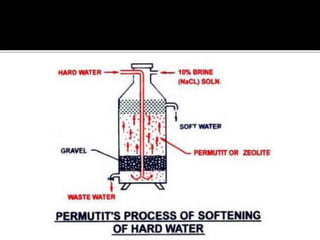
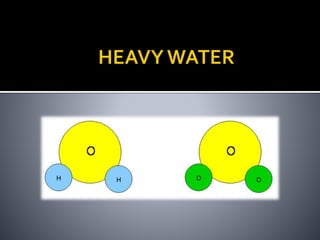
The document explains the concepts of hard and soft water, detailing their definitions, types, and methods to remove hardness, including temporary and permanent hardness. It also discusses heavy water (deuterium oxide), its properties, and compares it to regular water. Additionally, the document introduces hygroscopic and deliquescent substances, highlighting their moisture-absorbing characteristics and uses.