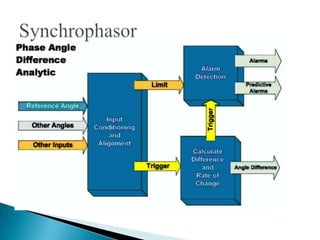
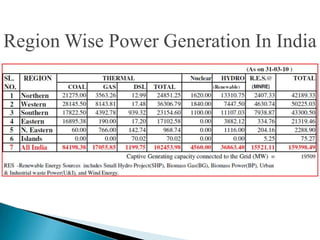
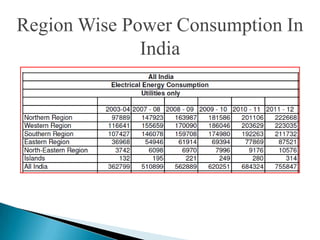
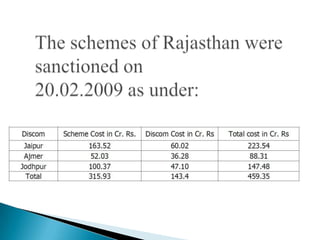
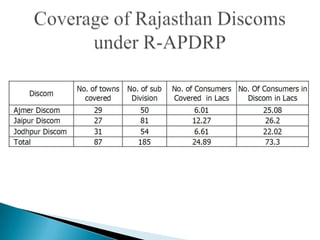
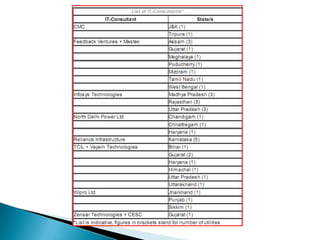
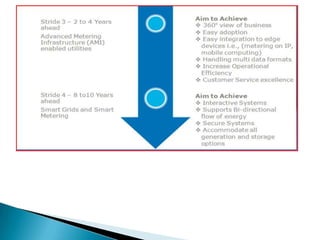
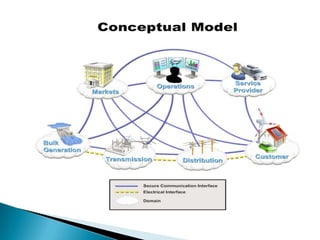
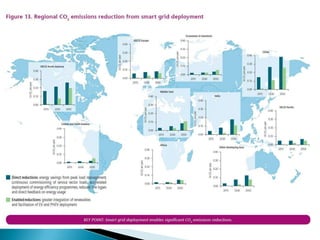
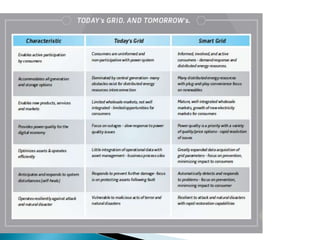
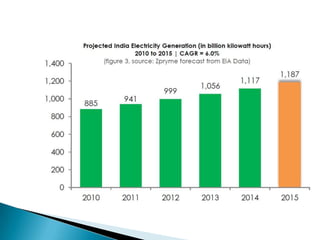
The document discusses the implementation of the Restructured Accelerated Power Development and Reforms Program (R-APDRP) in Rajasthan, India. Key points:
- R-APDRP aims to establish reliable baseline data and adopt IT in energy accounting to reduce losses before distribution strengthening projects.
- It has two parts - Part A focuses on IT applications for energy auditing and consumer services. Part B covers network renovation.
- The Discoms of Rajasthan have taken steps like forming implementation committees and appointing an IT consultant to timely execute the scheme and avail grants.
- Benefits of R-APDRP include increased consumer satisfaction, transparency, reduced out