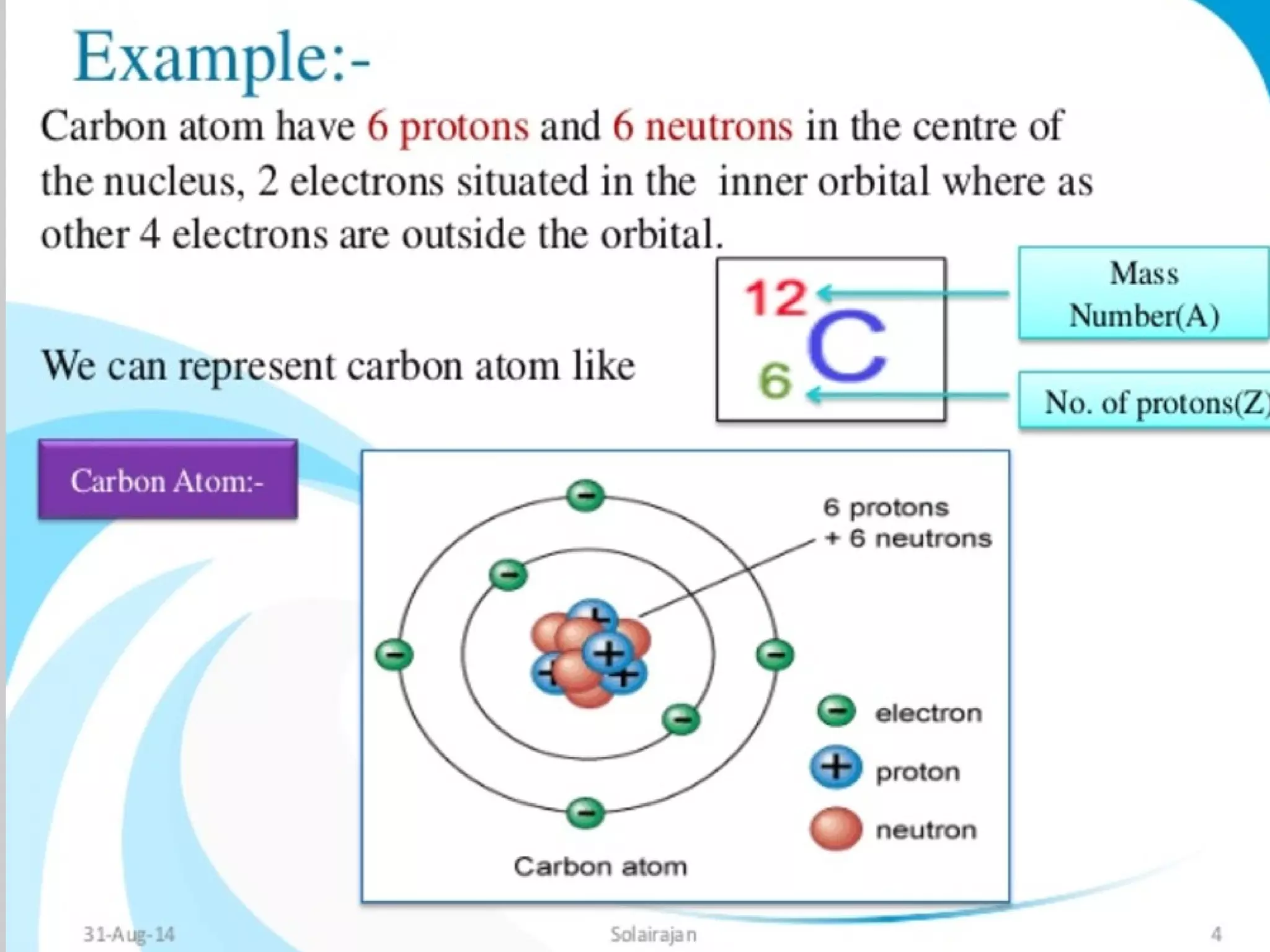
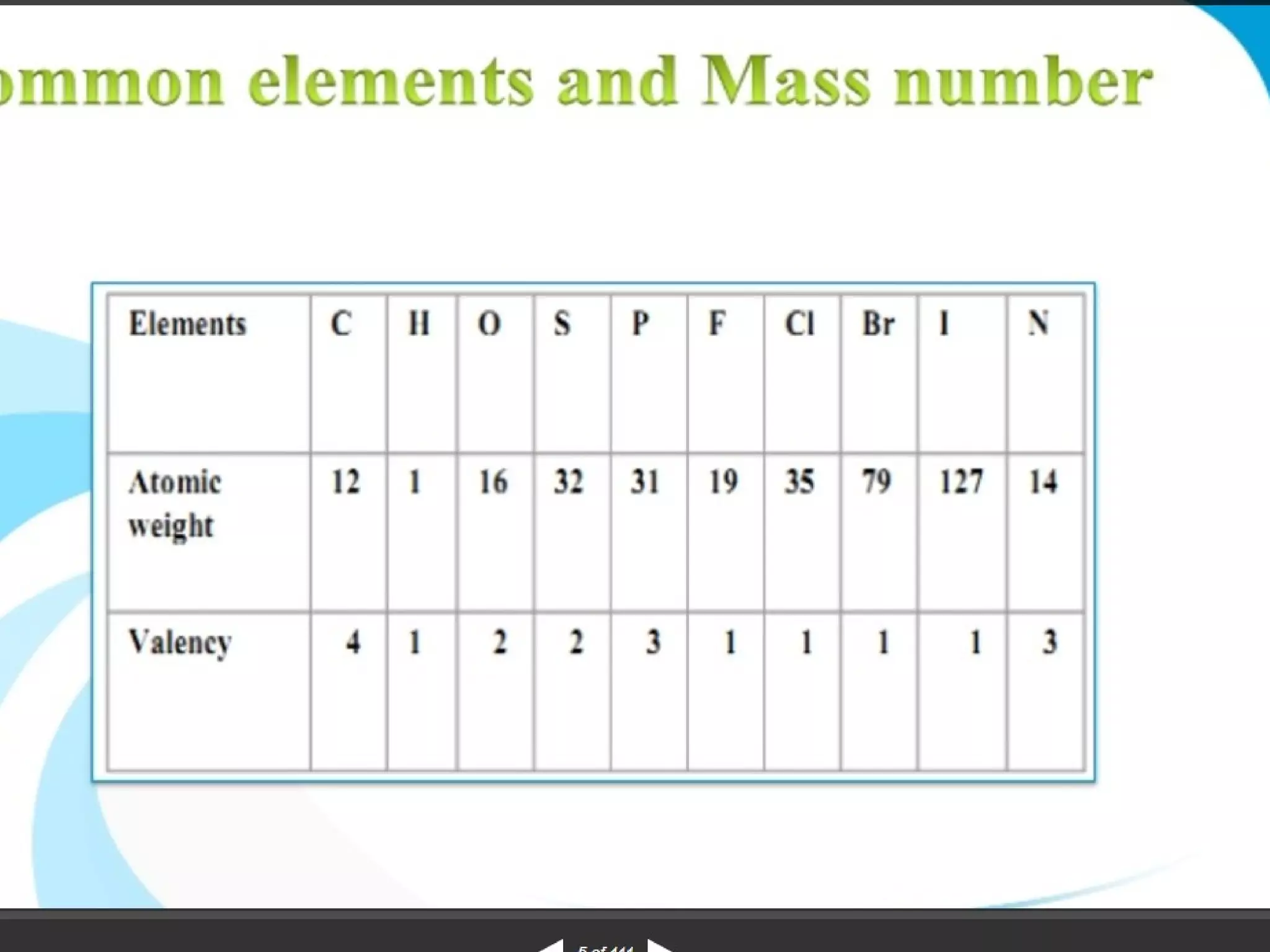
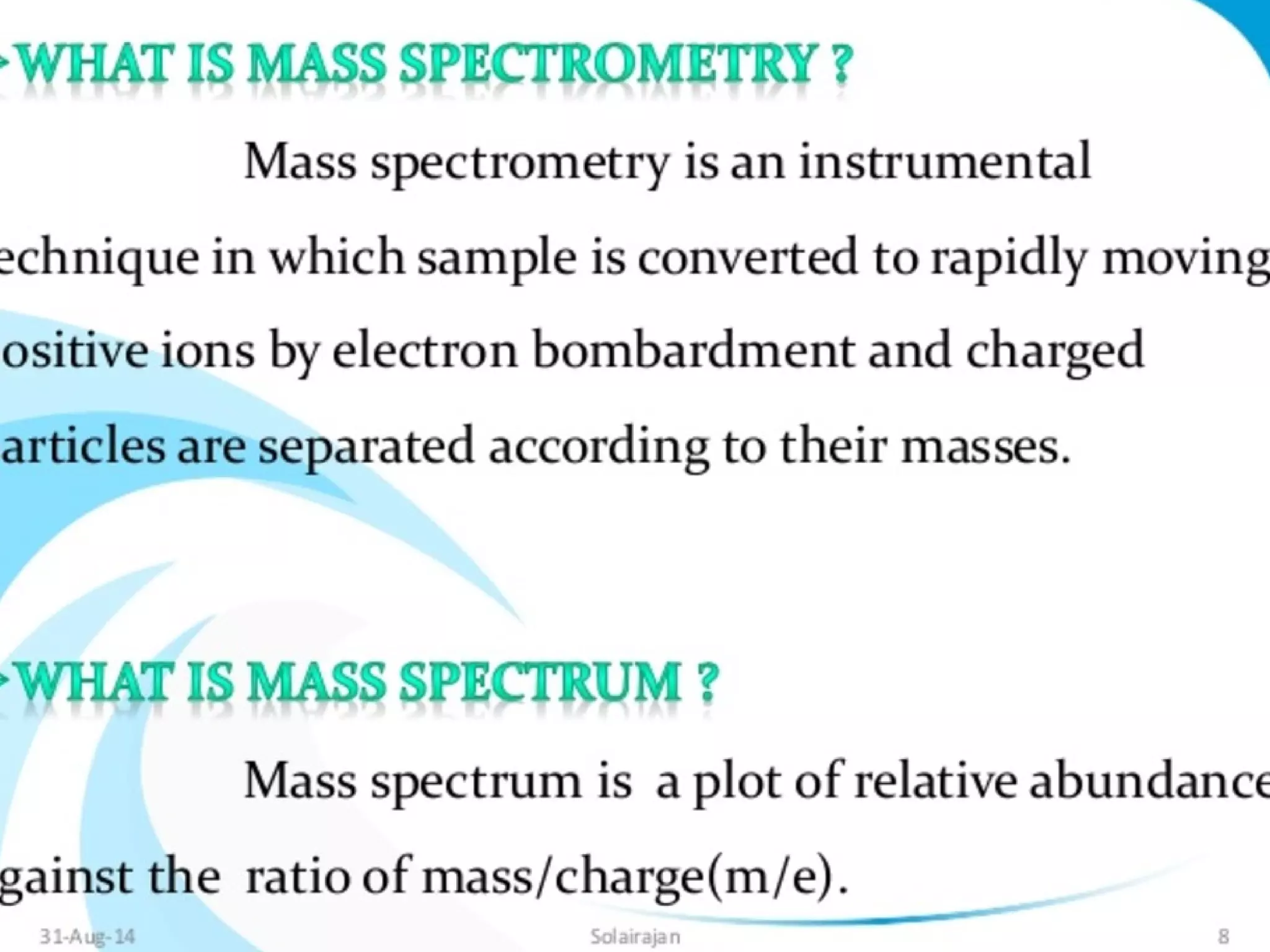
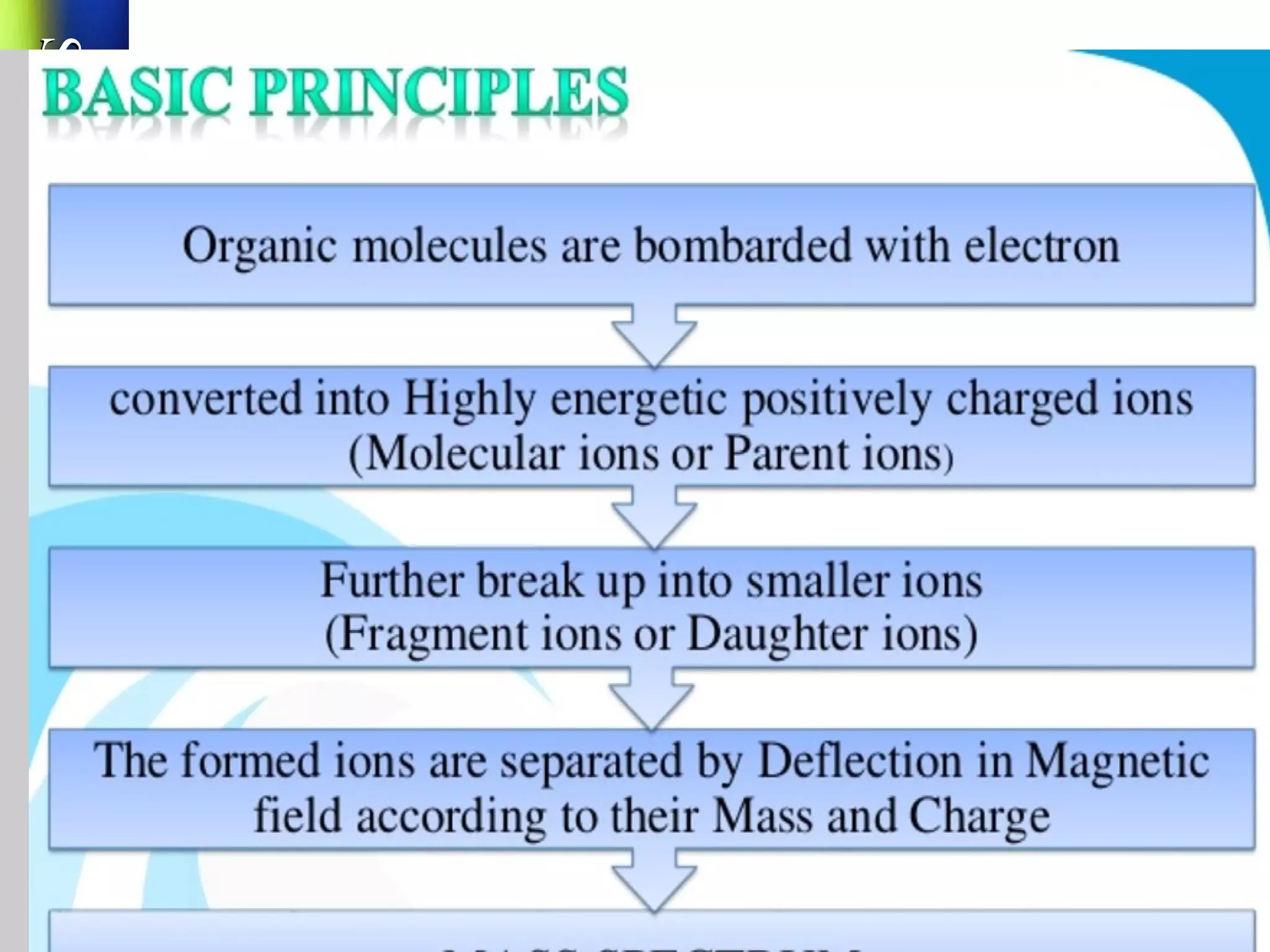
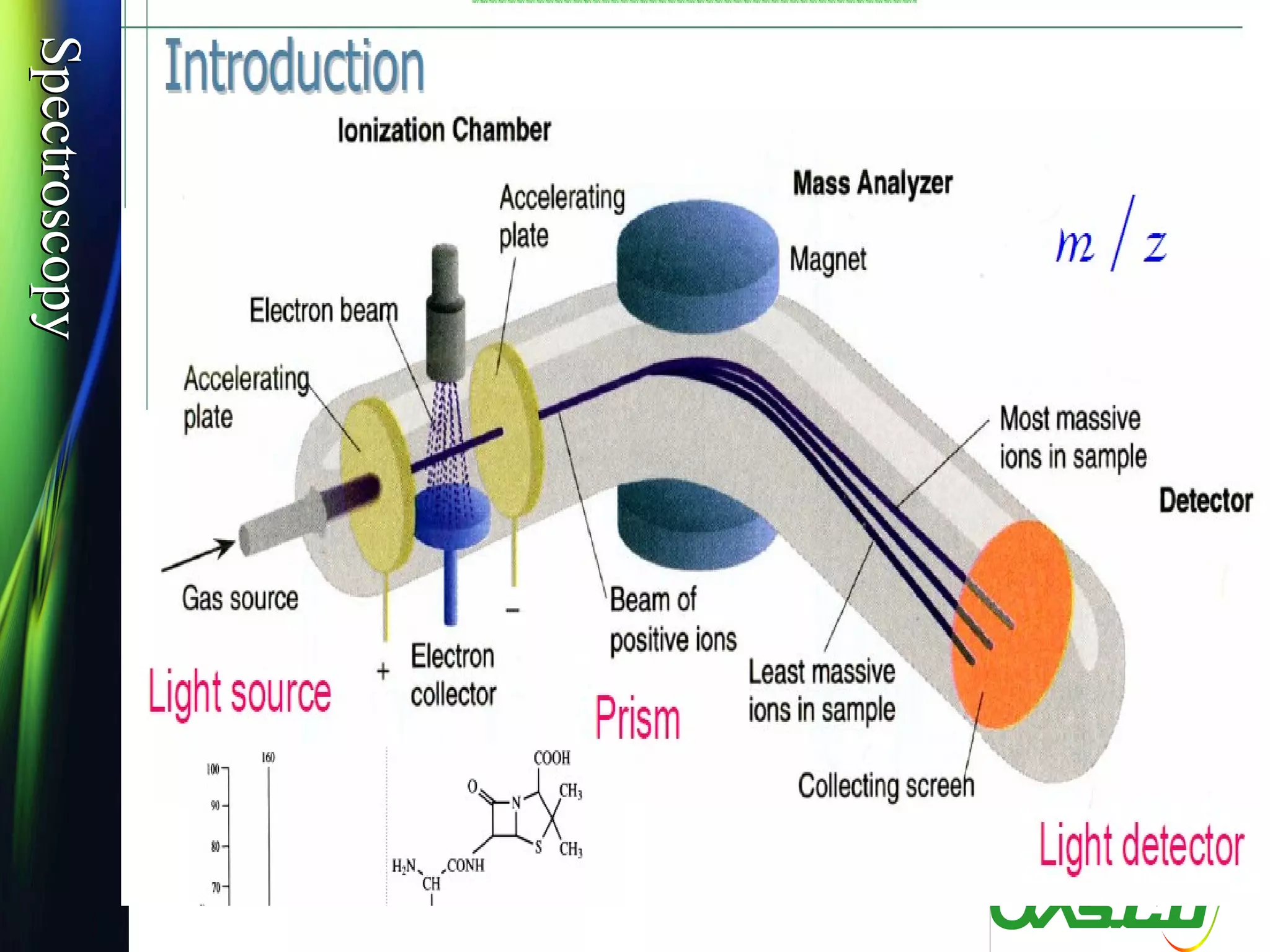
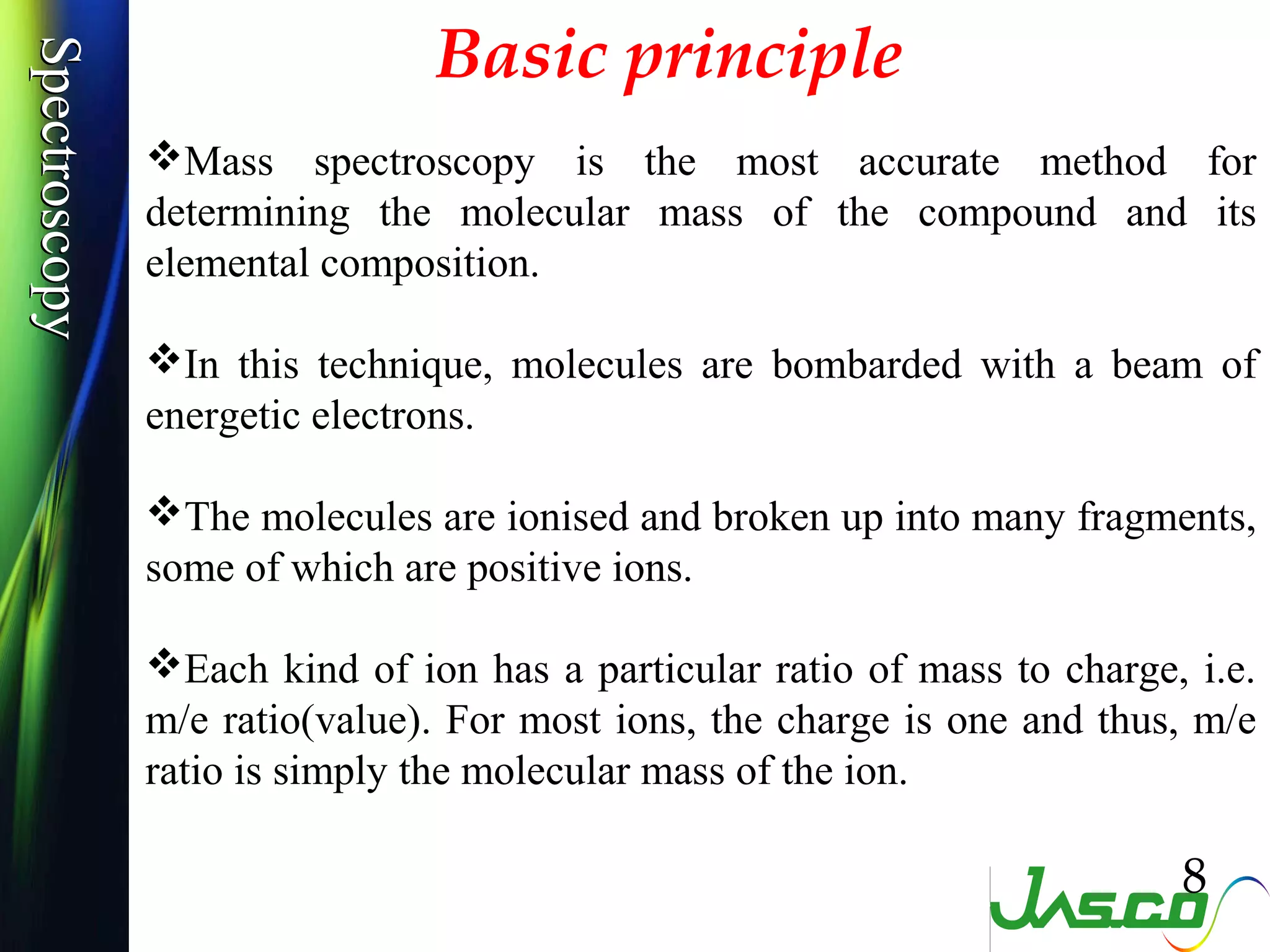
