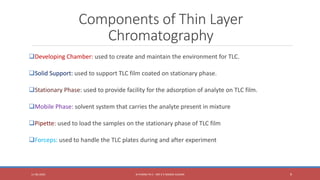
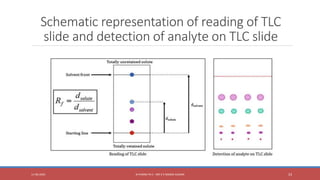
The document provides an overview of thin layer chromatography (TLC), a technique used for separating components in a mixture via a thin stationary phase. It details the principle, types, components, working process, advantages, disadvantages, and applications of TLC. The method is noted for its cost-effectiveness, speed, and ability to visualize separated components, although it has limitations in differentiating enantiomers and reproducibility.