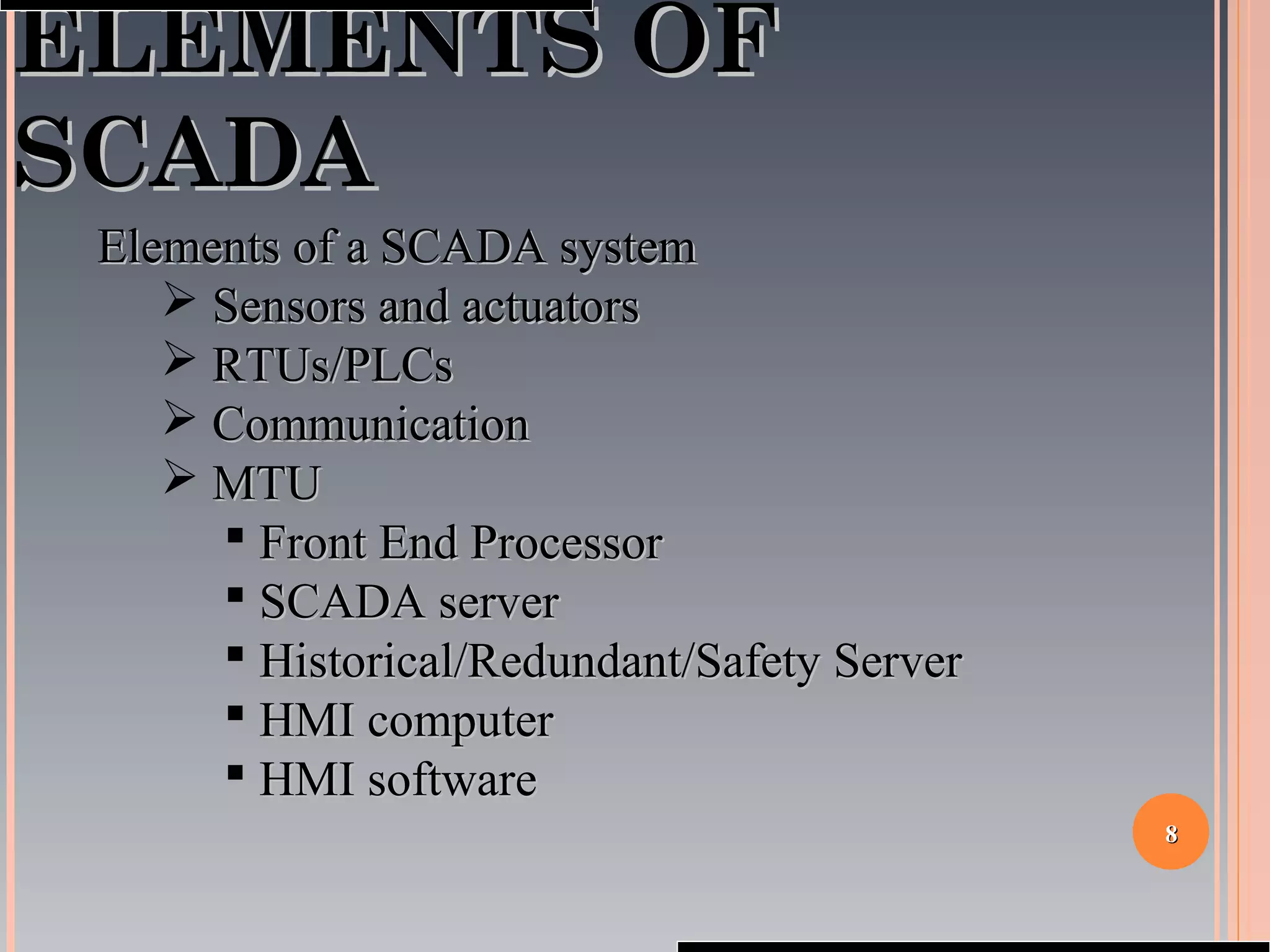
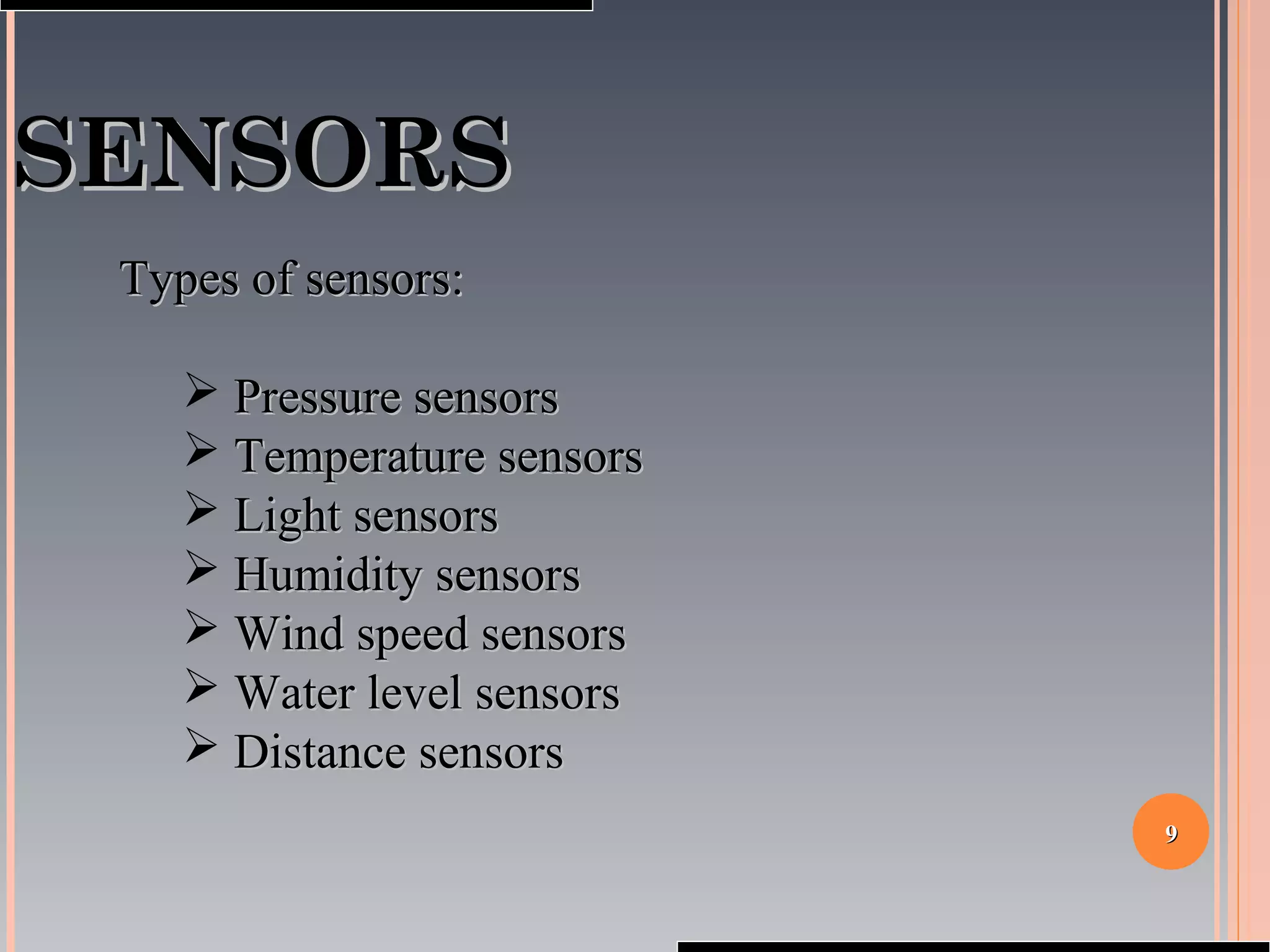
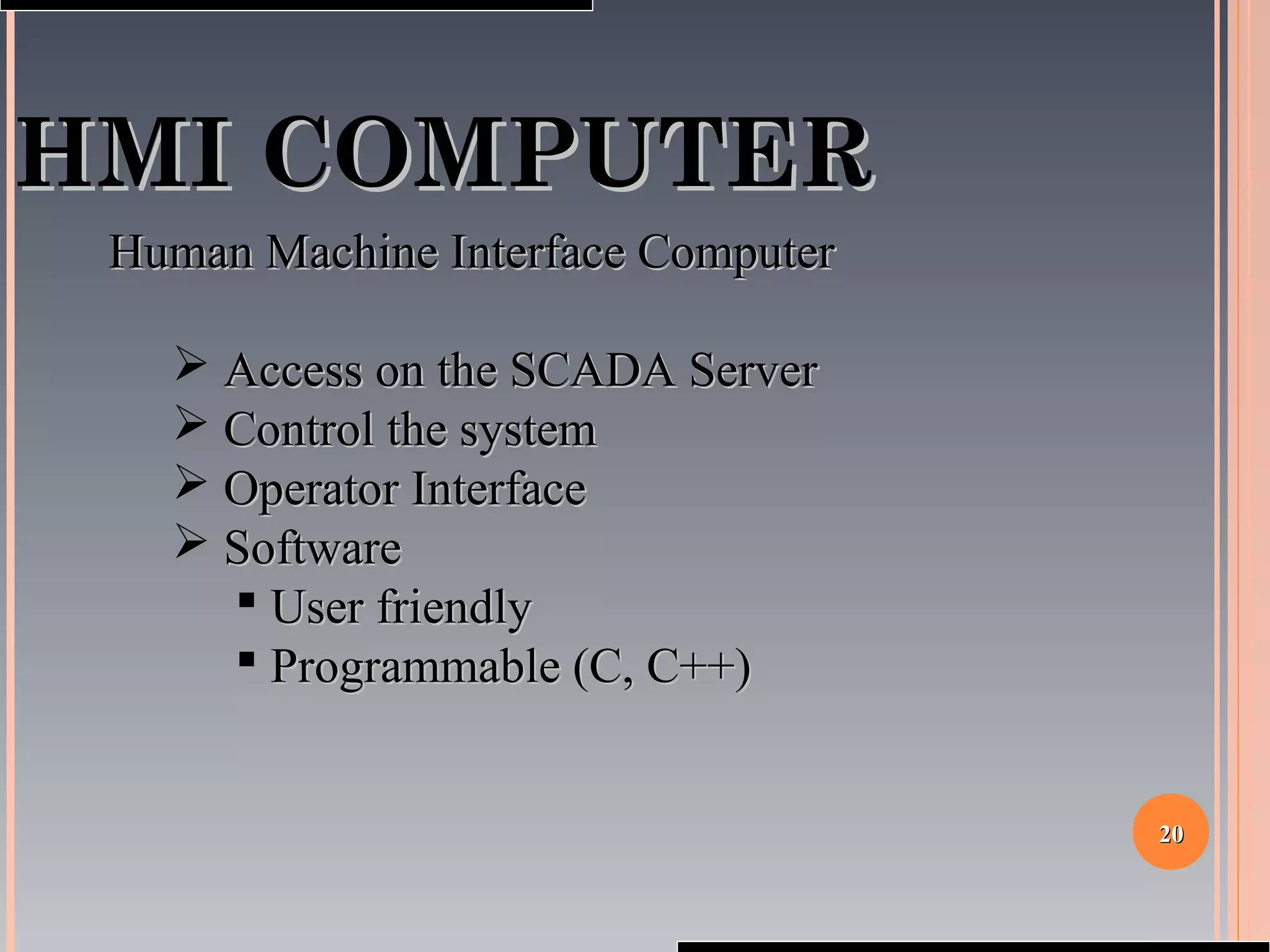
