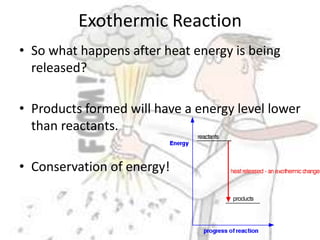
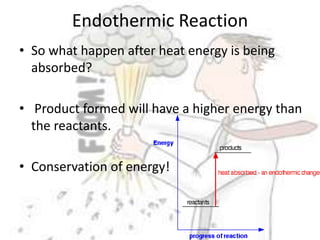
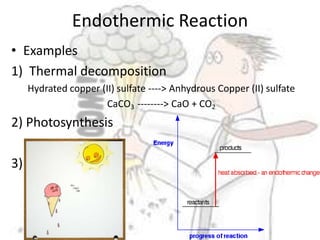
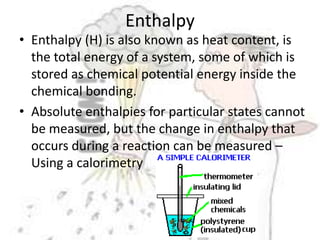
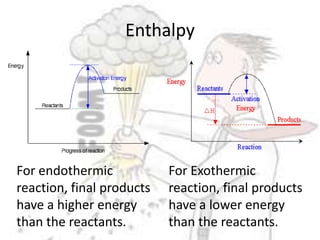
The document discusses chemical energetics, emphasizing the energy changes during reactions, distinguishing between exothermic and endothermic processes. It explains how to calculate enthalpy changes (∆h) and provides examples of reactions, showcasing the principles of energy absorption and release associated with bond breaking and formation. The conservation of energy in chemical reactions is highlighted, along with the significance of bond energies.