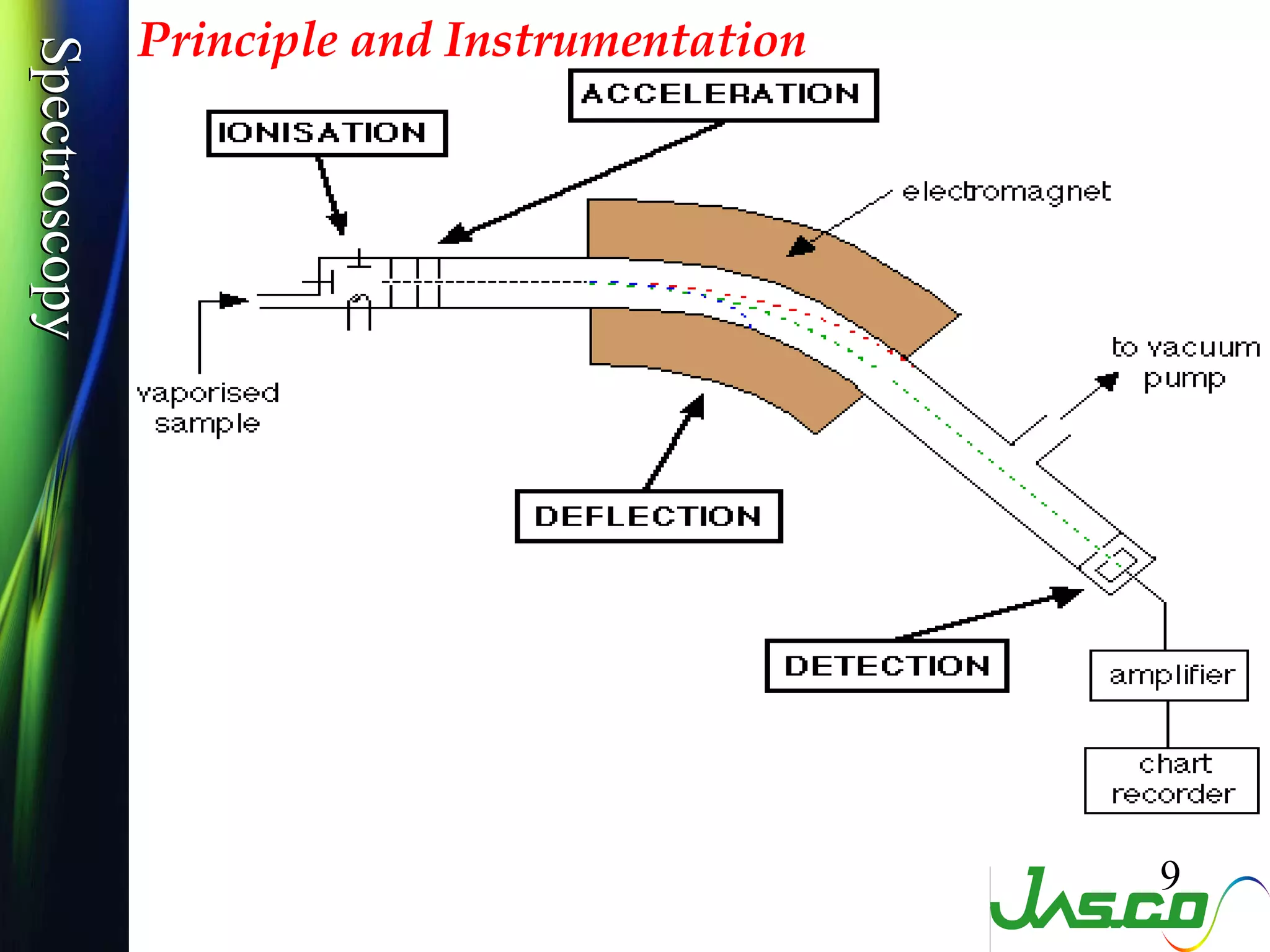
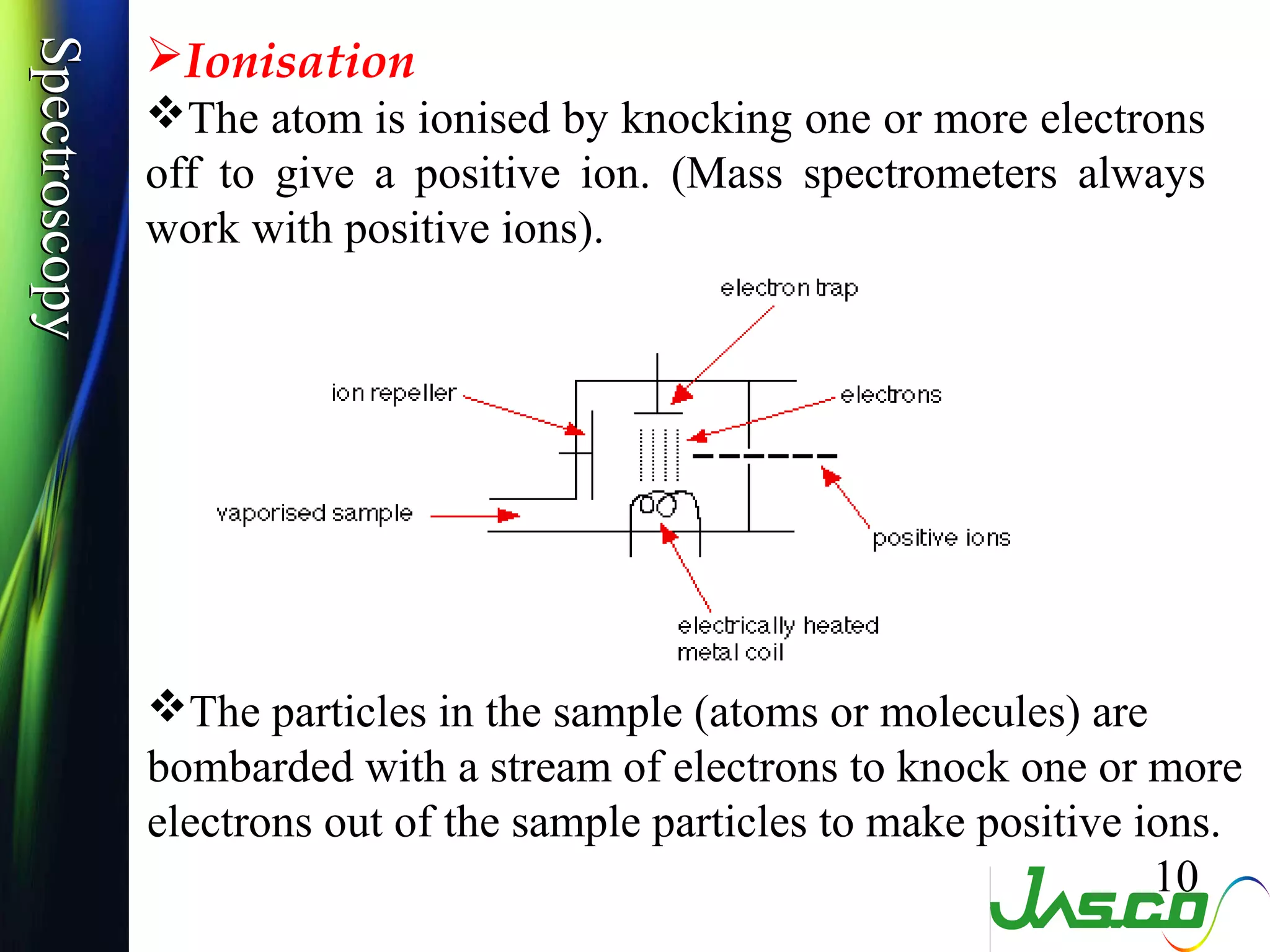
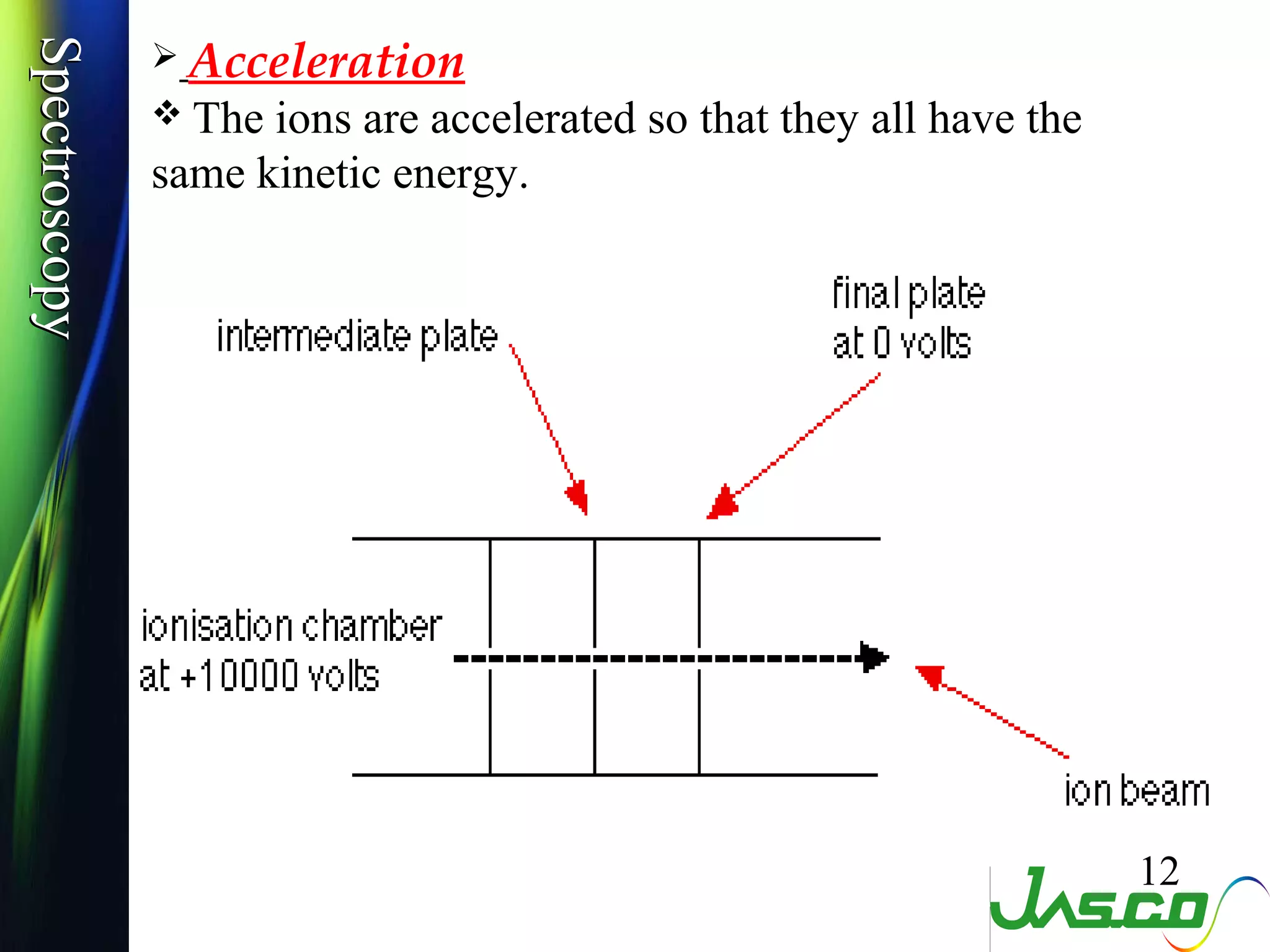
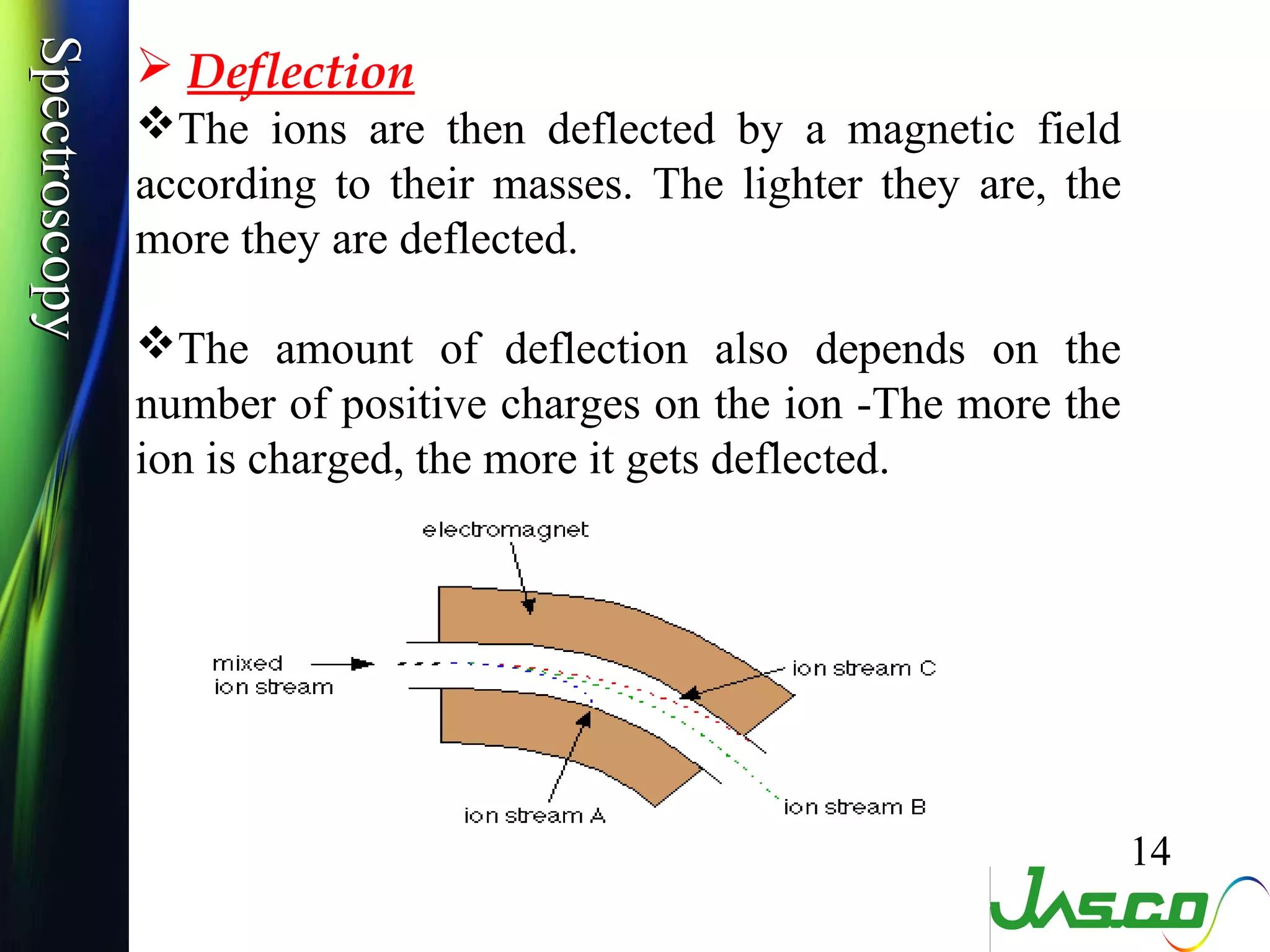
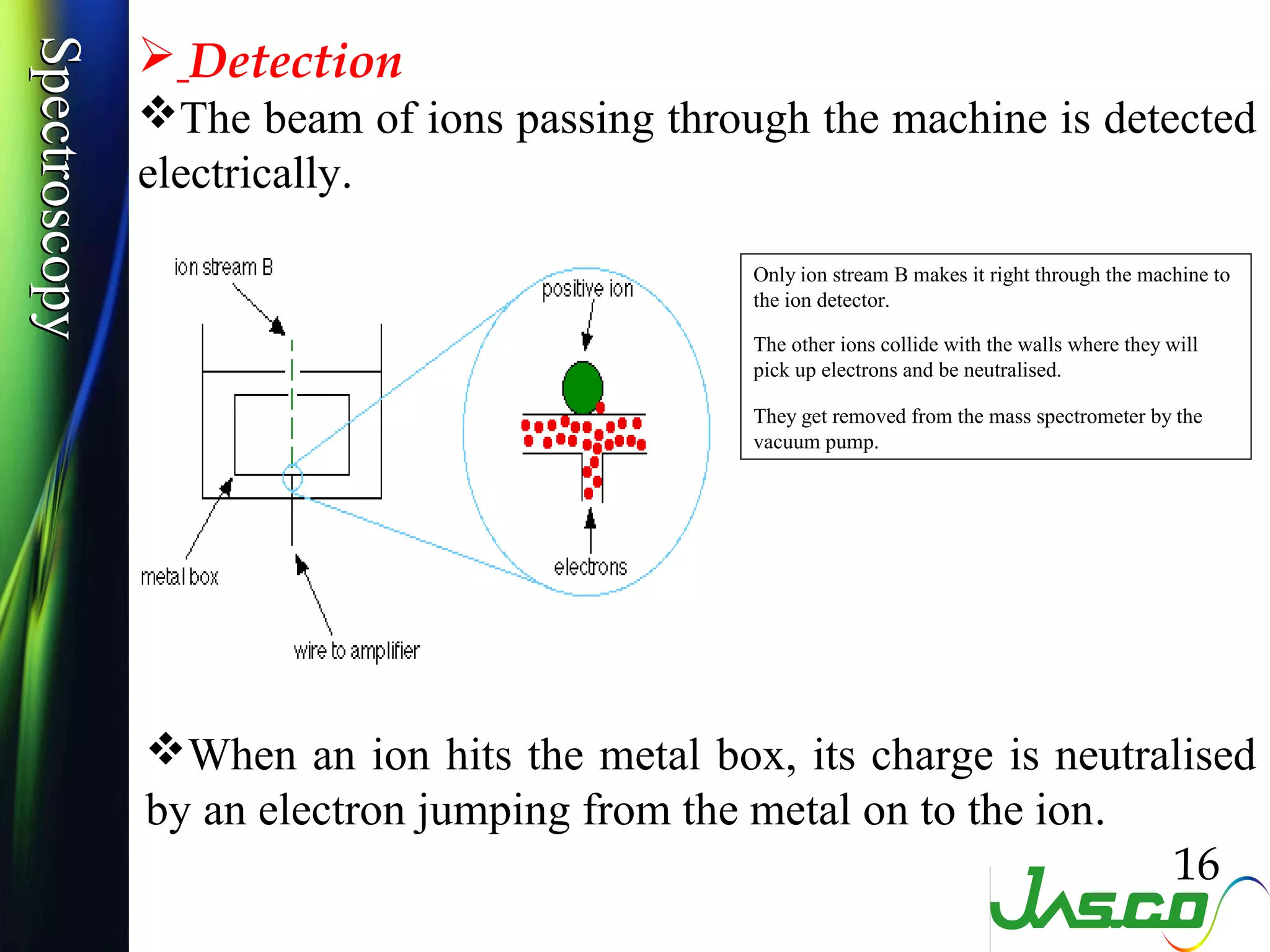
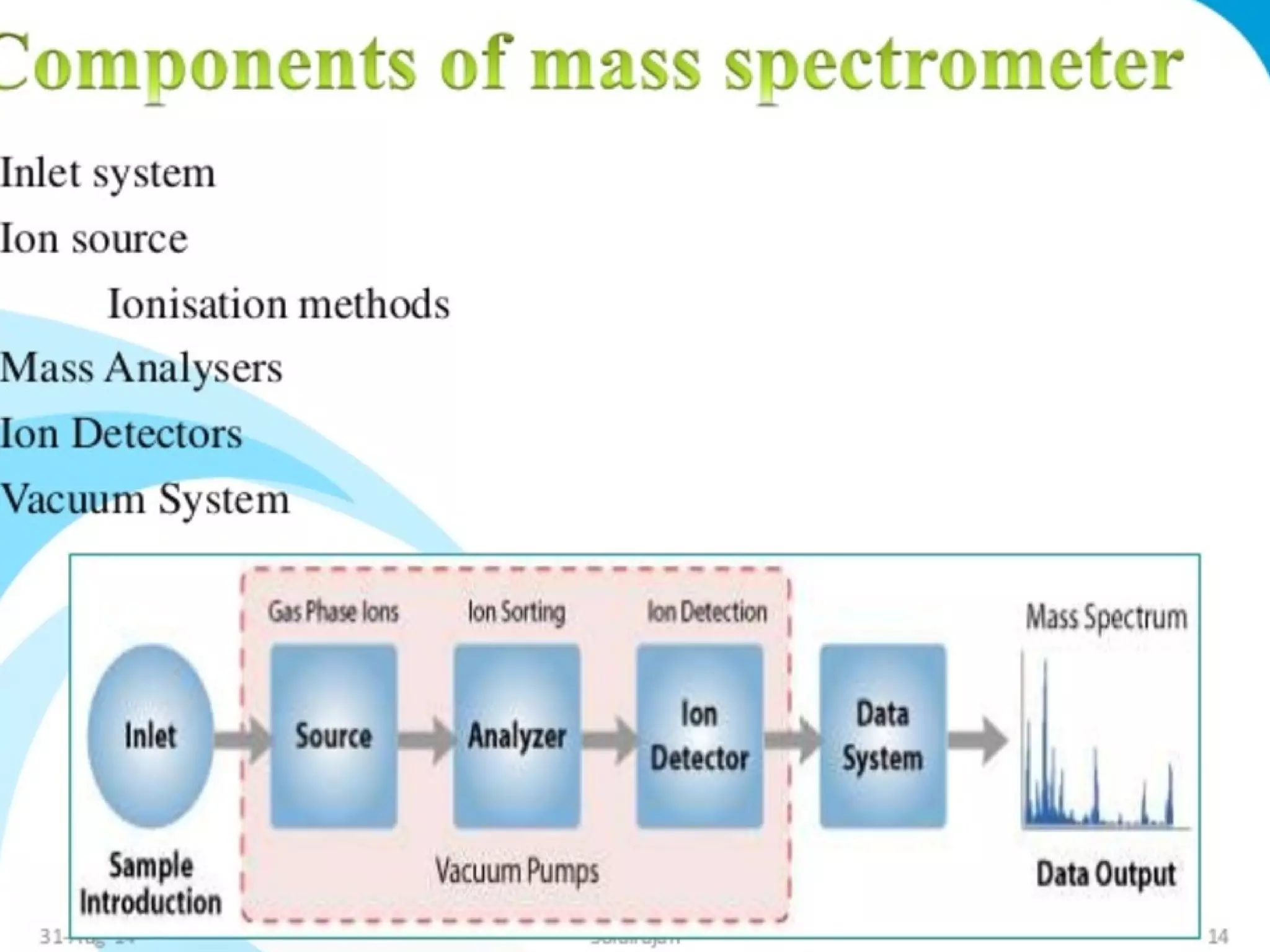
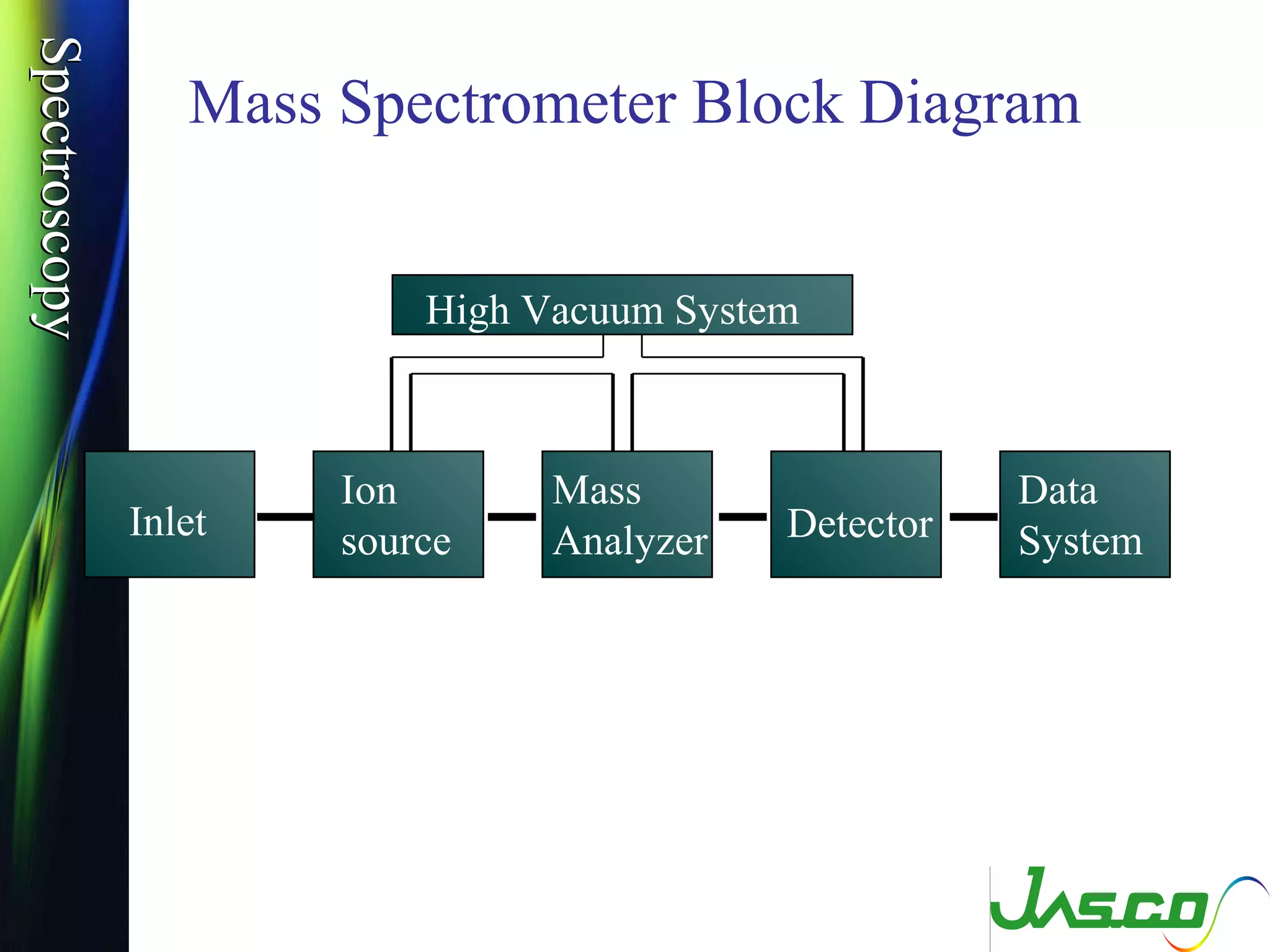
