exothermic and endothermic reactions ppt
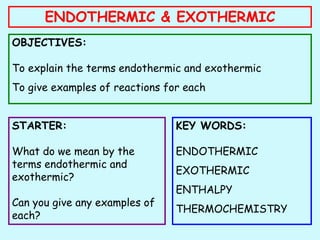
- 1. ENDOTHERMIC & EXOTHERMIC OBJECTIVES: To explain the terms endothermic and exothermic To give examples of reactions for each STARTER: What do we mean by the terms endothermic and exothermic? Can you give any examples of each? KEY WORDS: ENDOTHERMIC EXOTHERMIC ENTHALPY THERMOCHEMISTRY
- 2. Chemical reactions can either release energy to their surroundings, __________, or energy can be transferred to them from the surroundings, ____________. EXOTHERMIC ENDOTHERMIC KEY IDEA Bonds contain energy. You need to put in energy to break bonds apart in the REACTANTS in a chemical reaction. Energy is released when new bonds form in the PRODUCTS in a chemical reaction. When bonds break, energy is absorbed (endothermic). When bonds form, energy is released (exothermic). 7.1 ENDOTHERMIC & EXOTHERMIC http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p- 27I_osoaw
- 5. 7.1 ENDOTHERMIC & EXOTHERMIC EXAMPLES: Exothermic: • Neutralising an acid with an alkali • Burning magnesium • Adding water to anhydrous copper sulphate Endothermic: • Thermal decomposition of limestone • Photosynthesis • Heating blue copper sulphate A reaction endothermic in one direction is always exothermic in the other
- 6. 7.1 ENDOTHERMIC & EXOTHERMIC QUANTITIES: • Energy is measured in kilojoules per mole • kJmol-1 CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) CO2 (g) + 2H2O (l) • Combustion of methane one mole of methane reacts with 2 moles of oxygen • It gives out 890kJ of energy
- 7. 7.1 ENDOTHERMIC & EXOTHERMIC INVESTIGATION Follow the instructions on the handout and then answer the following questions: 1. The first reaction is between an acid and an alkali, what do we call this type of reaction? 2. Which gas is given off when sodium hydrogen carbonate reacts with citric acid? 3. Which type of reaction takes place between copper (II) sulfate and magnesium? 4. Which reactions are exothermic and which are endothermic? 5. Describe in terms of bond breaking and bond making, why some reactions are exothermic and some are endothermic.
- 8. 7.1 ENDOTHERMIC & EXOTHERMIC INVESTIGATION 1. Heat some blue copper sulphate in a boiling tube 2. Let it cool 3. Add a couple of drops of water and feel the bottom of the boiling tube 4. Write out an equation for the reaction 5. Which way is endothermic which is exothermic? How do you know?
- 9. 7.1 ENDOTHERMIC & EXOTHERMIC ANSWERS 1. Neutralisation. 2. Carbon dioxide. 3. Displacement reaction – magnesium is higher in the reactivity series so it displaces copper from its sulphate. 4. Sodium hydrogen carbonate solution + citric acid is endothermic, the other reactions are exothermic. 5. Reactions involve making and breaking bonds. Energy is required to break bonds. Energy is released when bonds are made. If more energy is required to break the bonds in a reaction than that released by making the bonds then the reaction is endothermic (heat is absorbed). If less energy is required to break the bonds than that released by making the bonds then the reaction is exothermic (heat is produced).
- 10. I CAN…I AM… How low can you go?? Write what you can do and what grade this is show some proof you can do this! I CAN… I AM… Describe the terms endothermic and exothermic C Give examples of endothermic and exothermic reactions B Explain endothermic and exothermic reactions using ideas of bond energy A
- 11. Can you answer this…? This is the first law of Thermodynamics. Using the words ‘system’ for an explosive and ‘surroundings’ for the air around the explosive, explain whether explosives break this law. “Energy cannot be made or destroyed.”
- 12. Reactions that give out HEAT energy to the surroundings are ____THERMIC Reactions that take in heat energy from the surroundings are
- 13. Reactions that give out HEAT energy to the surroundings are EXOTHERMIC Reactions that take in heat energy from the surroundings are ENDOTHERMIC
- 15. Lesson Objectives We are learning to:- Identify exothermic and endothermic reactions What I’m Looking For:- •You must be able to be able to assign thermic reactions as +ΔH or –ΔH •You should be able to construct a simple energy level diagram for endo- and exo- thermic reaction •You could be able to calculate the energy change in a reaction using bond enthalpies
- 16. • Magnesium + Hydrochloric acid Gets hot 25o C 45o C magnesium Hydrochloric acid Heat energy given out Exothermic Reactions
- 17. • If heat is given out this energy must have come from chemical energy in the starting materials (reactants). Reactants convert chemical energy to heat energy. The temperature rises. 25o C 45o C Exothermic Reactions
- 18. 45o C • Almost immediately the hot reaction products start to lose heat to the surroundings and eventually they return to room temperature. 25o C Chemical energy becomes heat energy. The reaction mixture gets hotter. Eventually this heat is lost to the surroundings. It follows that reaction products have less chemical energy than the reactants had to start with. Exothermic Reactions
- 19. Energy / kJ) Progress of reaction (time) Energy Level Diagram for an Exothermic Reaction reactants Reactants have more chemical energy. Some of this is lost as heat which spreads out into the room. products Products now have less chemical energy than reactants.
