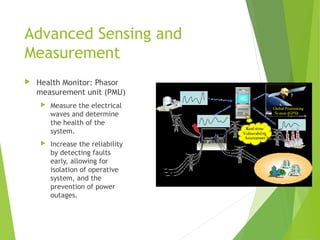
The document discusses the concept of a smart grid and its key components. It notes that power disturbances currently cost $25-188 billion per year and the 2003 Northeast blackout alone resulted in $6 billion in losses. A smart grid would have advanced sensing and measurement technologies like smart meters, phasor measurement units, and distributed weather sensors to improve reliability. It would also feature integrated communications, advanced energy storage, and control methods that allow for more decentralized energy generation and fault isolation. The smart grid aims to create a more intelligent, interactive electricity infrastructure.