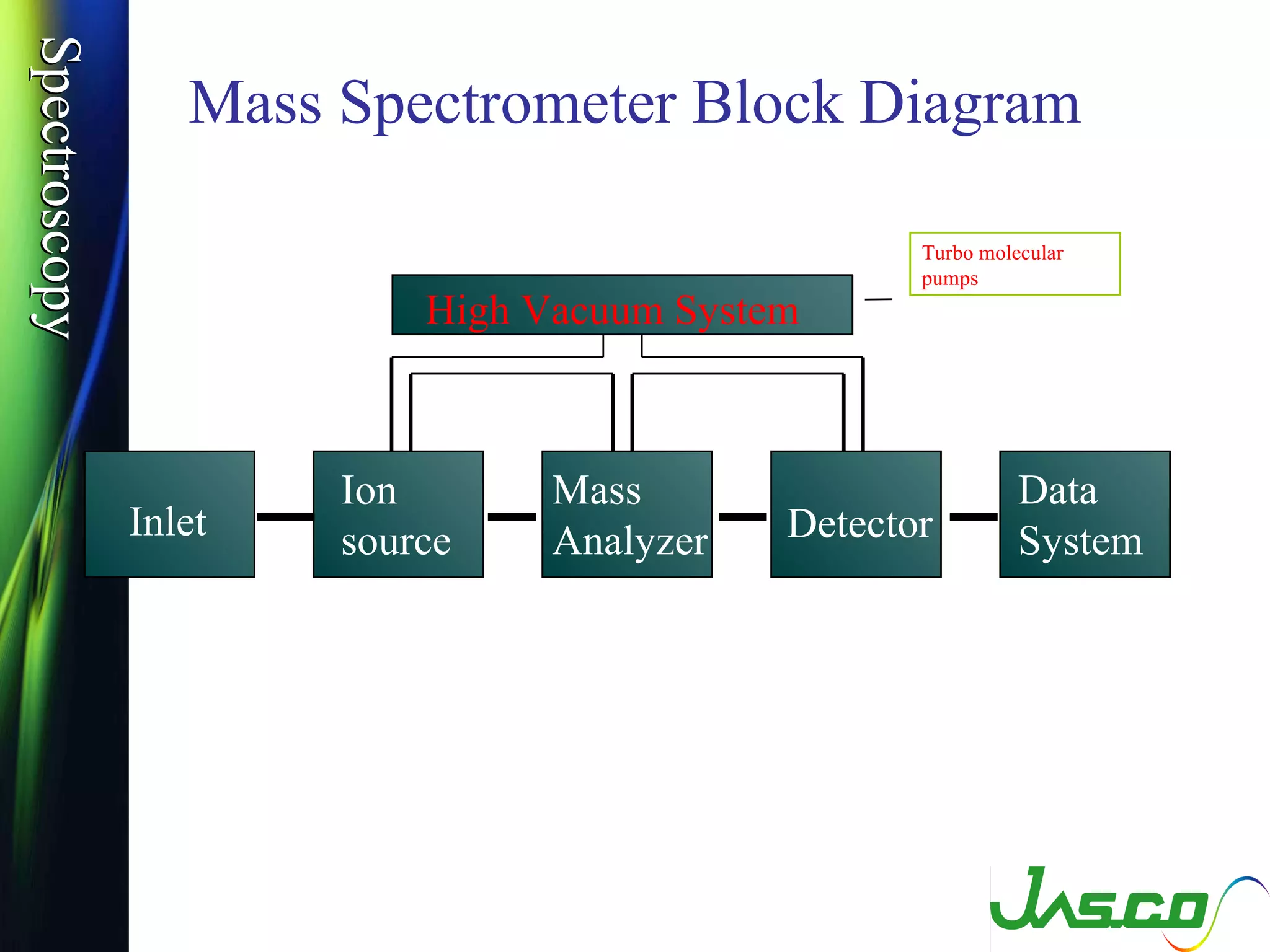
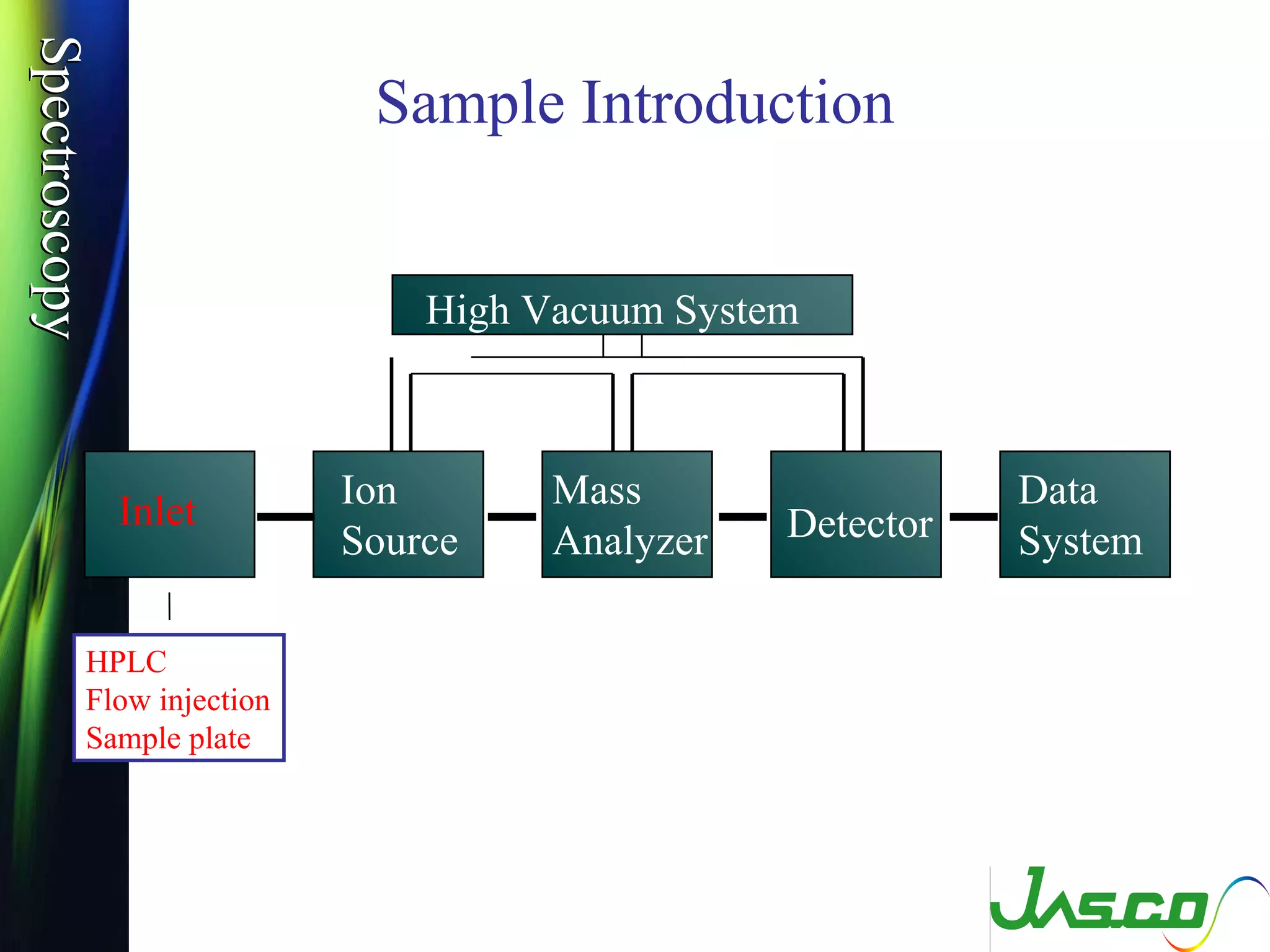
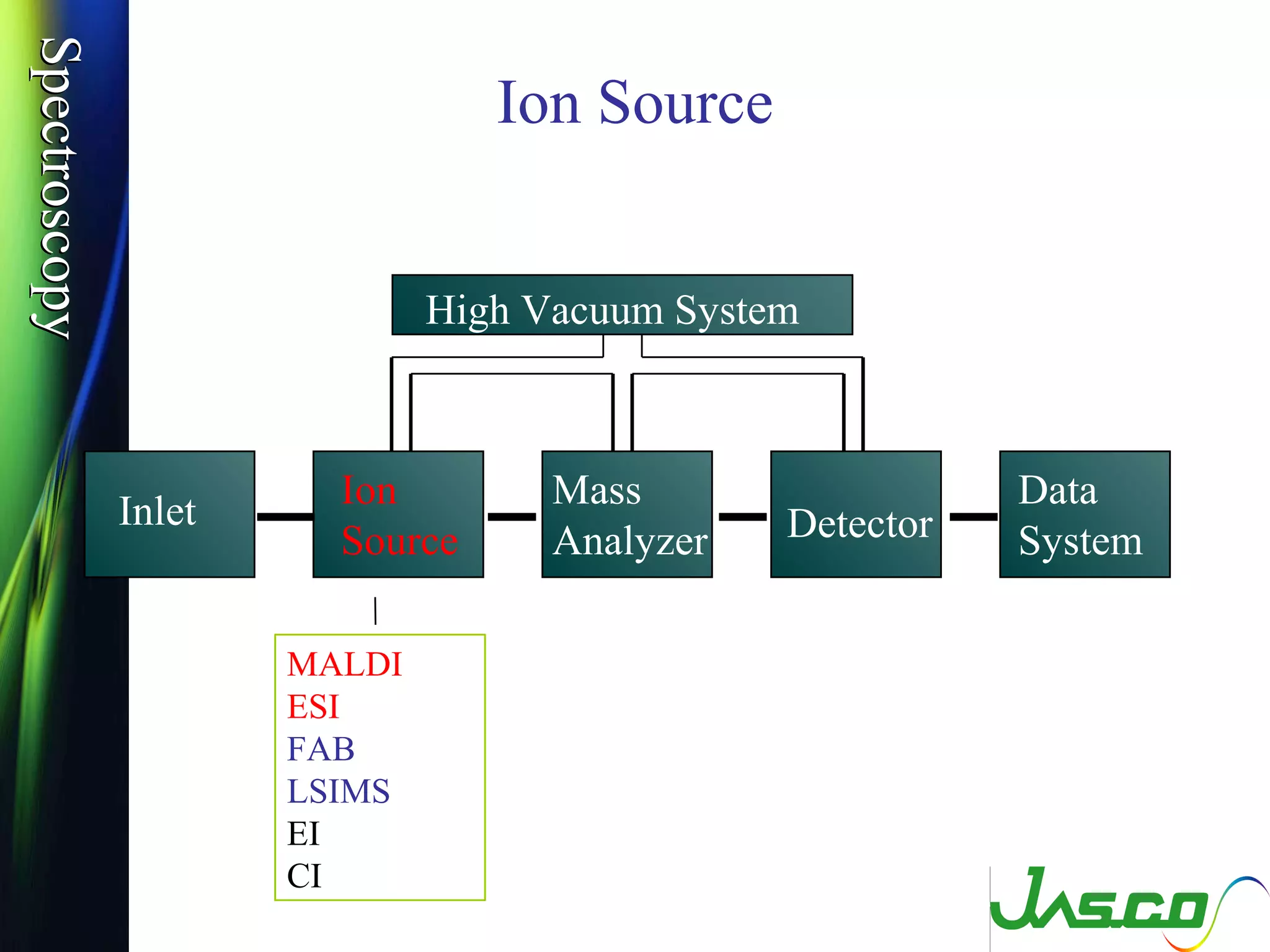
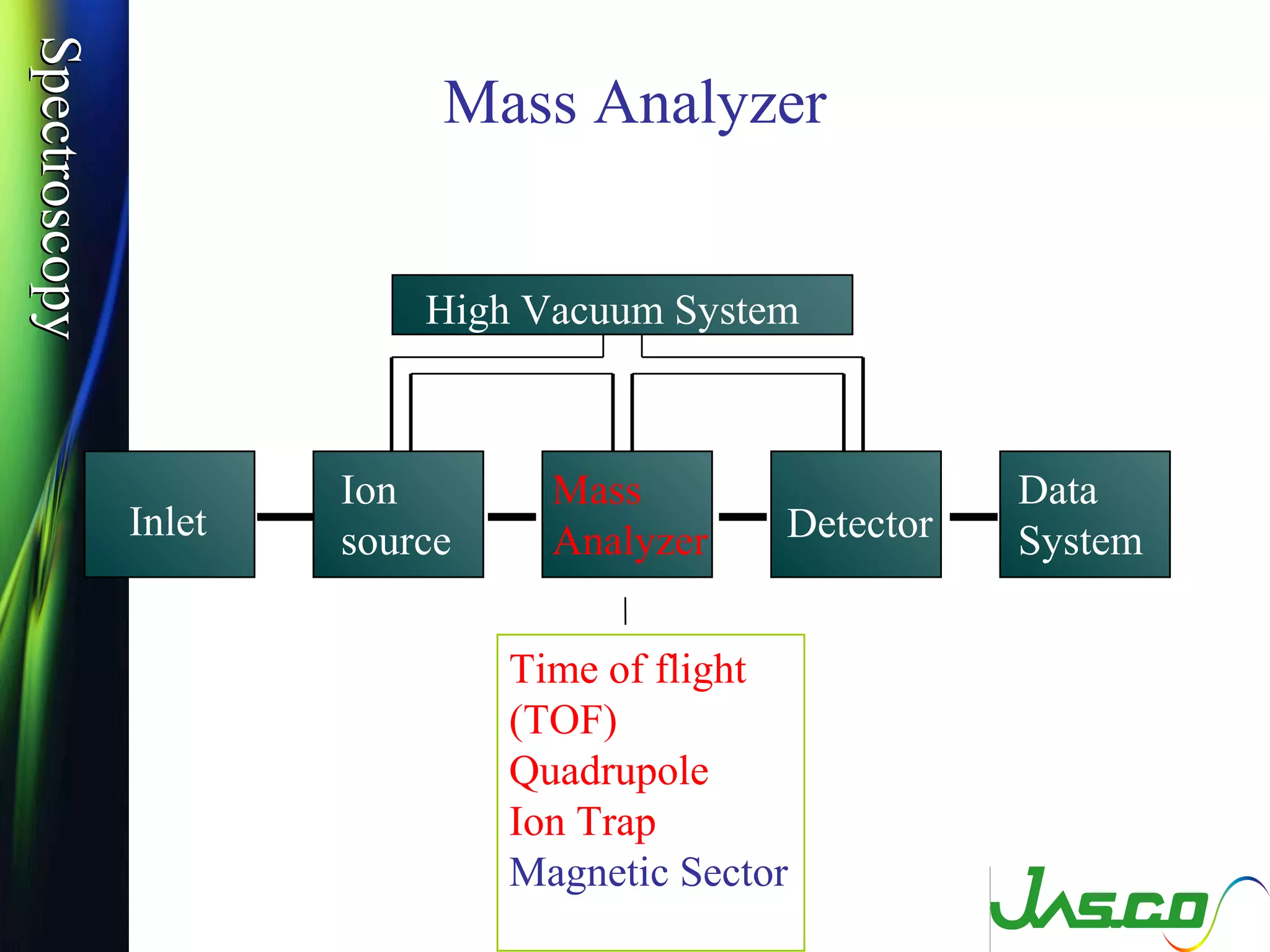
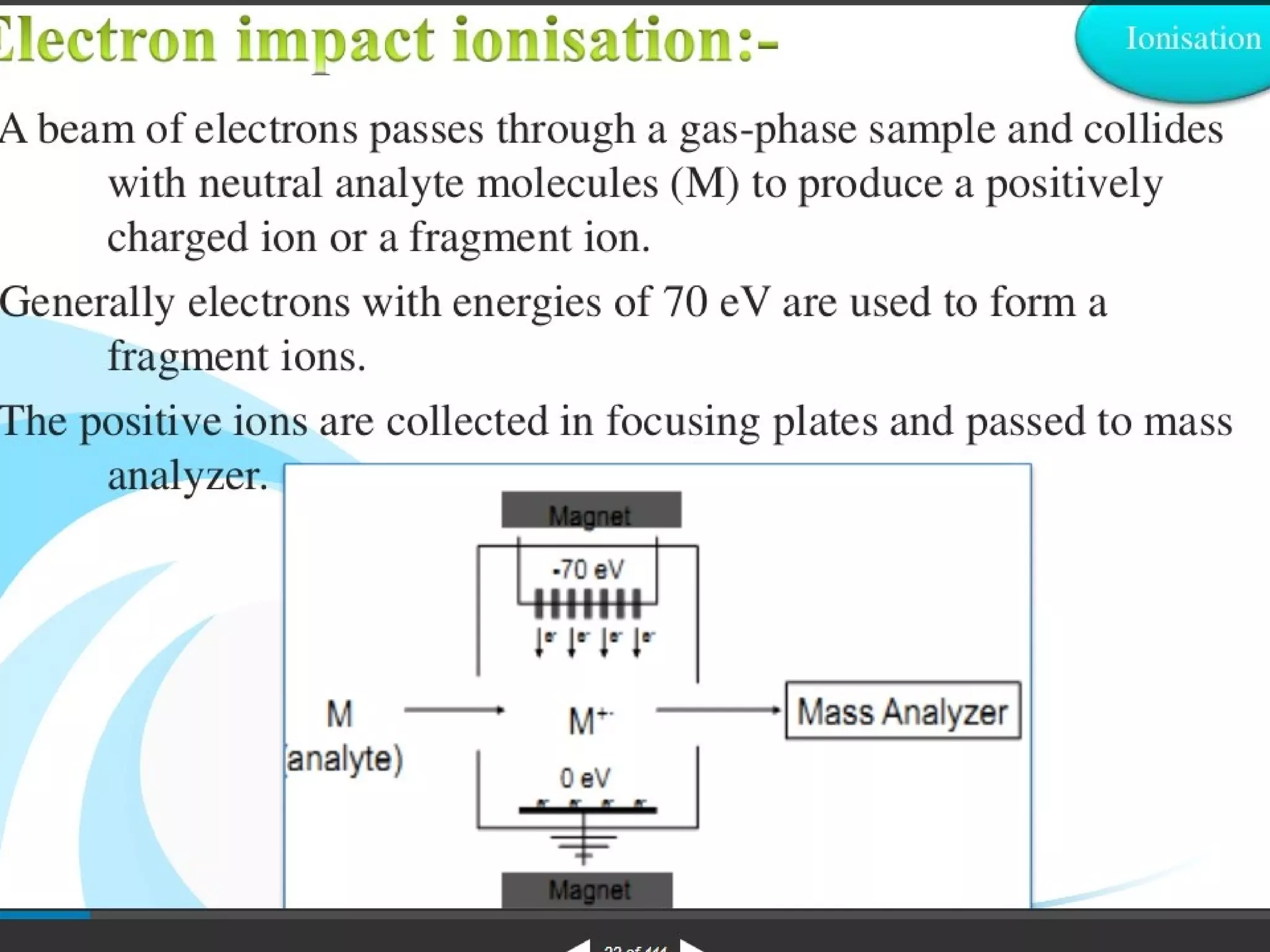
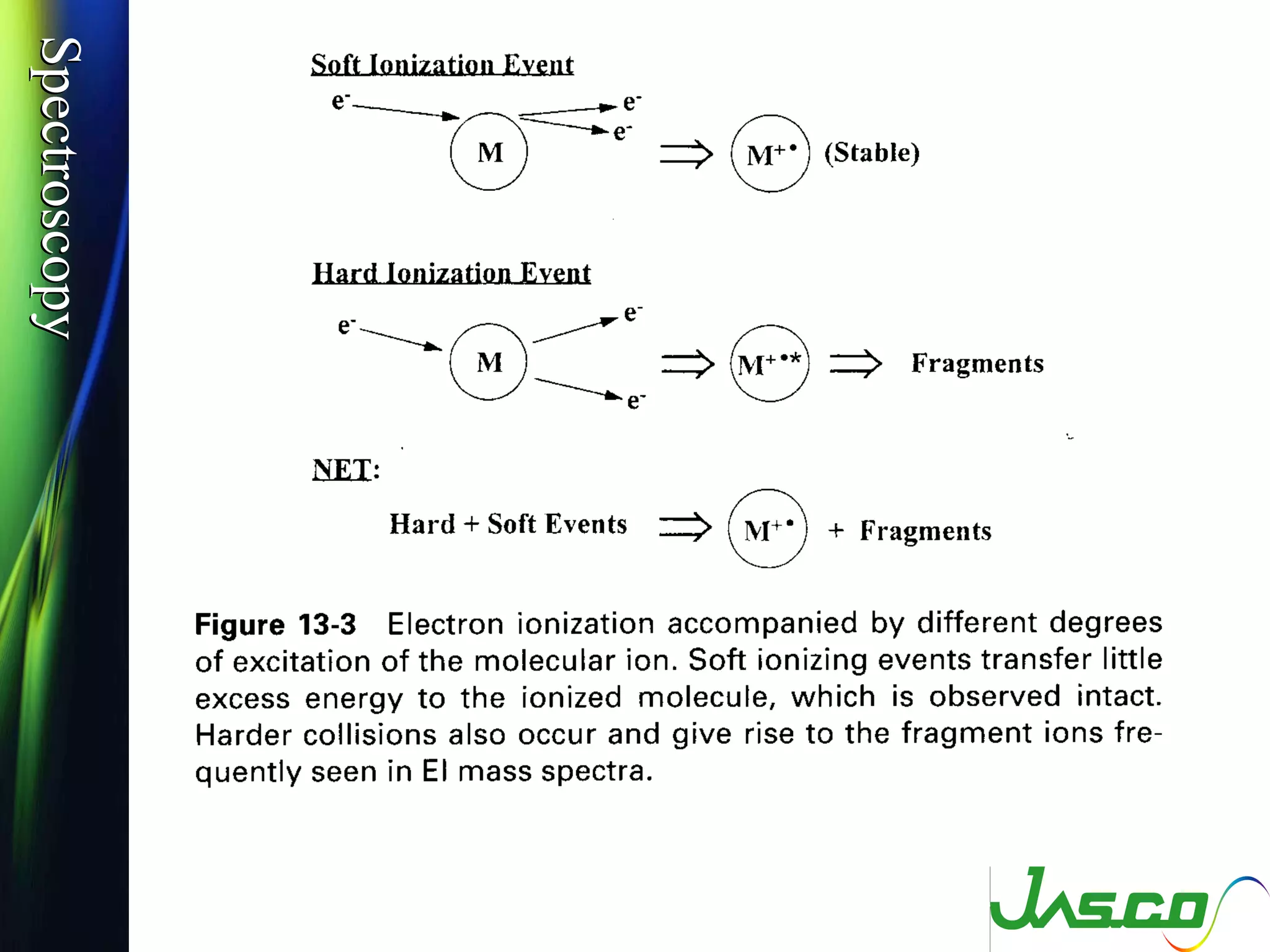
