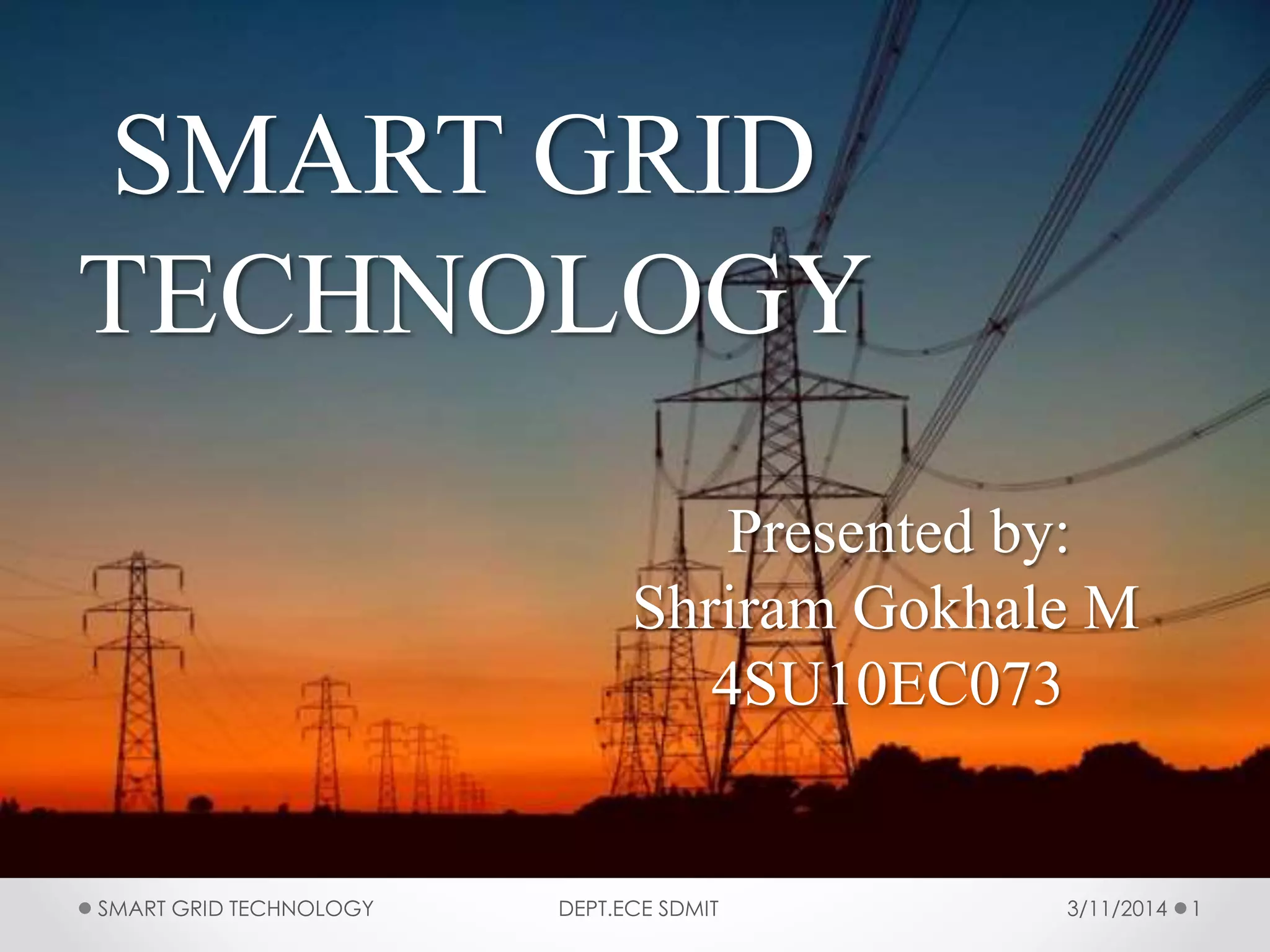
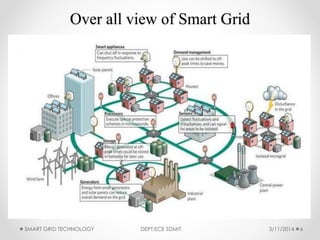
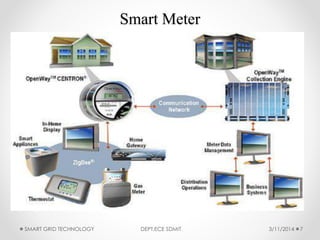
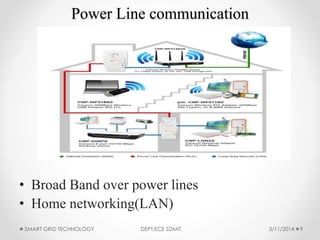
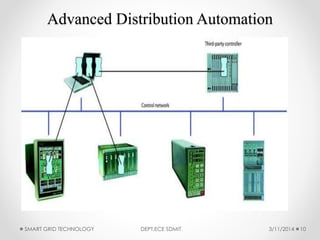
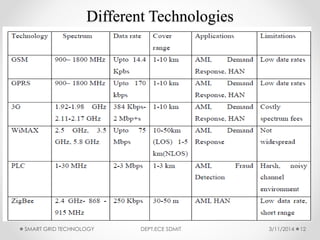
The document discusses smart grid technology, including its key features and components. A smart grid uses two-way digital communication to deliver power more efficiently by integrating renewable energy, automated demand response, and distributed generation. It allows for better management of supply and demand through technologies like smart meters, power line communication, and advanced distribution automation. The smart grid aims to address issues with existing power grids like high outage costs and inefficient peak load management through real-time monitoring and control enabled by communication networks and technologies. Future work is still needed in areas like security, standardization, and reducing upfront consumer expenses.