- 20. Energy / kJ Progress of reaction reactants products H=negative Energy Level Diagram for an Exothermic Reaction 2. H is how much energy is given out H is negative because the products have less energy than the reactants. Energy Level Diagram for an Exothermic Reaction
- 21. Exothermic reactions give out energy. There is a temperature rise and H is negative. Exothermic Reaction - Definition products Energy / kJ) Progress of reaction reactants H is negative
- 22. Activity
- 23. Endothermic Reactions • Endothermic chemical reactions are relatively rare. • A few reactions that give off gases are highly endothermic - get very cold. • Dissolving salts in water is another process that is often endothermic. Endothermic reactions cause a decrease in temperature.
- 24. Cools Heat energy taken in as the mixture returns back to room temp. Starts 25°C Cools to 5°C Ammonium nitrate Water Endothermic reactions cause a decrease in temperature. Returns to 25°C Endothermic Reactions
- 25. • Extra energy is needed in order for endothermic reactions to occur. • This comes from the thermal energy of the reaction mixture which consequently gets colder. Reactants convert heat energy into chemical energy as they change into products. The temperature drops. 25o C 5o C Endothermic Reactions
- 26. 25o C • The cold reaction products start to gain heat from the surroundings and eventually return to room temperature. 5o C The reactants gain energy. 25o C This comes from the substances used in the reaction and the reaction gets cold. Eventually heat is absorbed from the surroundings and the mixture returns to room temperature. Overall the chemicals have gained energy. Endothermic Reactions
- 27. products Energy / kJ) Progress of reaction reactants H=+ Energy Level Diagram for an Endothermic Process This is positive because the products have more energy than the reactants. This is how much energy is taken in
- 28. Endothermic reactions take in energy. There is a temperature drop and H is positive. Endothermic Reaction Definition H=+ products Energy / kJ Progress of reaction reactants
- 29. Exothermic reactions give out energy. There is a temperature rise and H is negative. Exothermic Reaction - Definition products Energy / kJ) Progress of reaction reactants H is negative
- 30. Activity
- 31. Endothermic Reactions • Endothermic chemical reactions are relatively rare. • A few reactions that give off gases are highly endothermic - get very cold. • Dissolving salts in water is another process that is often endothermic. Endothermic reactions cause a decrease in temperature.
- 32. Are these endothermic or exothermic? 1. A red glow spread throughout the mixture and the temperature rose. 2. The mixture bubbled vigorously but the temperature dropped 150C. 3. Hydrazine and hydrogen peroxide react so explosively and powerfully that they are used to power rockets into space. 4. The decaying grass in the compost maker was considerably above the outside temperature. exo endo exo exo Activity
- 33. Sketch the two energy diagrams and label exothermic and endothermic as appropriate. H=+ products Energy / kJ Progress of reaction reactants products Energy / kJ) Progress of reaction reactants H=- Activity
- 34. Breaking chemical bonds • Most chemicals will decompose (break up) if we heat them strongly enough. • This indicates that breaking chemical bonds requires energy – is an endothermic process. Heat taken in Energy needed to overcome the bonding between the atoms Energy in chemicals Energy needed
- 35. Making chemical bonds • It is reasonable to assume that bond making will be the opposite of bond breaking • Energy will be given out in an exothermic process when bonds are formed. Heat given out Energy given out as bonds form between atoms Energy in chemicals Energy given out
- 36. Changes to chemical bonds Endothermic Reactions • In most chemical reactions some existing bonds are broken (endothermic) Energy taken in as old bonds break • But new bonds are made (exothermic) Energy in chemicals reactants products Energy given out as new bonds form H Overall endothermic in this case
- 37. Changes to chemical bonds Exothermic Reactions • Again some existing bonds are broken (endothermic) Energy taken in as old bonds break • And new bonds are formed (exothermic) Energy in chemicals reactants products Energy given out as new bonds form H Overall exothermic – in this case
- 38. Summary – Bond Changes • Where the energy from bond forming exceeds that needed for bond breaking the reaction is exothermic. • Where the energy for bond breaking exceeds that from bond forming the reaction is endothermic. Energy in chemicals reactants products H Bonds break Bond forming Energy in chemicals reactants products H Bonds break Bonds form Exo Endo