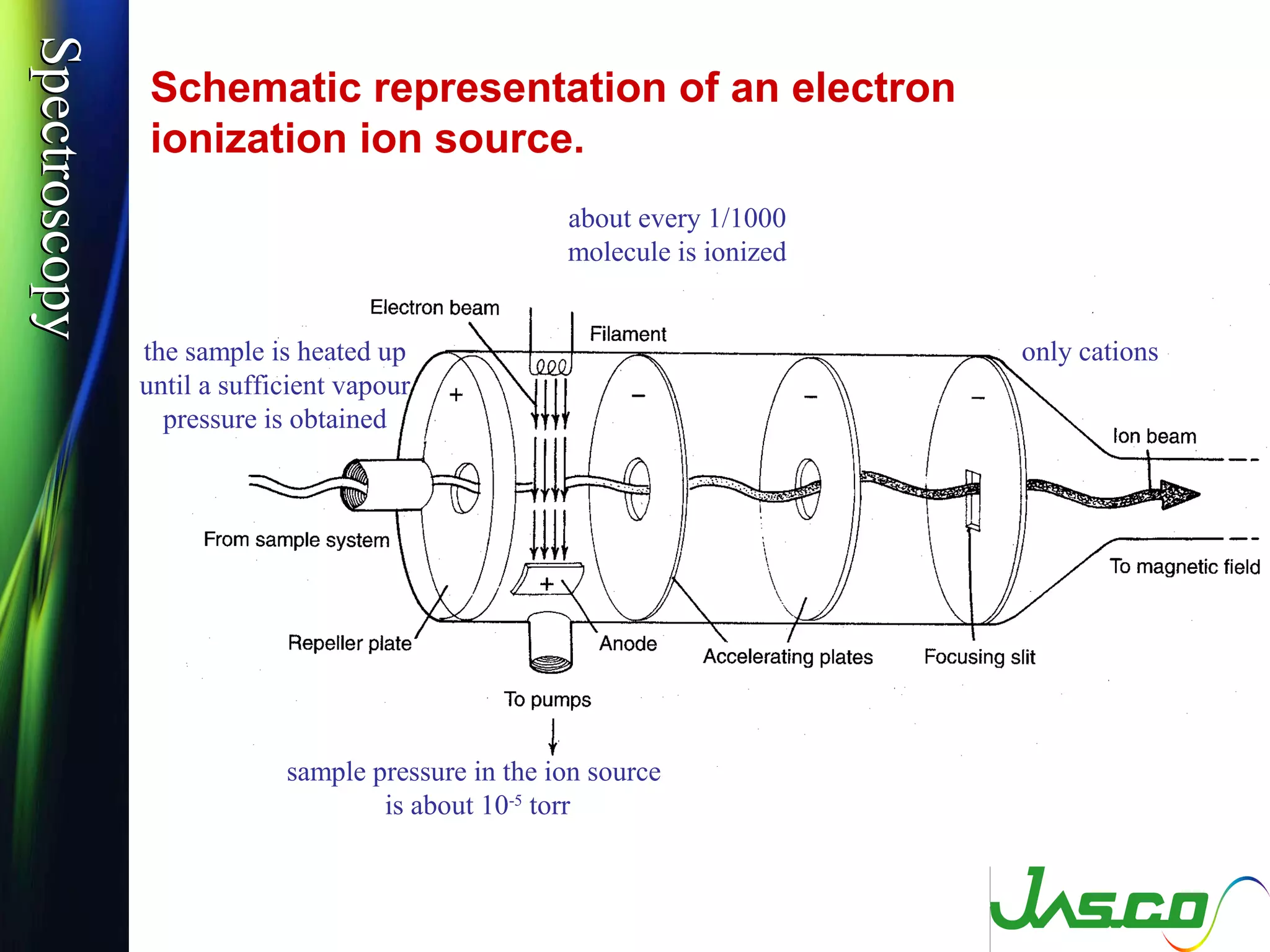
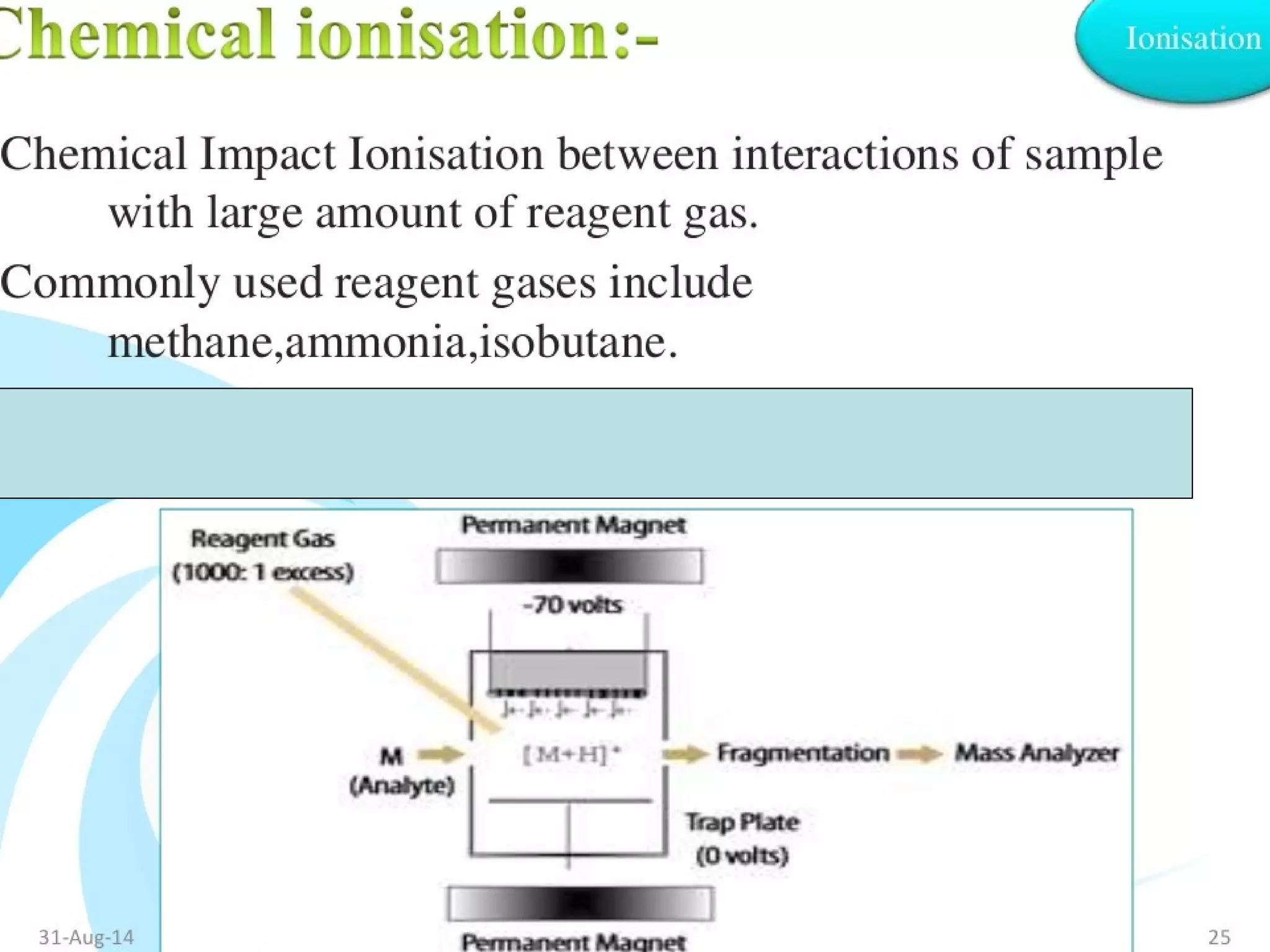
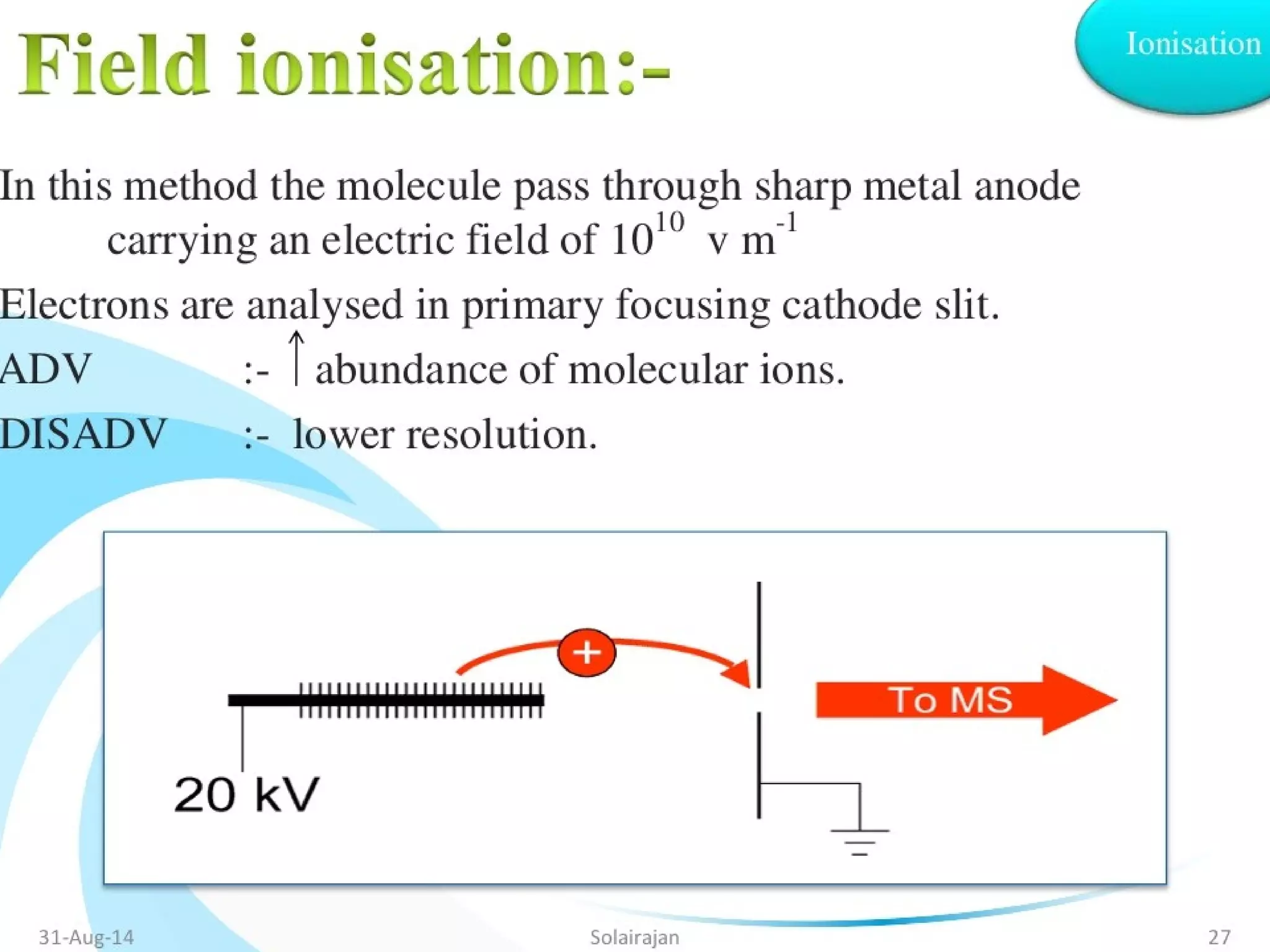
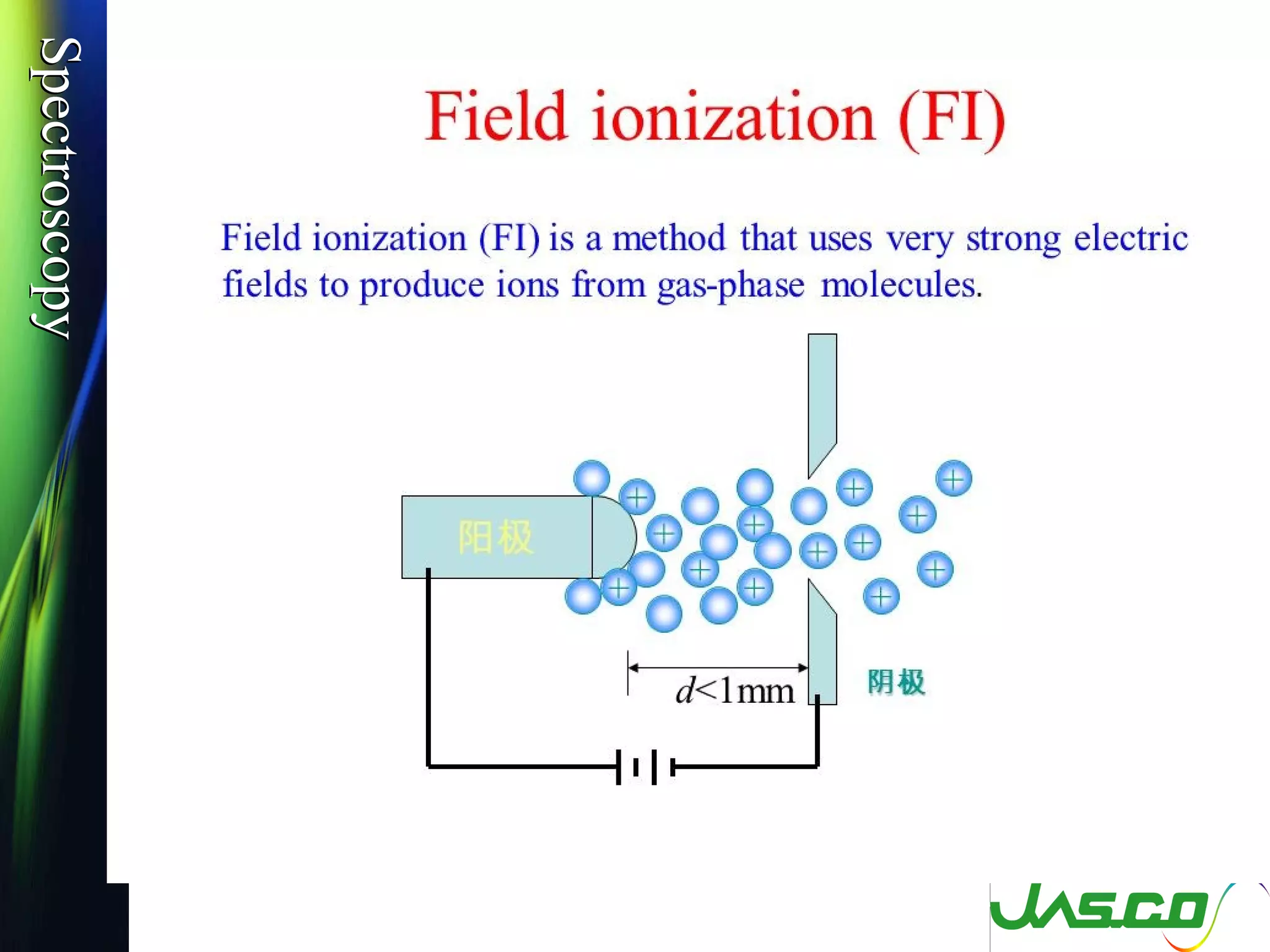
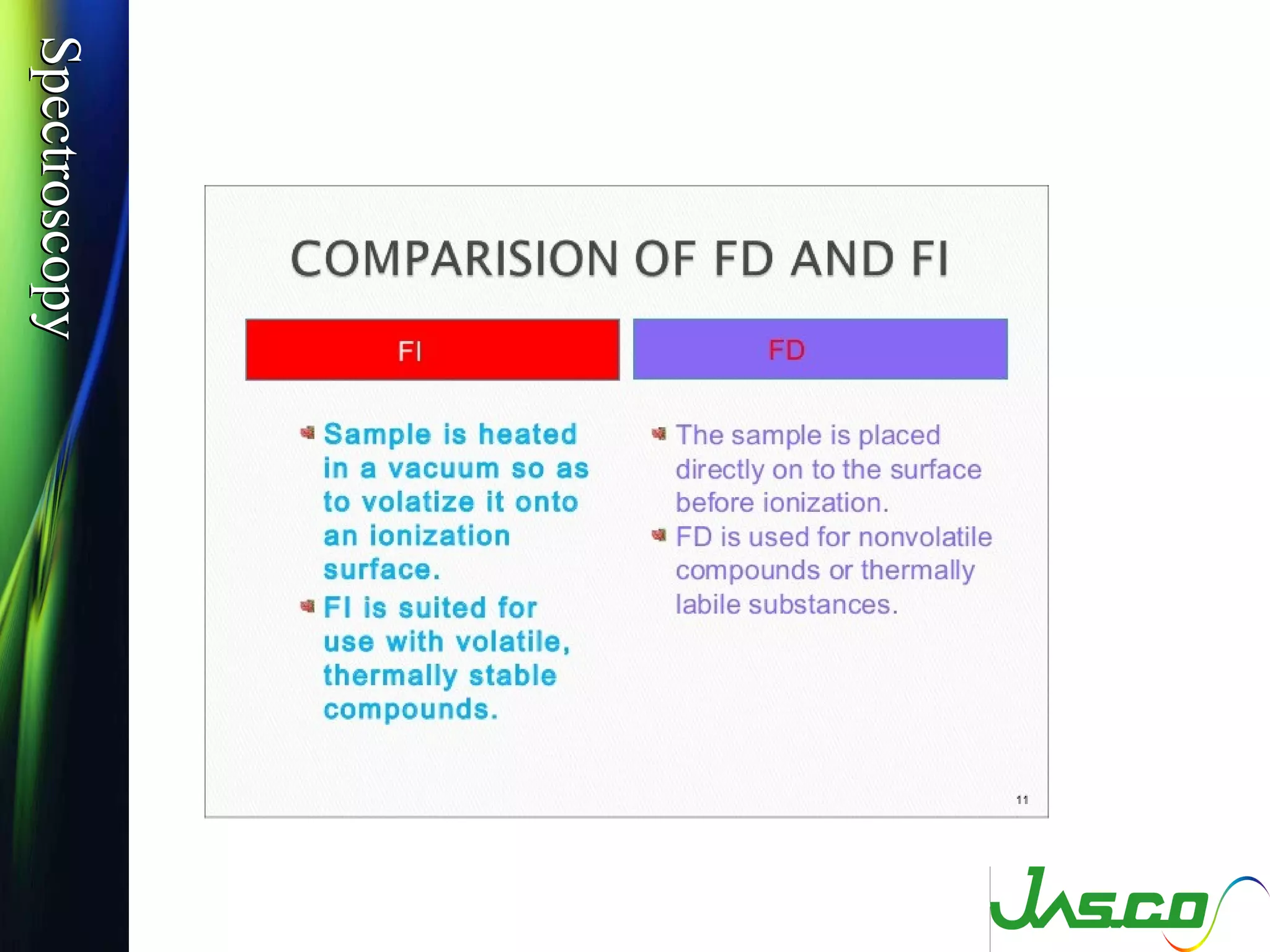
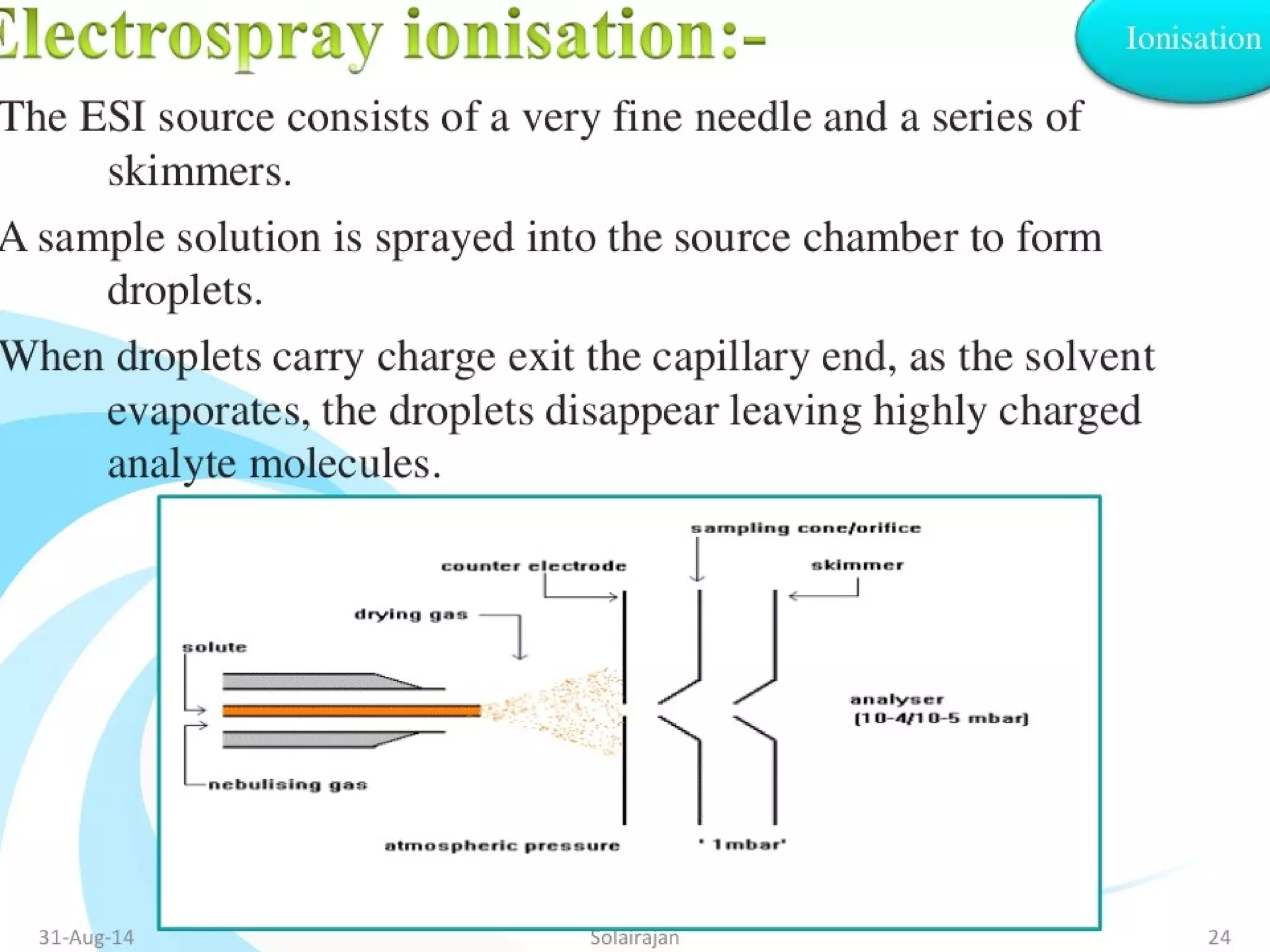
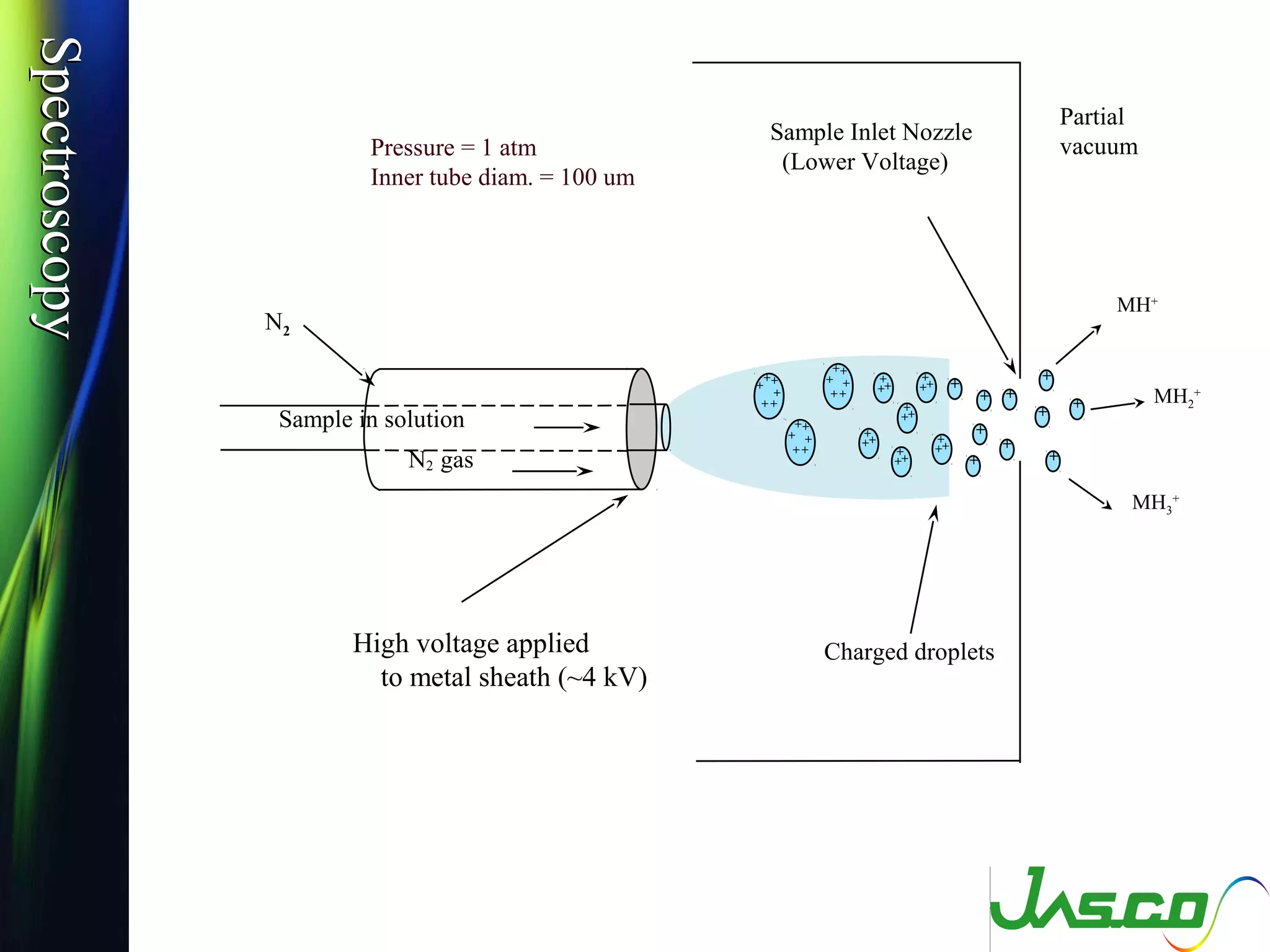
