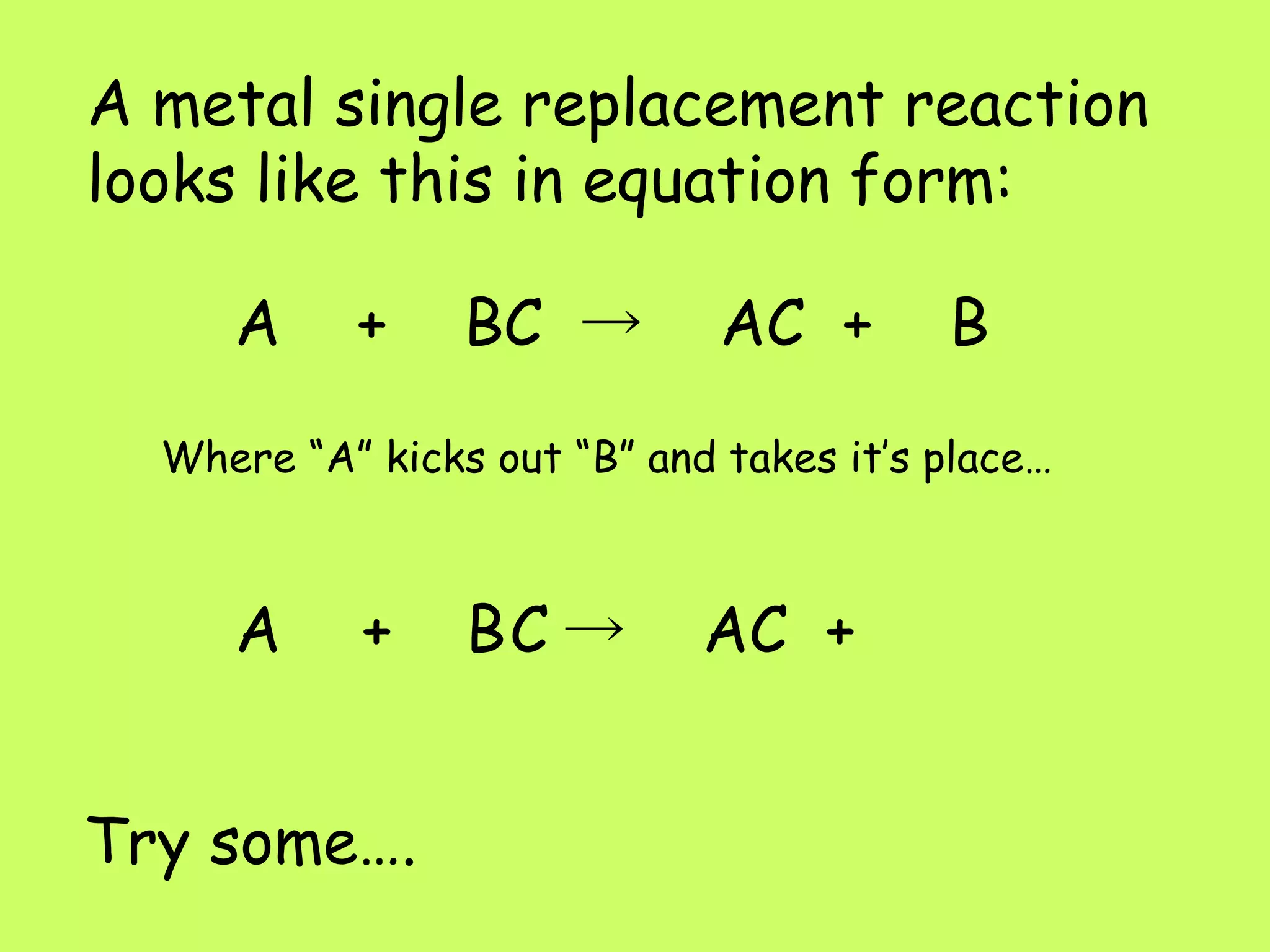
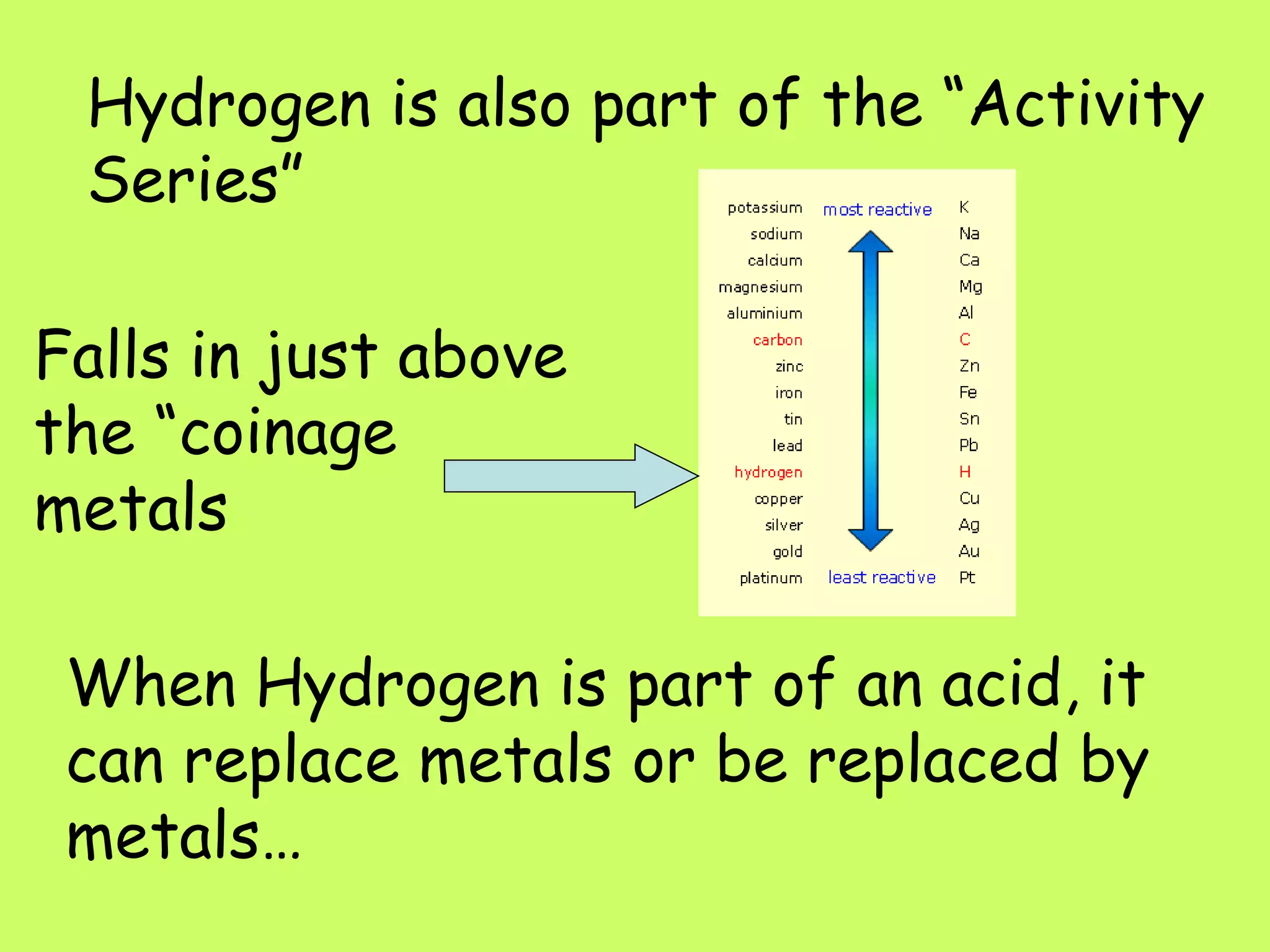
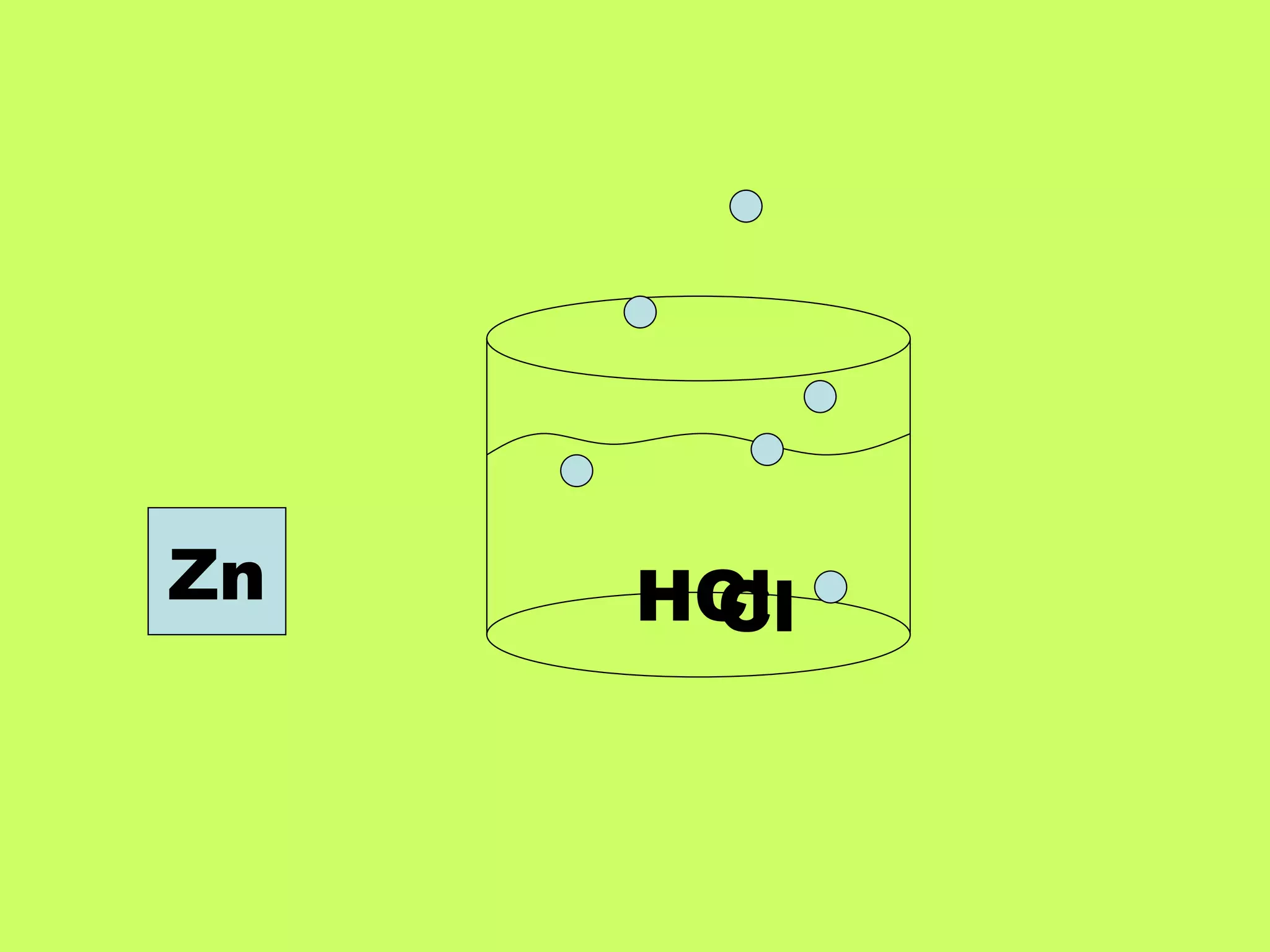
Single replacement reactions occur when a metal replaces another metal in a solution. The metal activity series determines which metal is more reactive and able to displace another. Metals higher on the activity series are stronger and can replace metals lower on the list. A metal single replacement reaction involves a metal (A) displacing another metal (B) from a compound (BC) to form a new compound (AC) and leave the displaced metal (B) on its own. Halogens also undergo single replacement reactions where a halogen replaces another halogen in a compound.