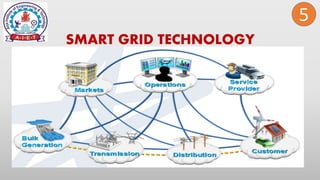
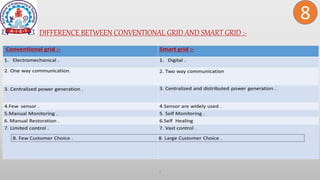
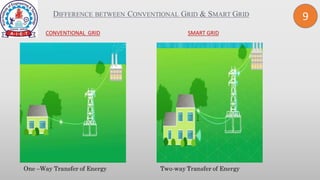
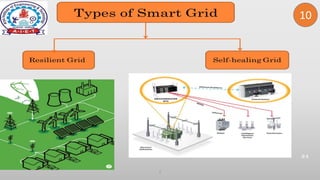
This document discusses smart grid technology. It begins by defining the electric grid as the network that delivers electricity from power plants to homes. It then defines smart grid as a two-way system of transmitting electricity and communication. The document outlines the need for smart grids to satisfy increasing demand, reduce losses, integrate renewable energy, and establish utility-consumer communication. It lists benefits like improved reliability, economic savings, efficiency, environmental gains, safety, and security. It also discusses the differences between conventional and smart grids, types of smart grids, key drivers for smart grids, and challenges to smart grid implementation.