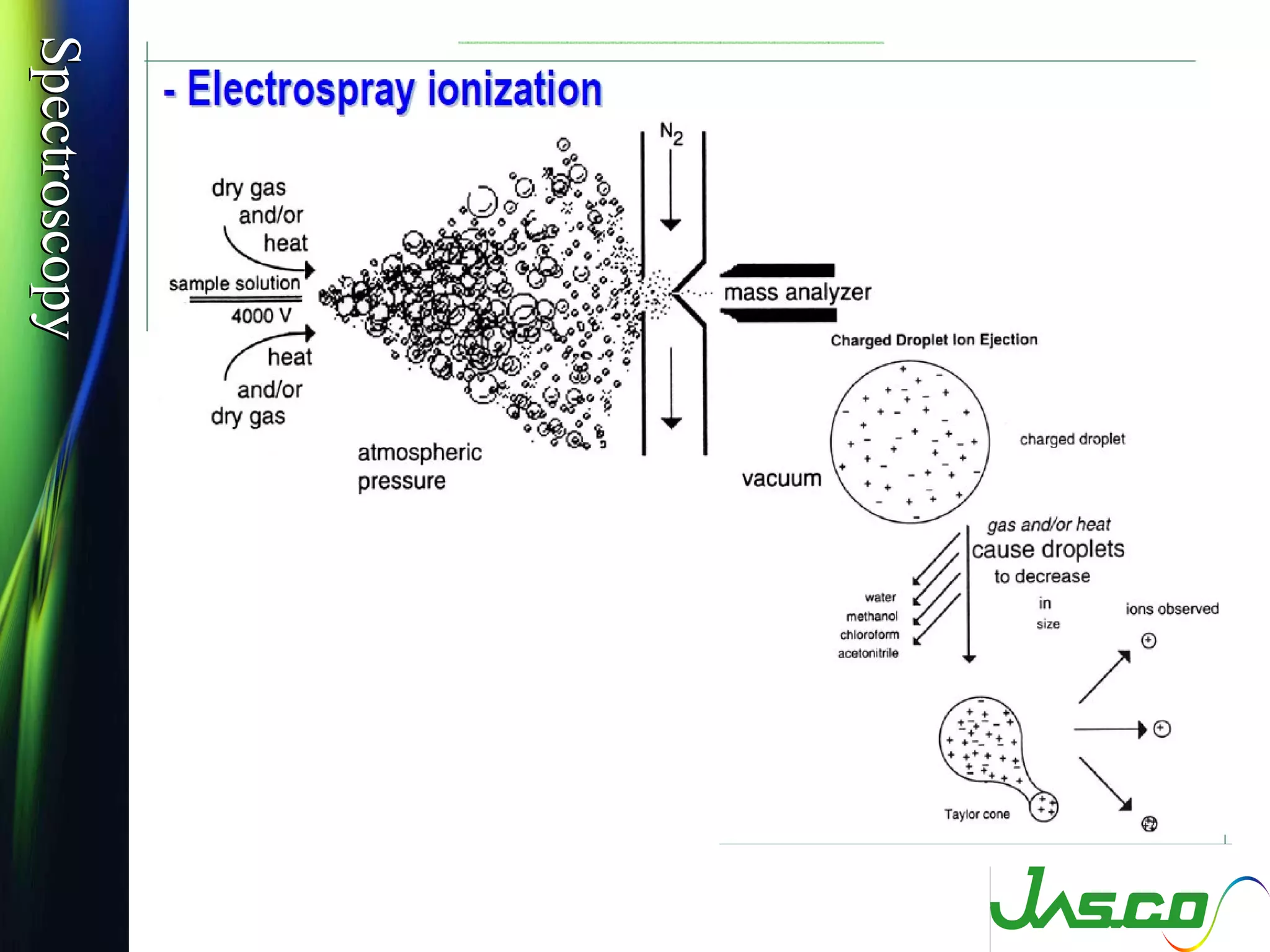
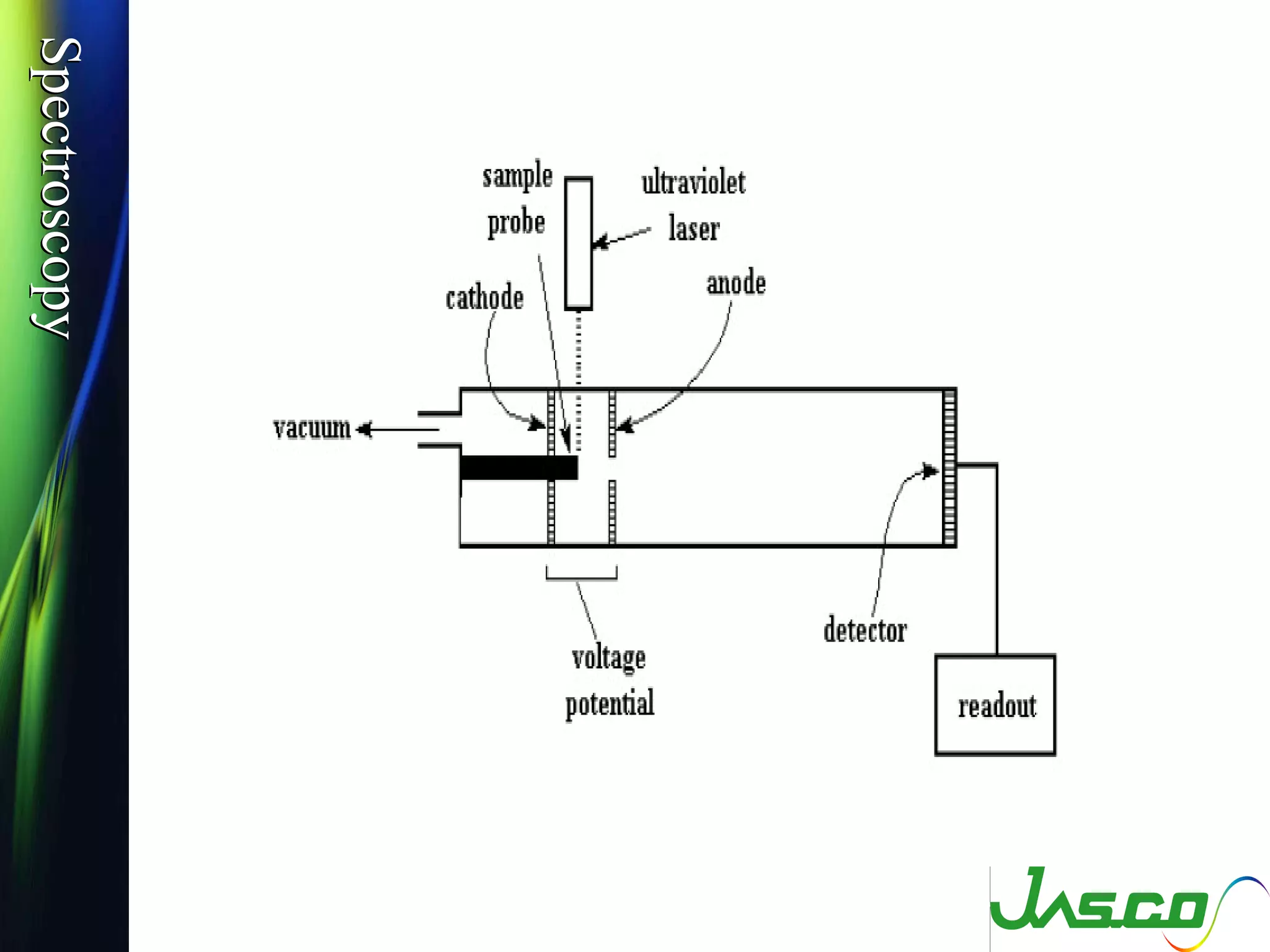
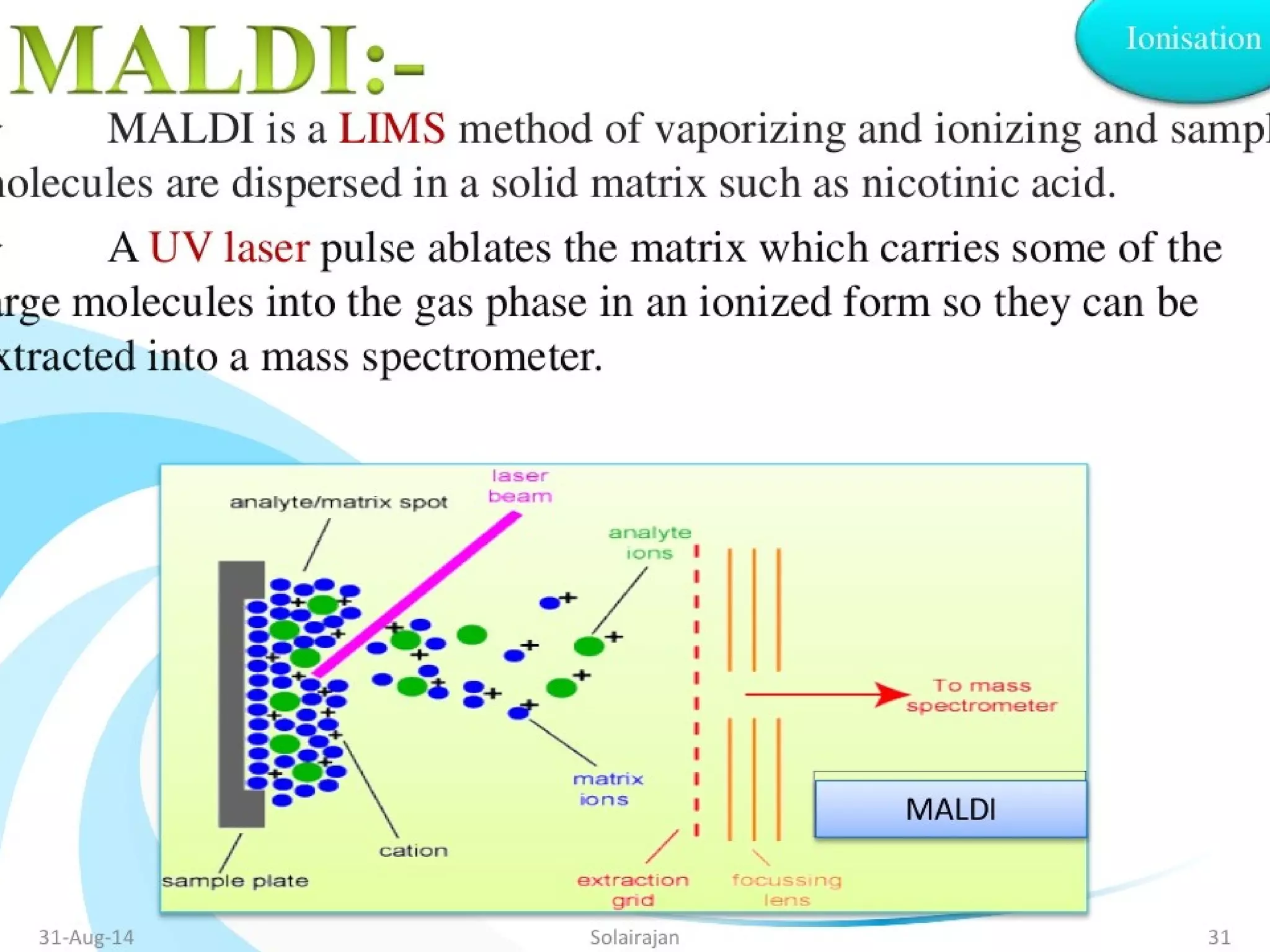
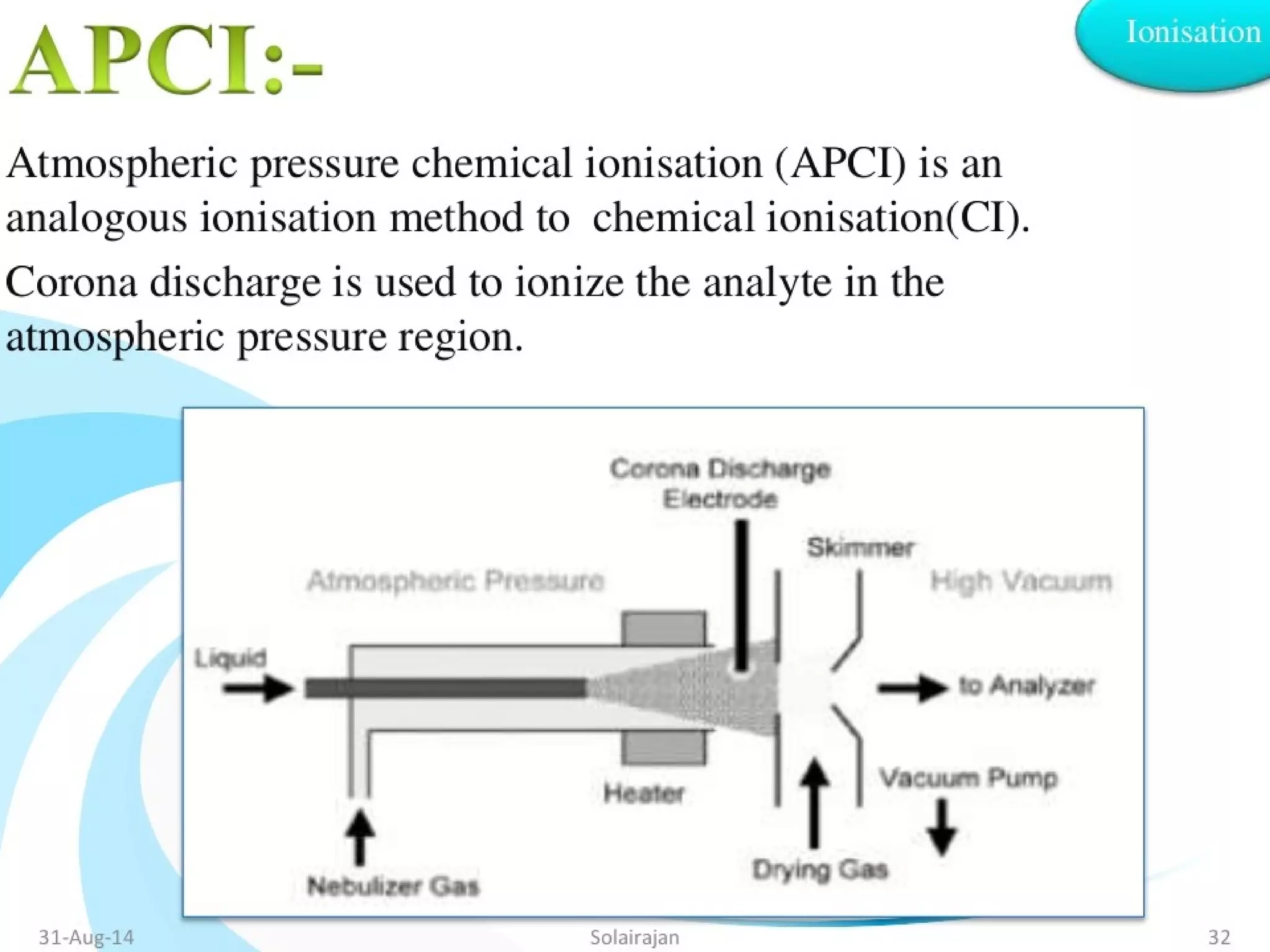
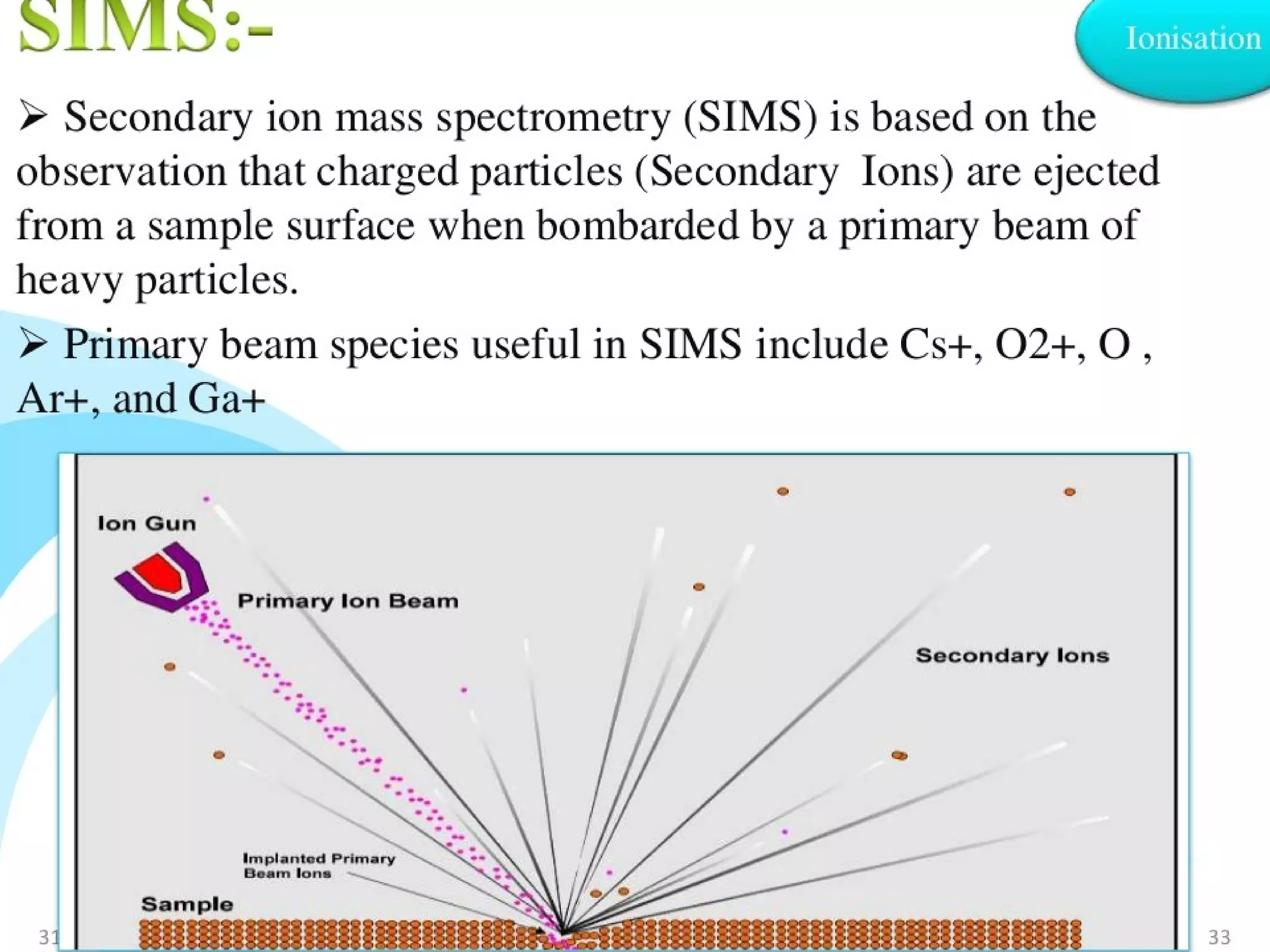
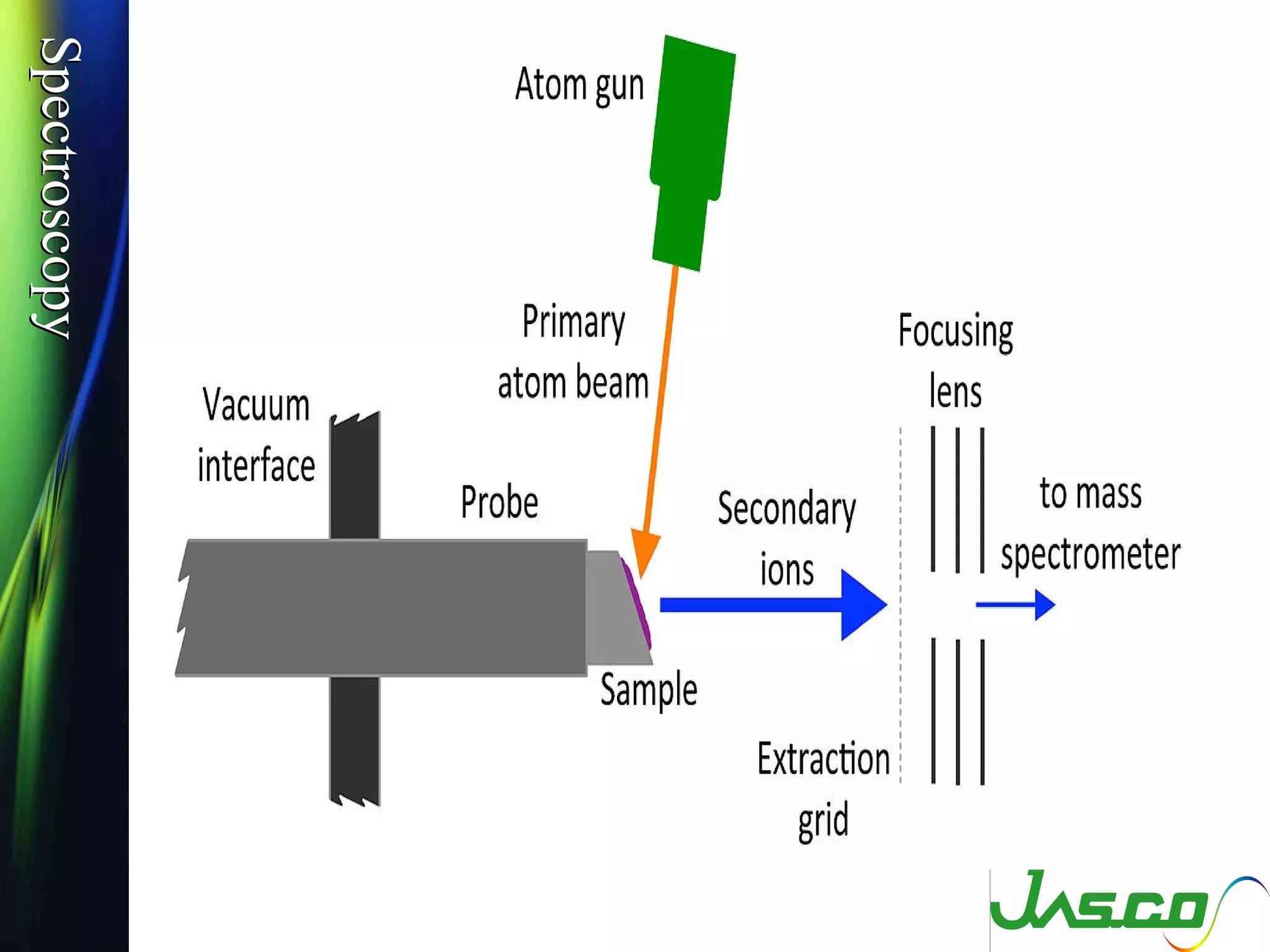
