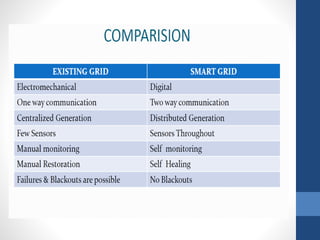
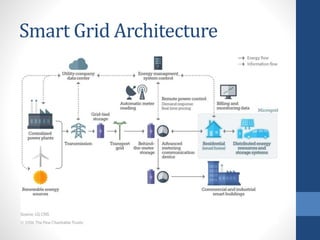
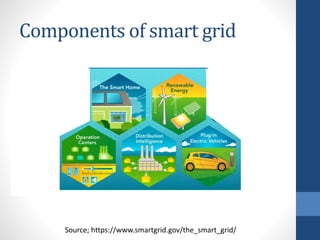
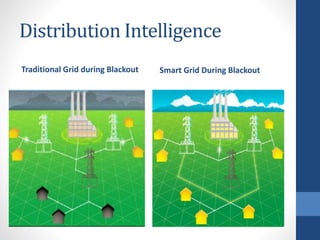
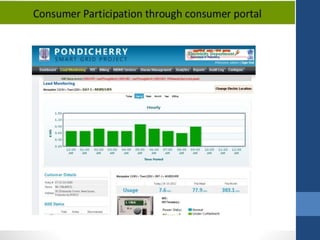
The document discusses the concept of smart grids, which modernize traditional electrical grids by enabling bi-directional energy flow and real-time communication. Key benefits include more efficient electricity transmission, quicker restoration after disturbances, and the integration of renewable energy sources. It also highlights the components, architecture, and ongoing projects in India aimed at implementing smart grid technology.