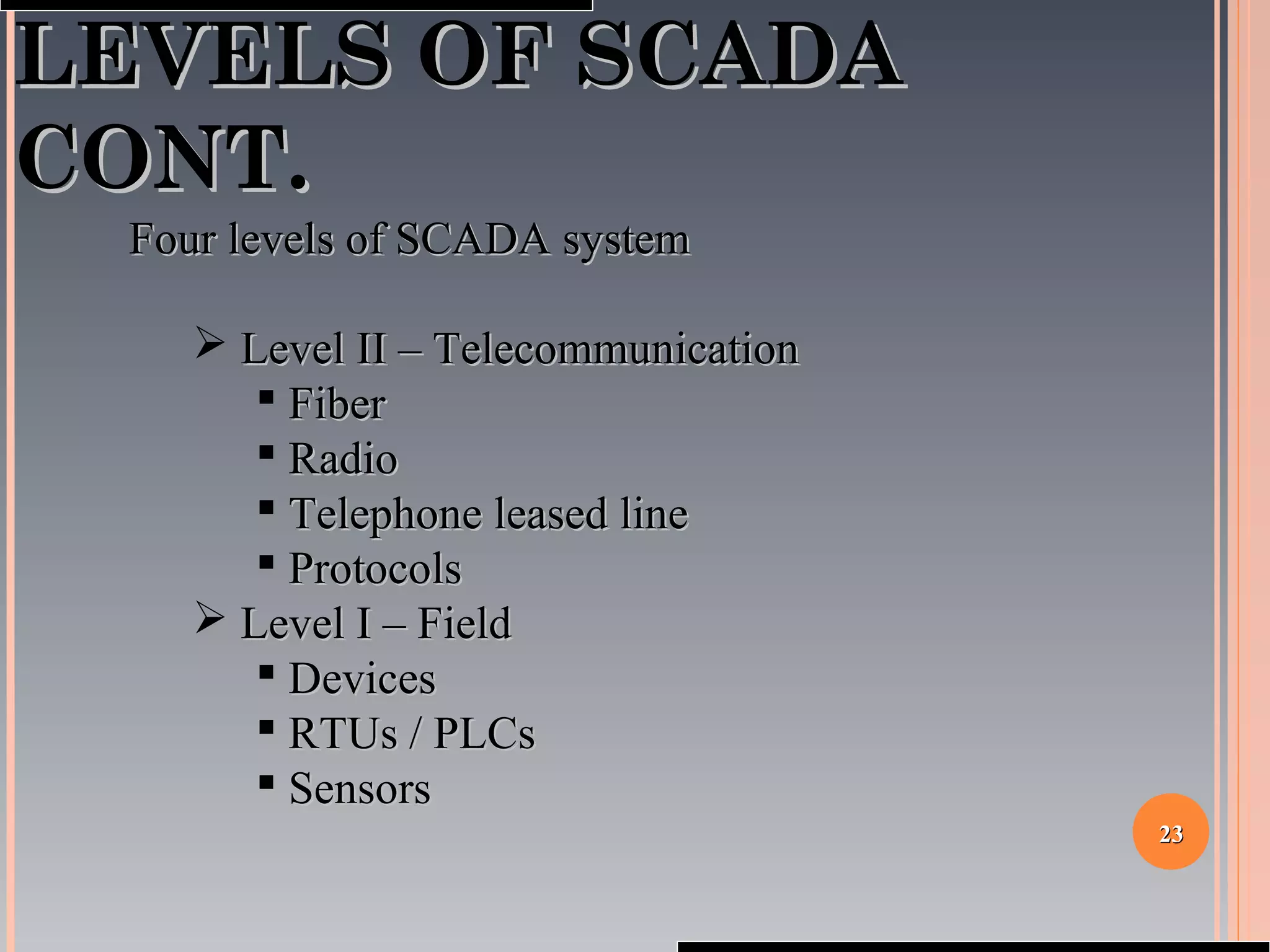
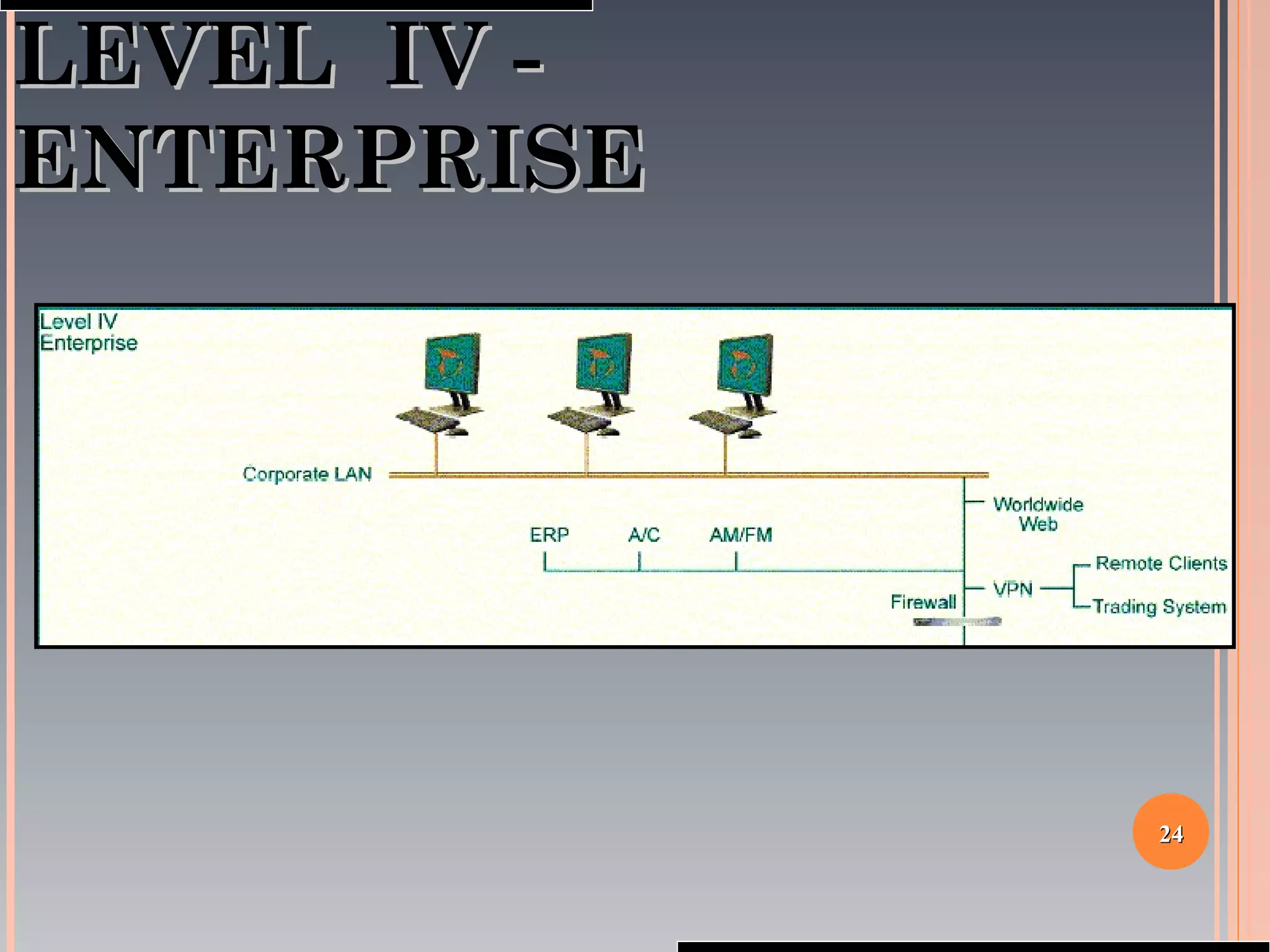
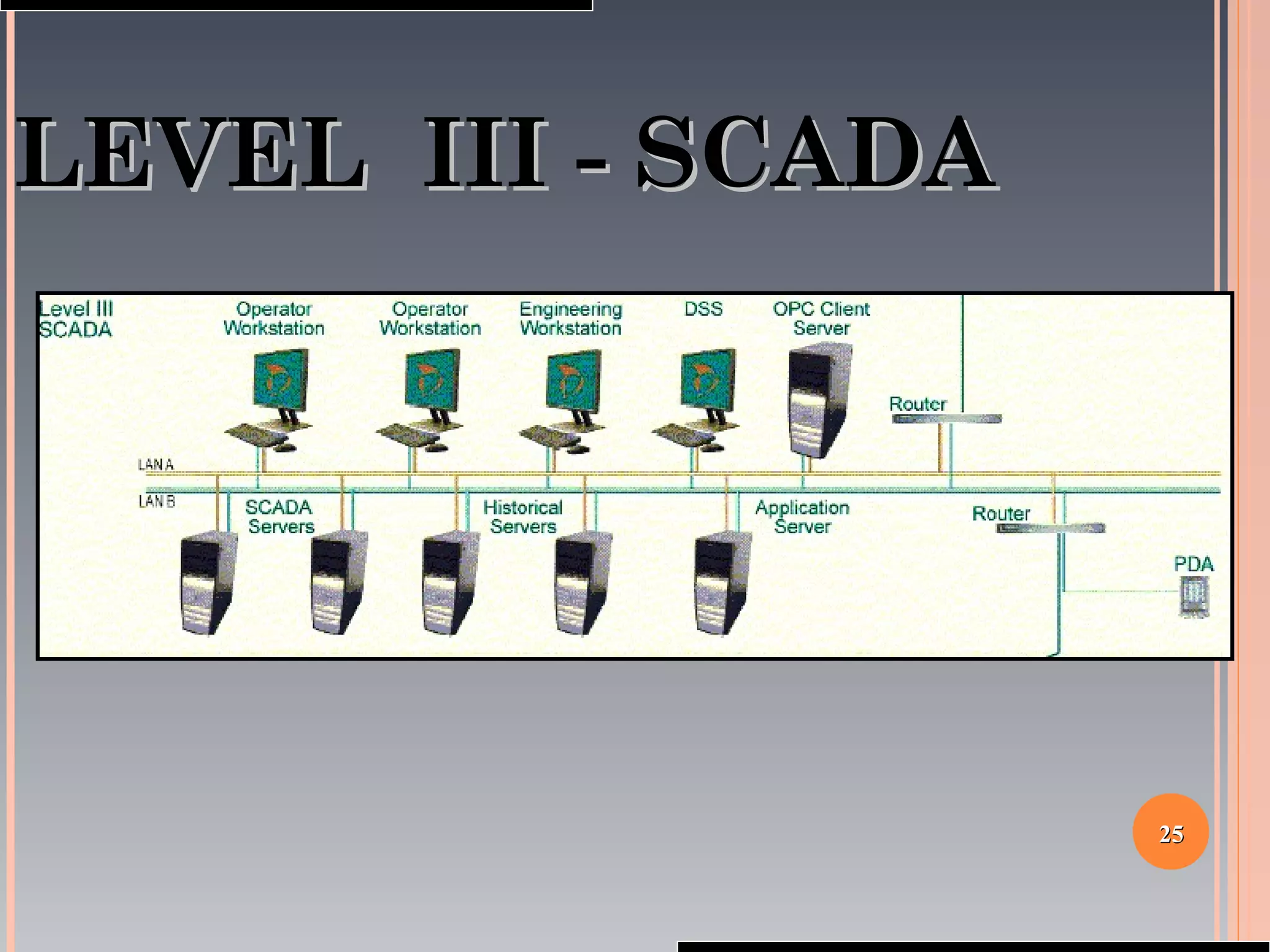
