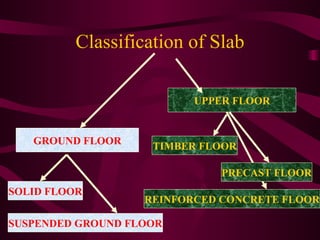
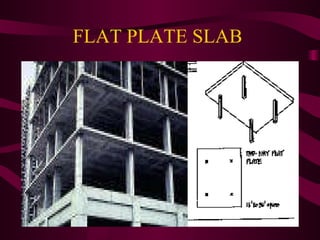
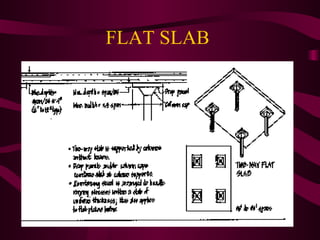
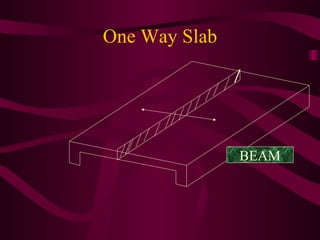
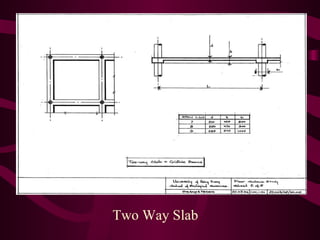
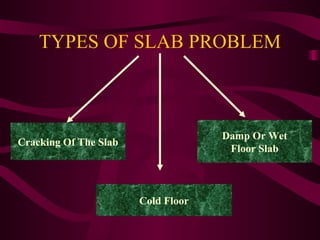
The document discusses different types of slabs used in construction. It describes solid ground floors, suspended ground floors, upper floors, precast concrete floors, reinforced concrete slabs, flat plate slabs, waffle slabs, one-way and two-way slabs. It also discusses potential problems with slabs like cracking and dampness, and their causes such as poor construction practices, uneven settlement, inadequate strength of concrete, and improper reinforcement placement.