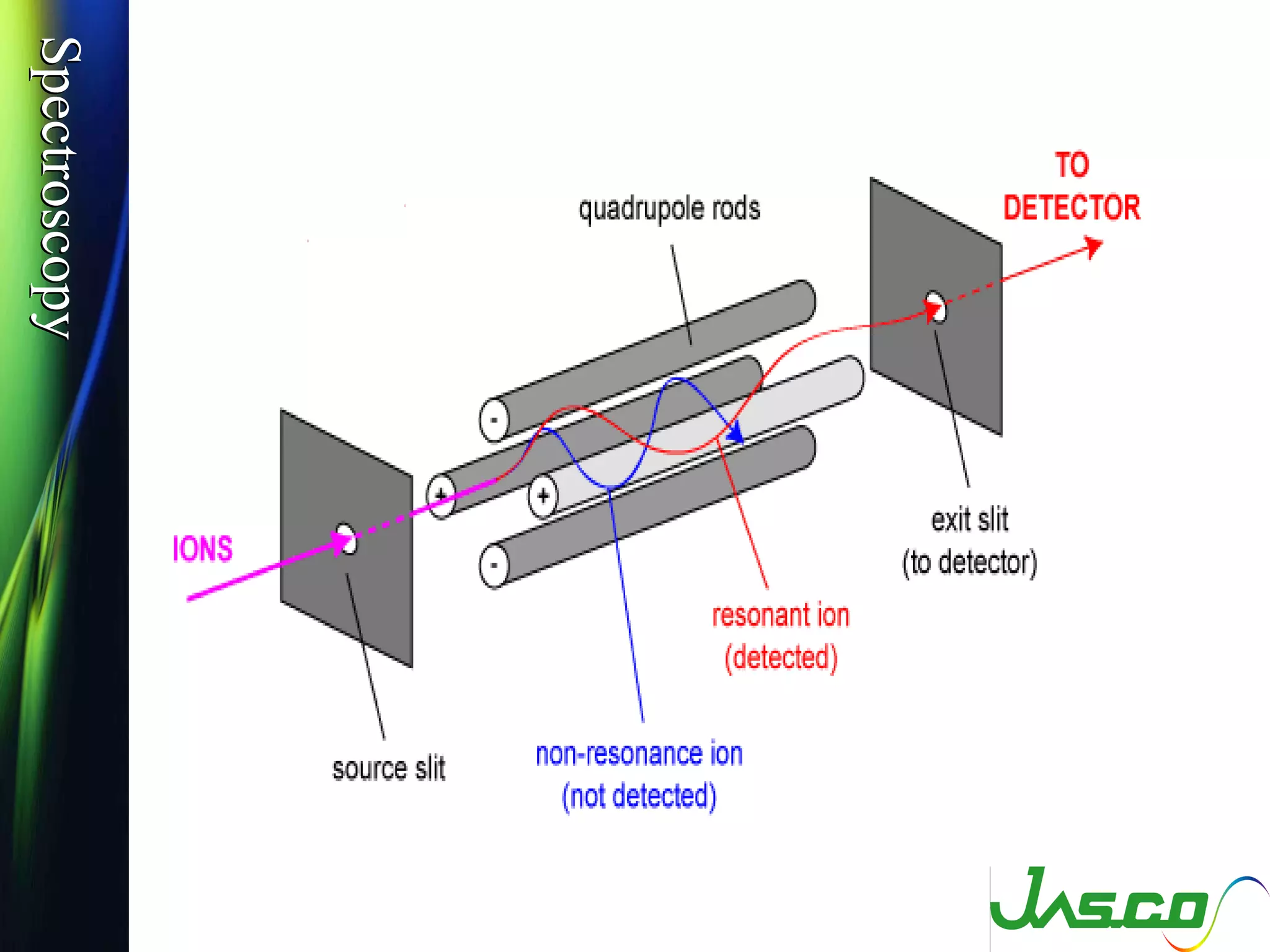
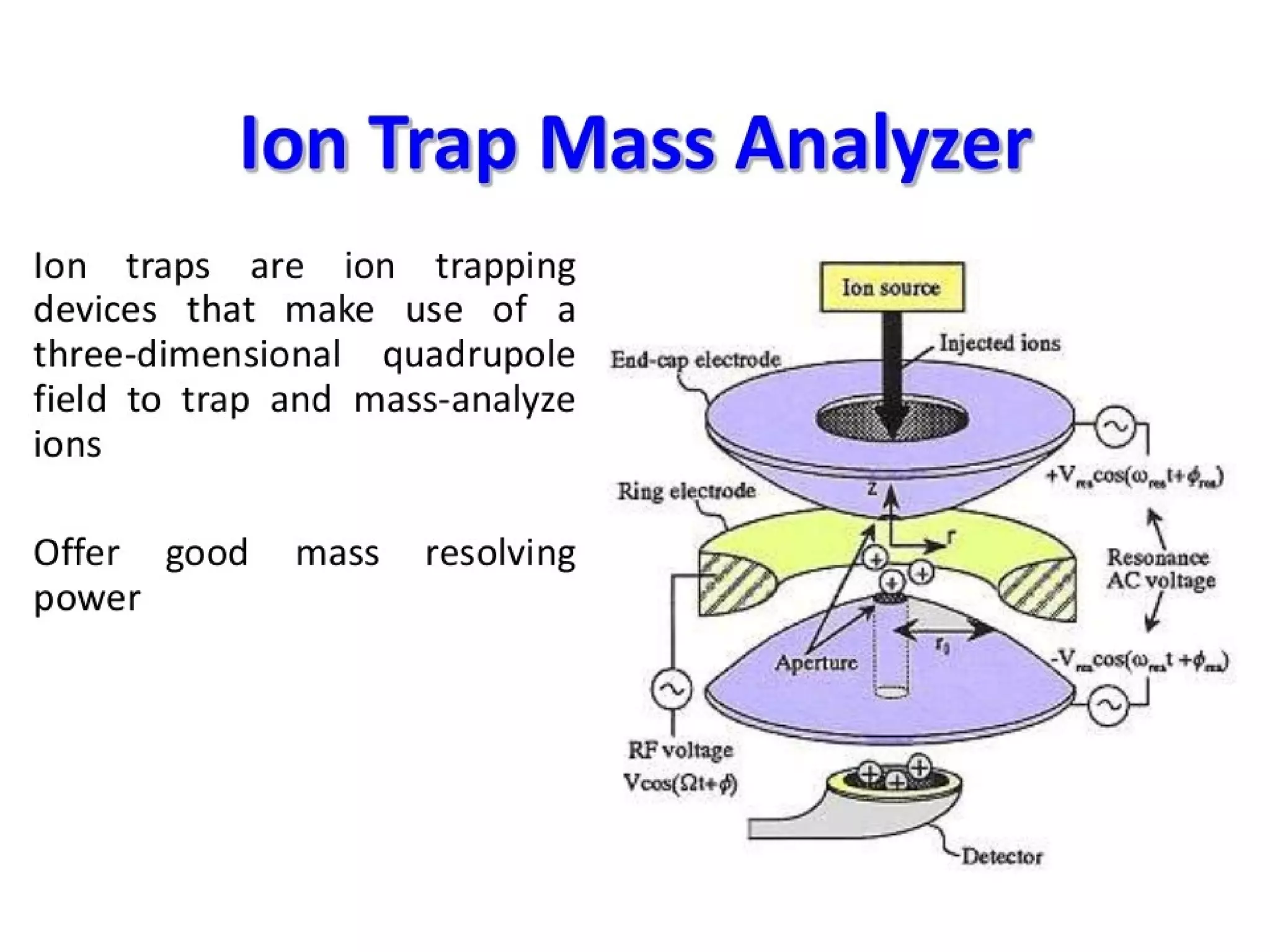
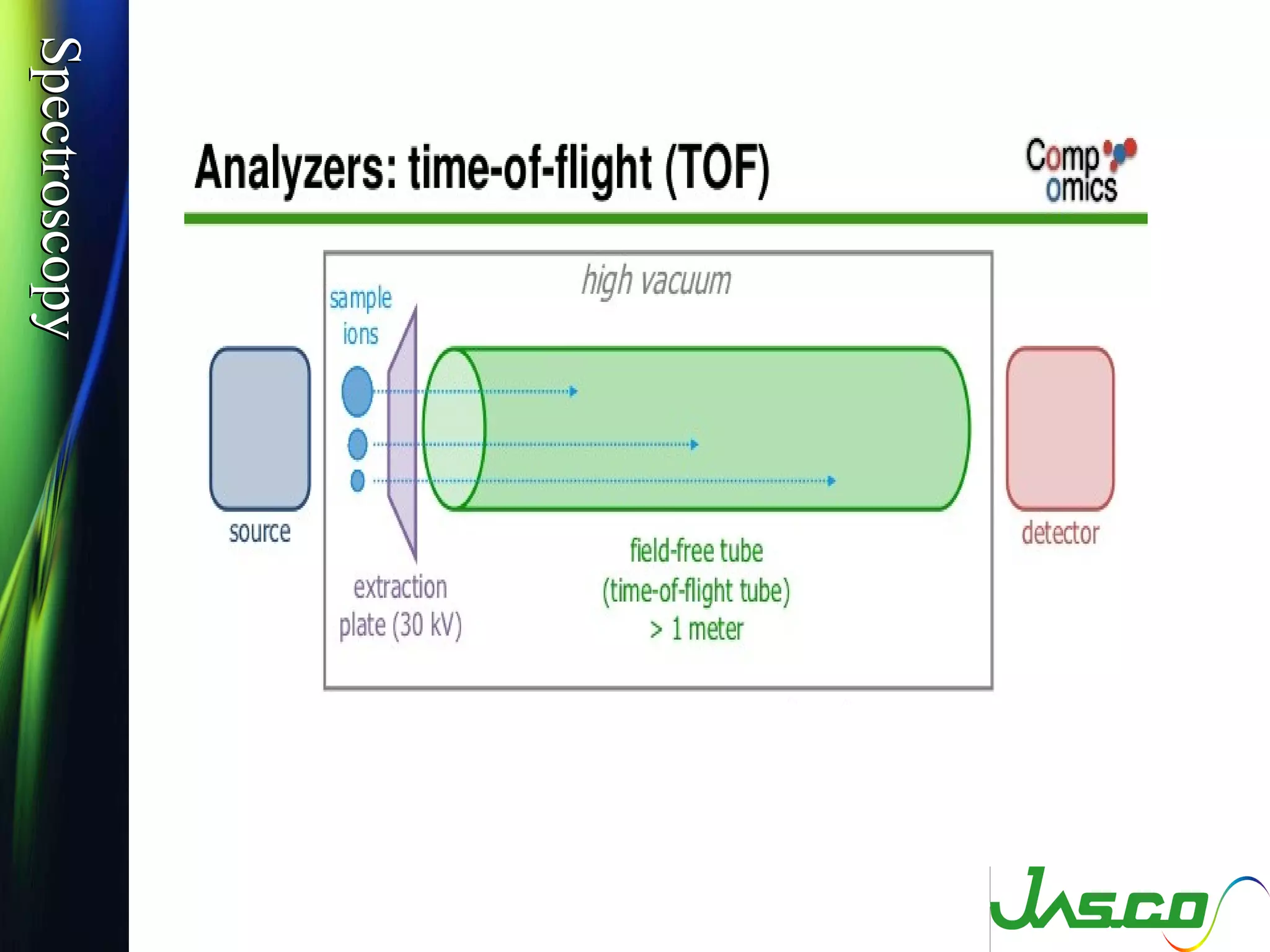
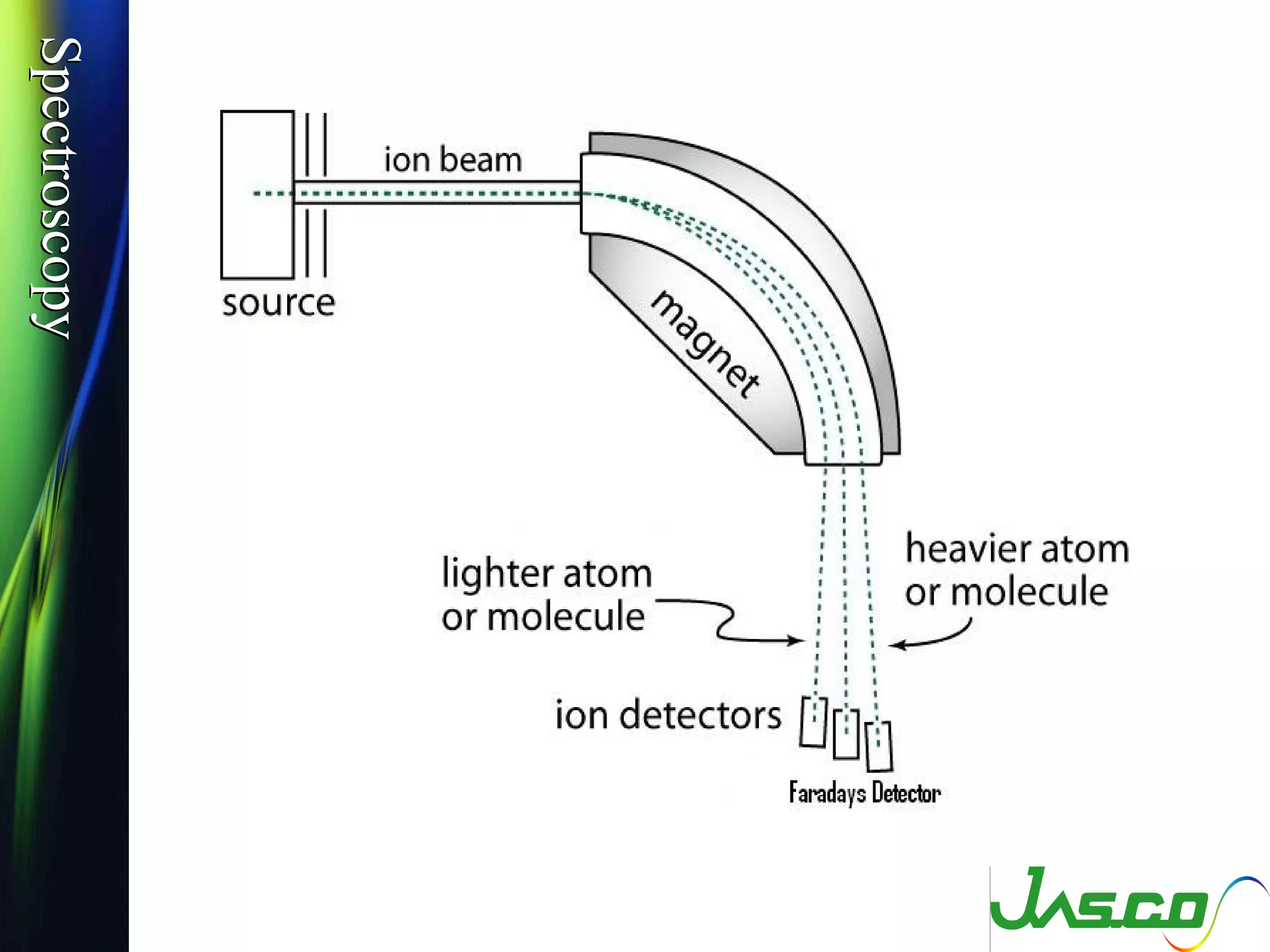
Mass spectroscopy is a technique used to determine the molecular mass and elemental composition of a compound. It works by ionizing molecules using electron bombardment or chemical ionization and then separating the resulting ions based on their mass-to-charge ratio using electric and magnetic fields. The instrument consists of an ion source, a mass analyzer, and an ion detector. Common ion sources include electron impact, chemical ionization, and electrospray ionization, with each having advantages for different types of samples. The document provides detailed explanations of the basic principles and components of mass spectroscopy.