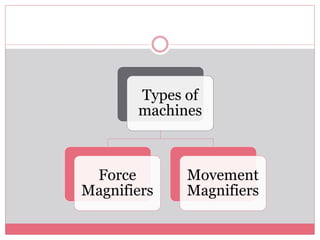
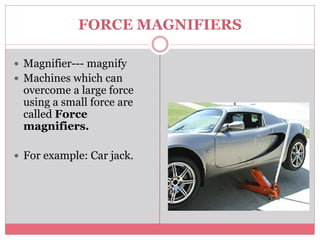
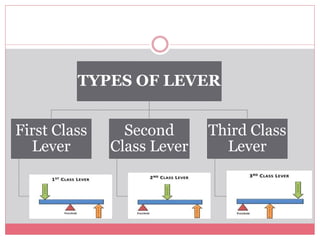
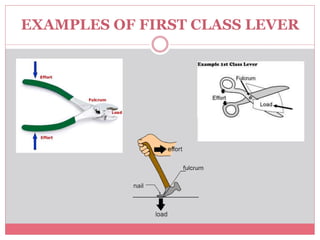
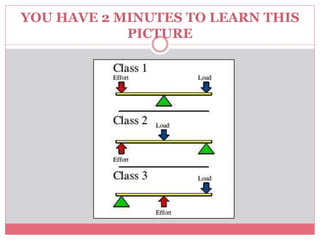
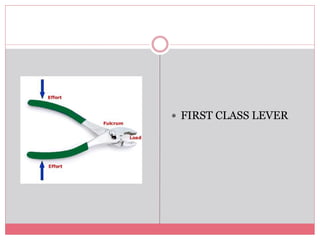
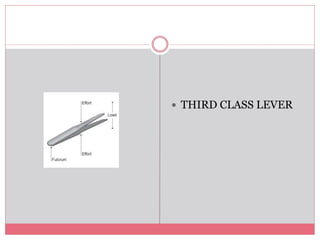
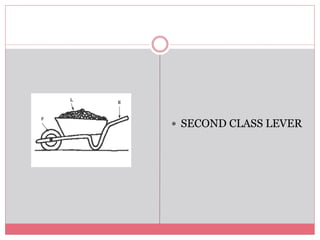
The document introduces simple machines and their classifications, explaining their function as devices that make work easier. It details the different types of levers—first class, second class, and third class—highlighting their mechanics and examples. The content includes interactive elements for review and comprehension.