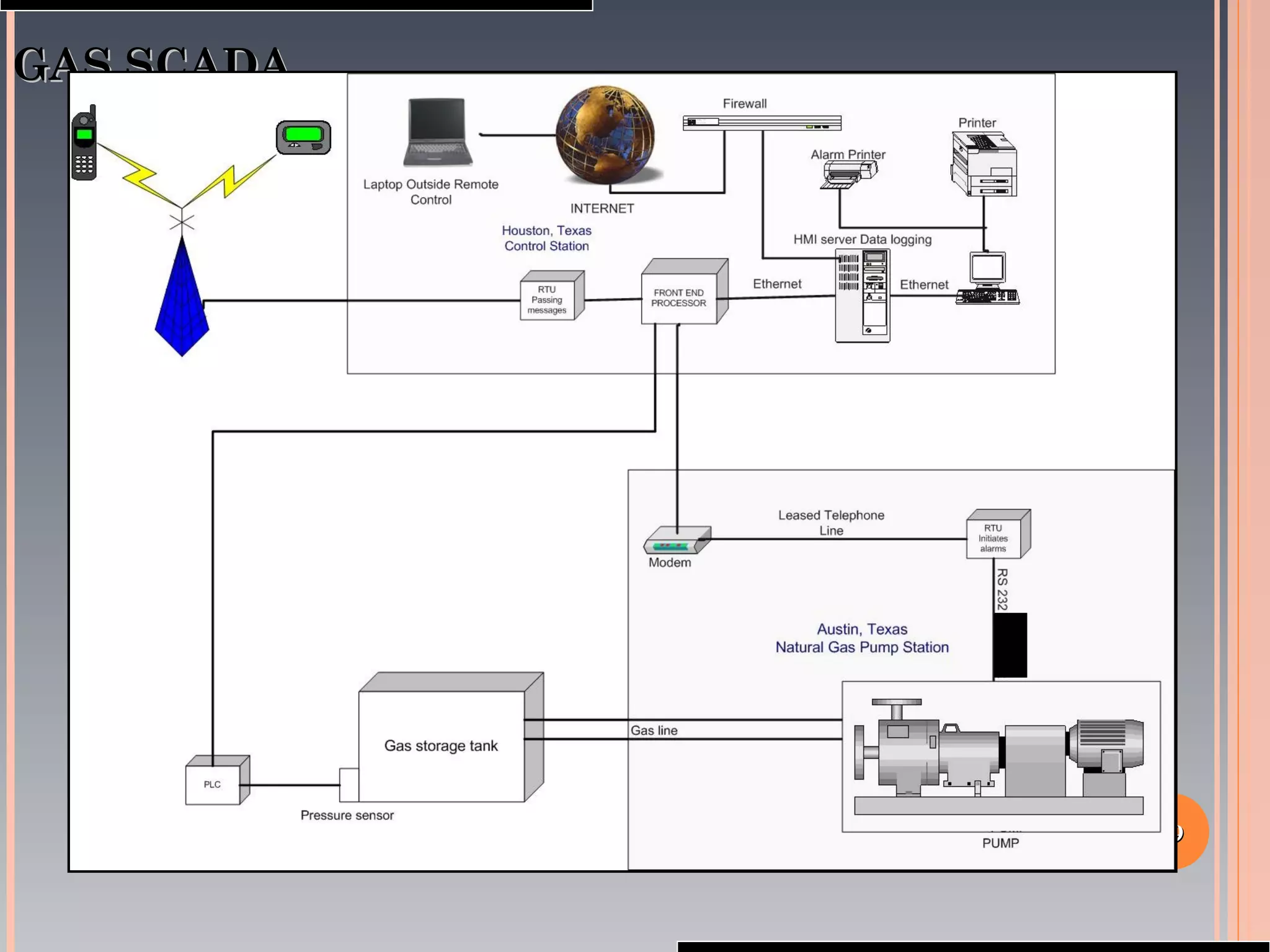
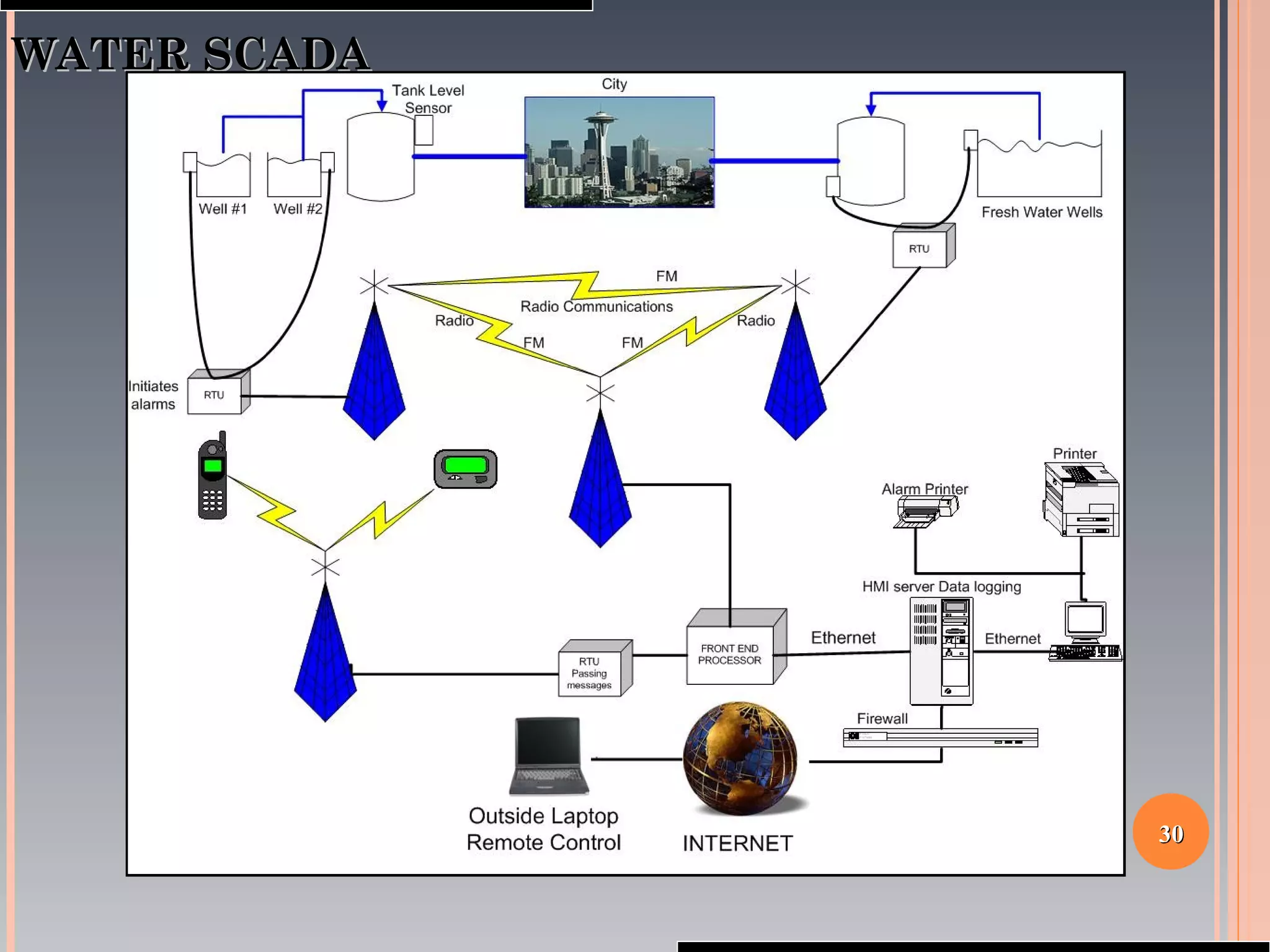
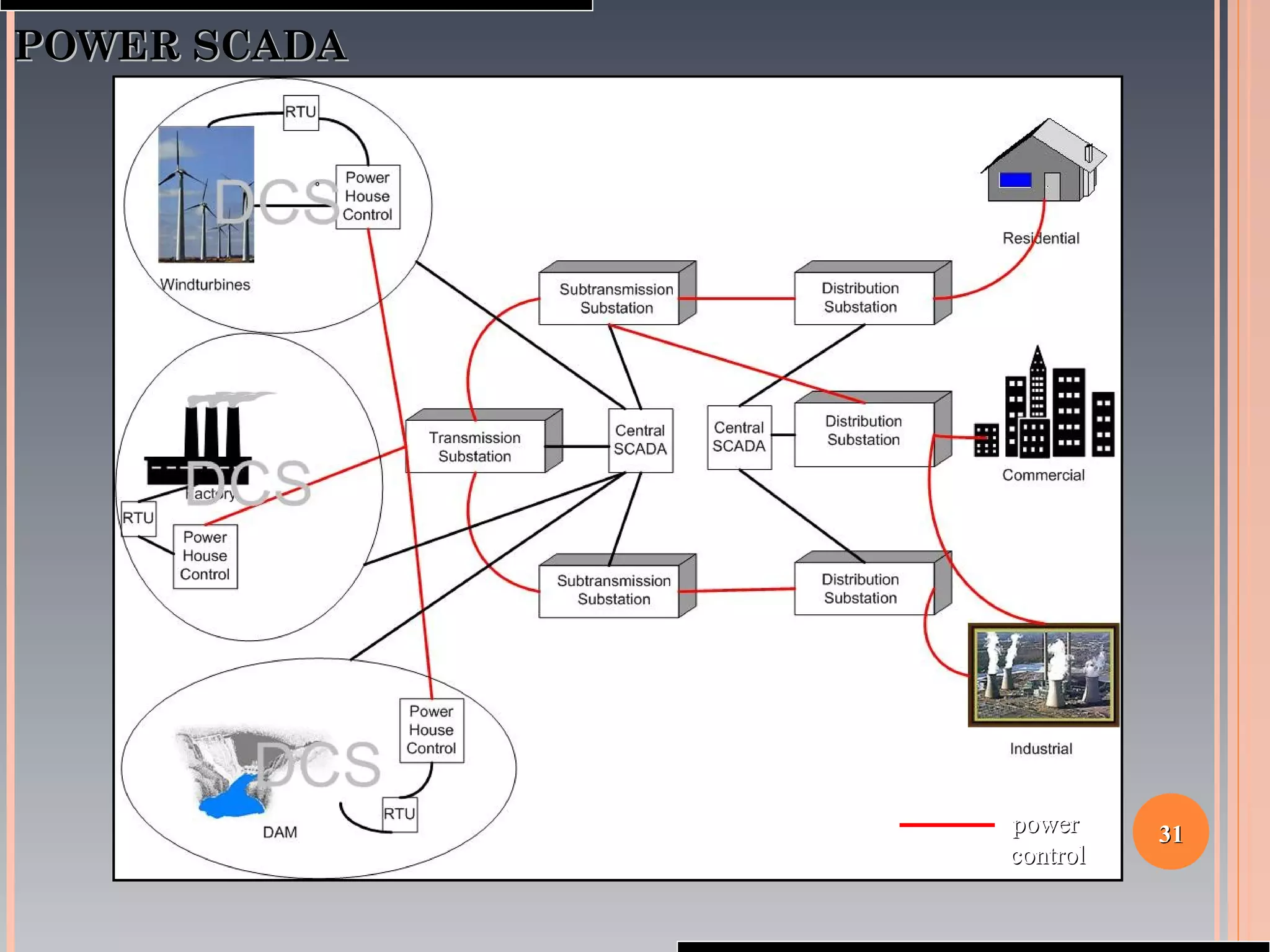
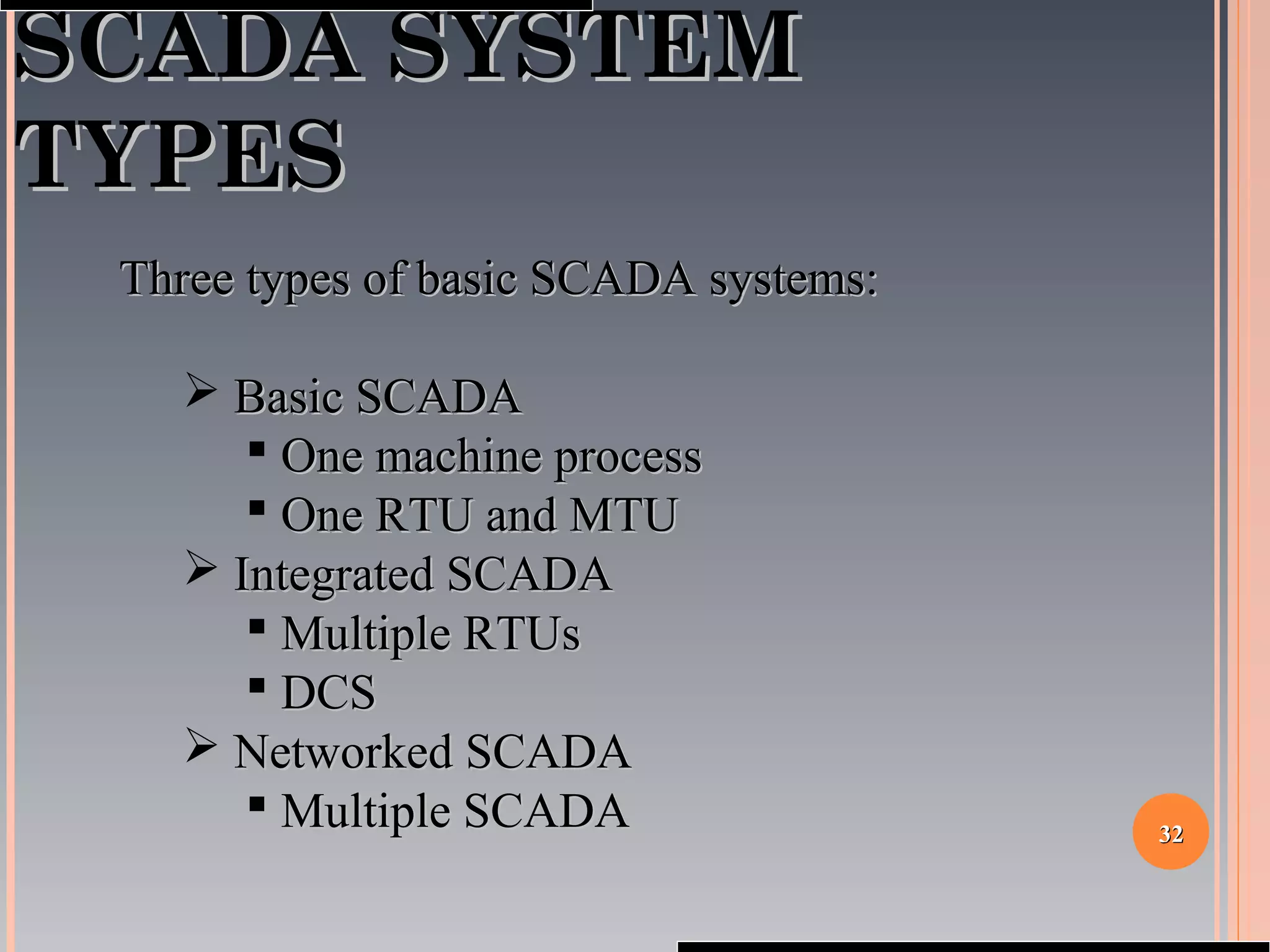
