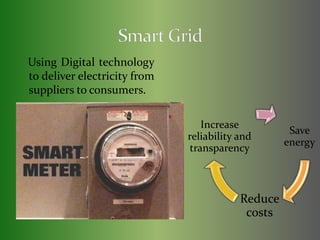
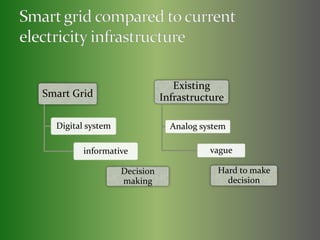
The presentation covers the implementation and benefits of smart grid technology in energy management, focusing on its ability to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and support informed decision-making for consumers and energy suppliers. Challenges include high costs, consumer perception issues, privacy concerns, and the need for infrastructure upgrades. The document also advocates for consumer participation and highlights the integration of smart water systems as part of the smart grid initiative.