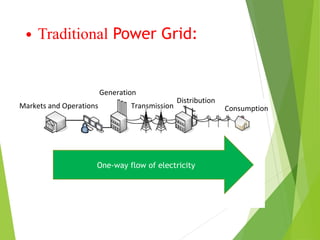
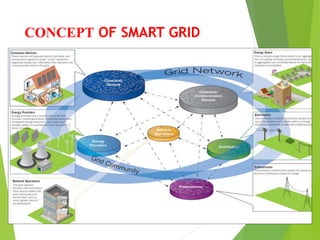
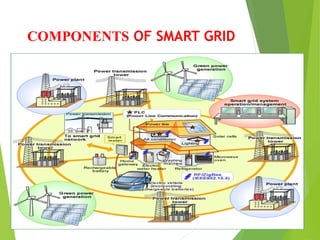
The document discusses smart grids, which use digital technology to allow two-way communication between electricity suppliers and consumers. This allows utilities to remotely control appliances to save energy and reduce costs and outages. Key benefits are increased reliability, lower costs, and reduced emissions. Smart grids automate control of individual devices or millions of devices from a central location. They are needed due to increasing energy demand, limited resources, and reliability issues with traditional grids. Components include power infrastructure, communication infrastructure, and markets and operations systems that allow two-way electricity and information flows.