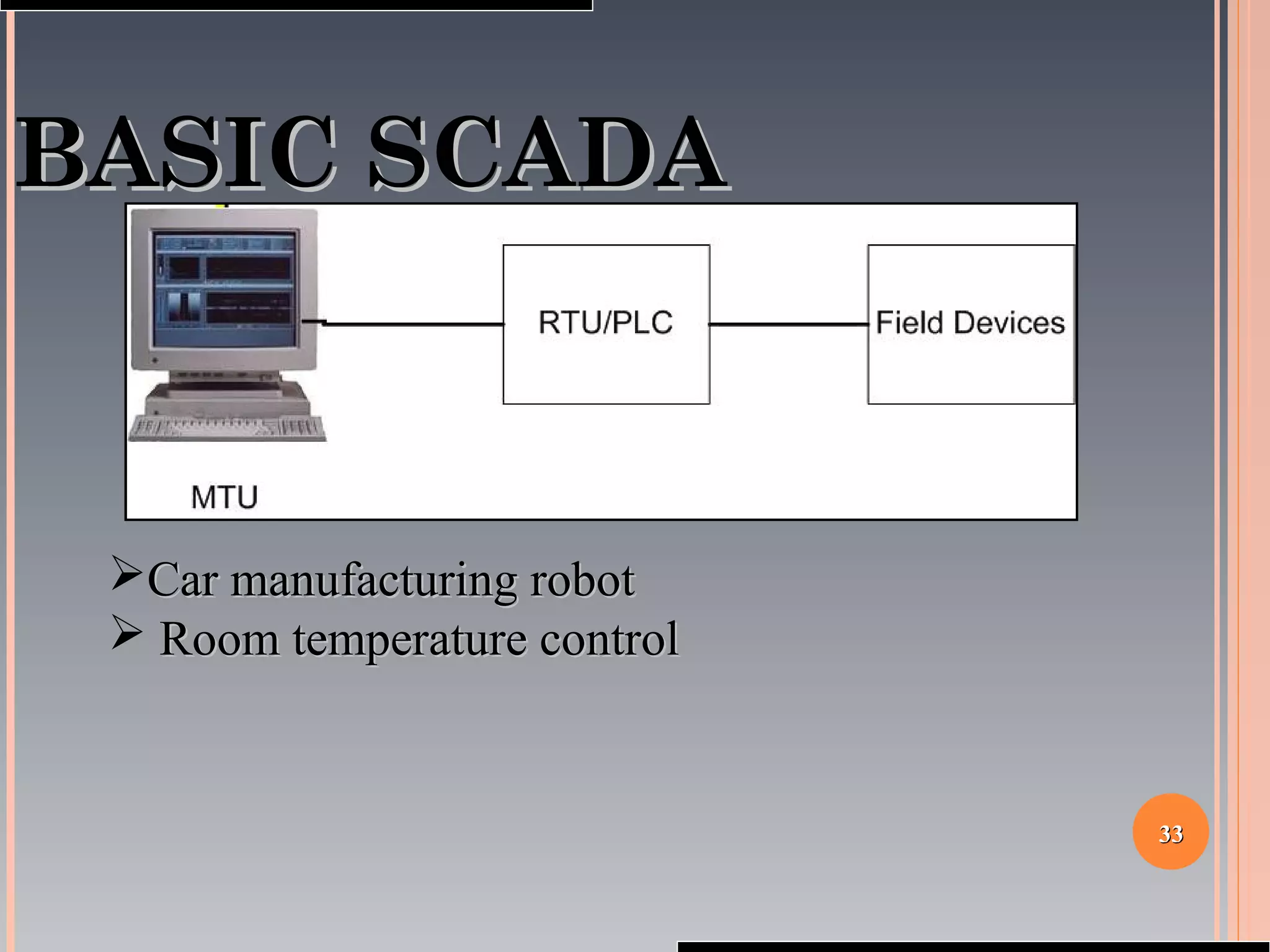
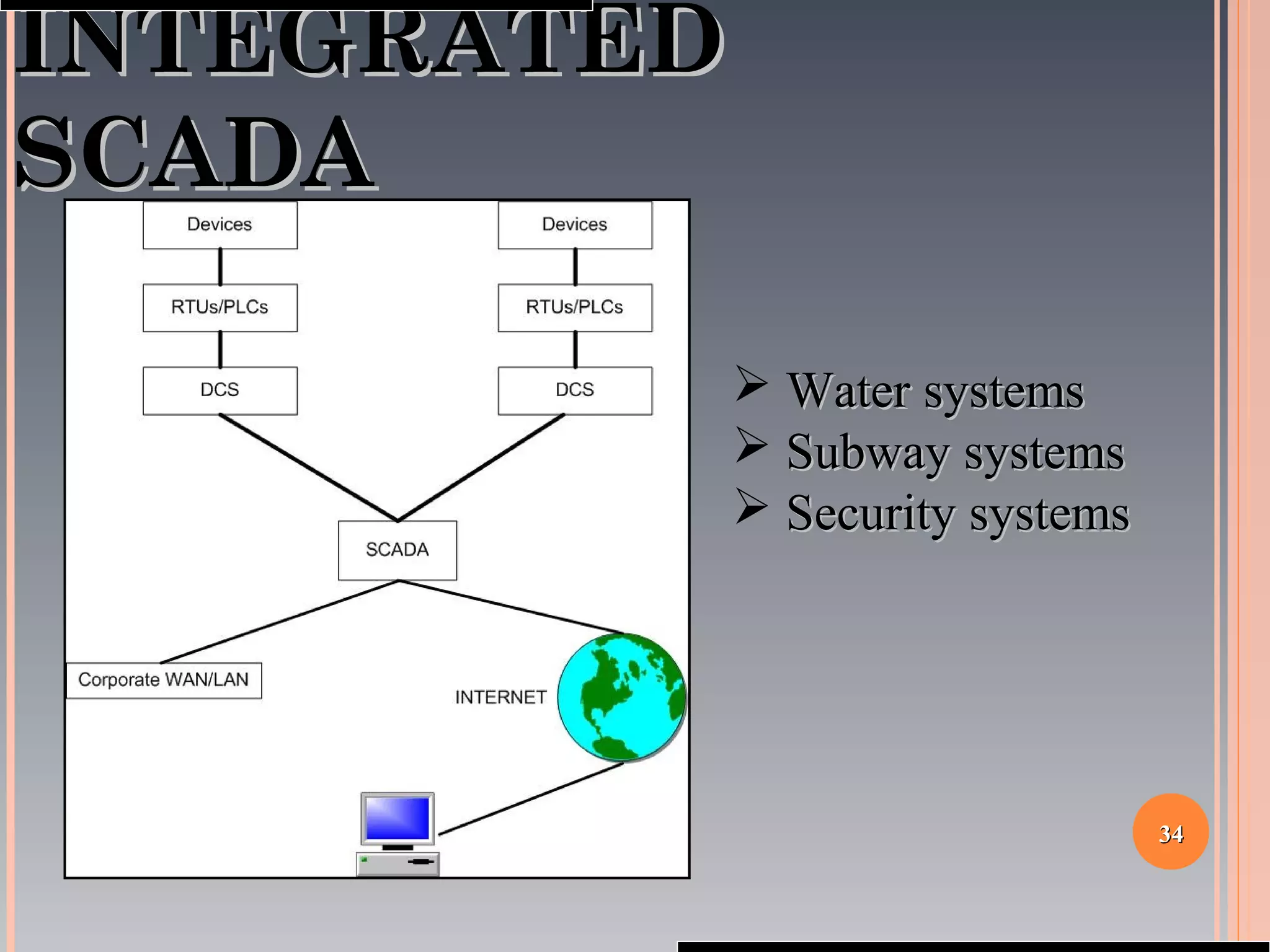
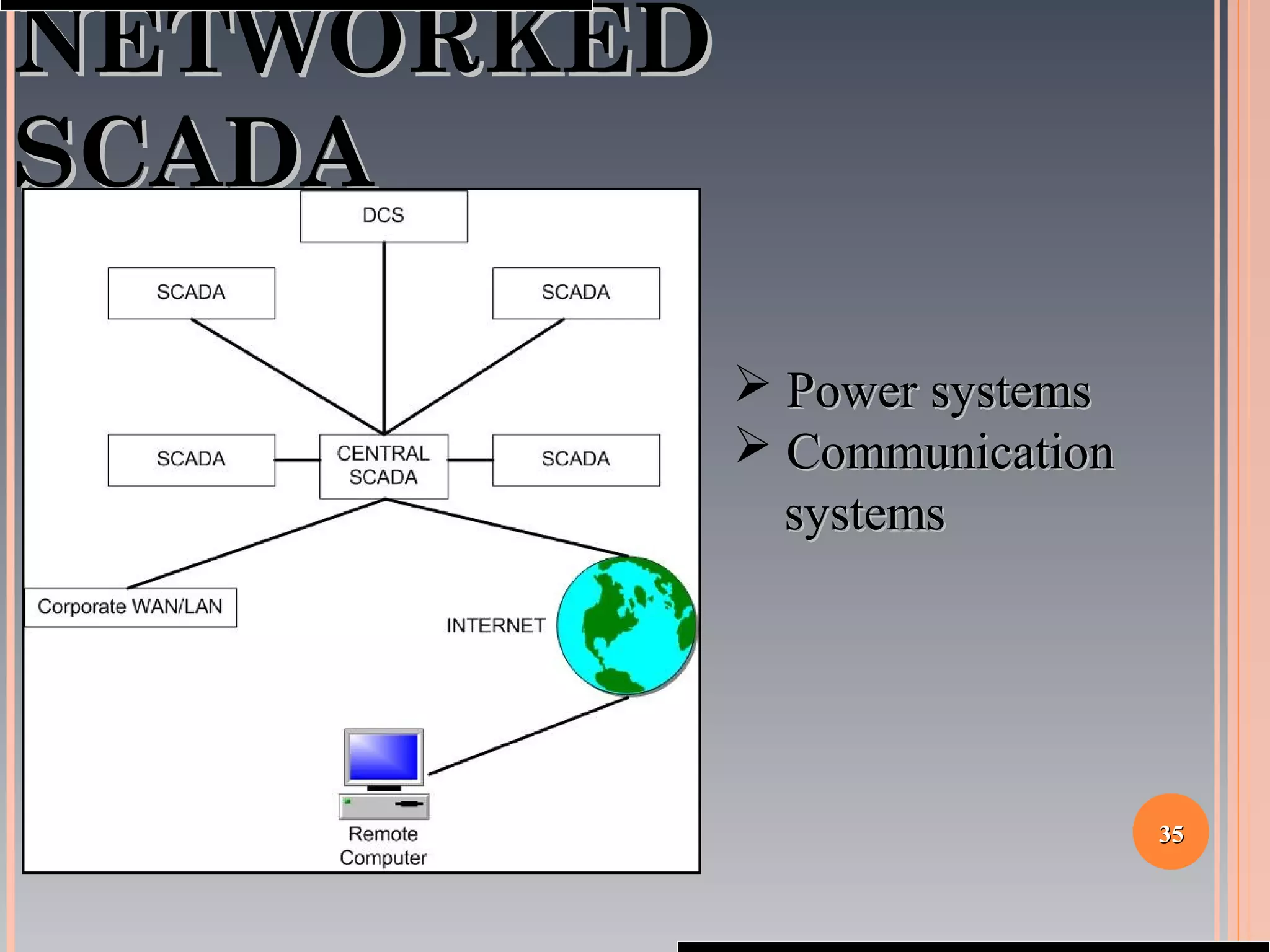
The document provides a comprehensive overview of SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems, including their history, definitions, classifications, and applications across various industries. It discusses the elements of SCADA systems, such as sensors, actuators, and communication methods, while emphasizing the importance of communication in SCADA operations. The research aims to develop educational materials and a general model of SCADA systems, highlighting the vulnerabilities and types of systems used.