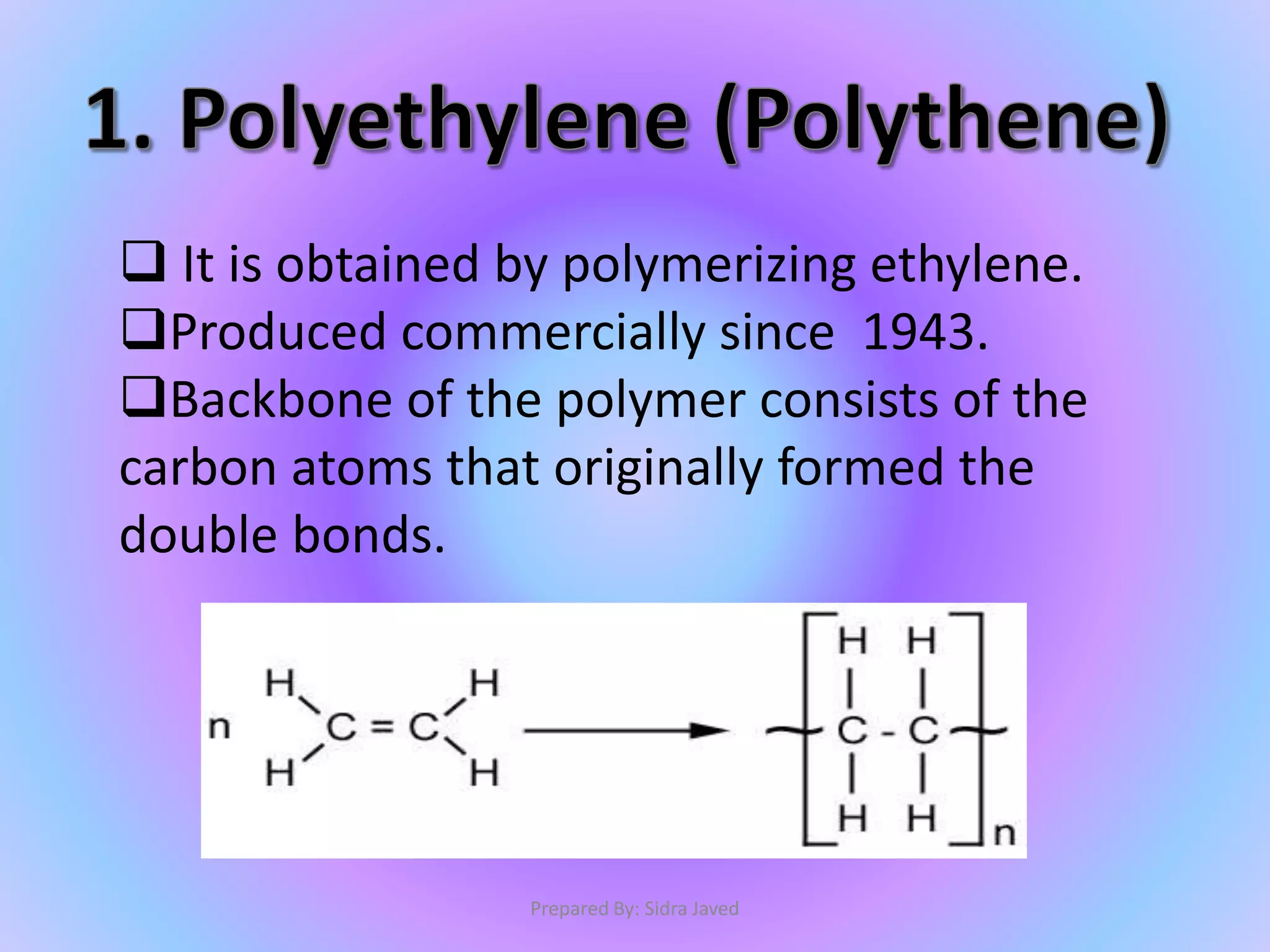
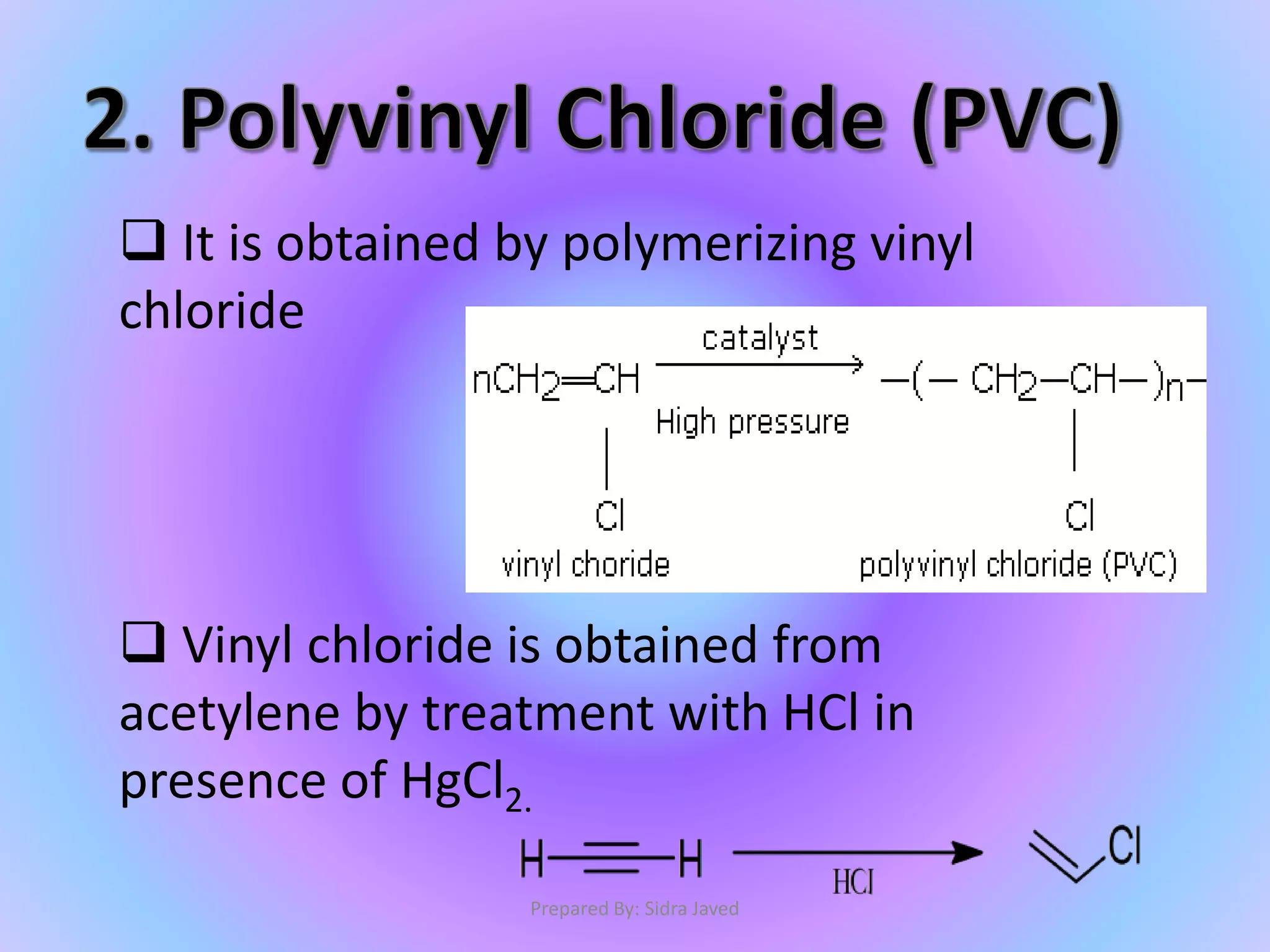
Polymers are composed of repeating monomer units that are linked through polymerization reactions. There are two main types of polymerization: addition and condensation. Polyethylene is an example of an addition polymer formed from ethylene monomers under high pressure and temperature. Nylon-6,6 is a condensation polymer formed from adipic acid and hexamethylene diamine monomers. Polyethylene and nylon-6,6 have a variety of commercial uses including packaging materials, textiles, and carpeting.