This document discusses precipitation reactions and salt families. It provides the following key points:
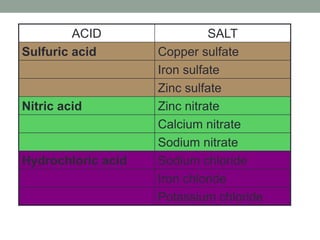
1. Salts are produced from chemical reactions between acids and other substances. Each acid produces a characteristic family of salts, such as sulfates from sulfuric acid and nitrates from nitric acid.
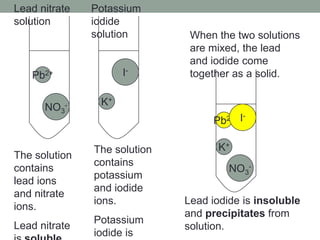
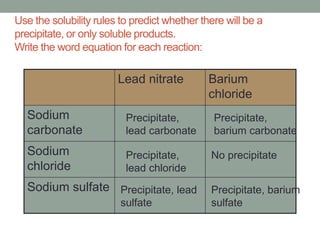
2. Precipitation occurs when two solutions are mixed and an insoluble compound forms, coming out of solution as a solid precipitate. Solubility rules can be used to predict whether a precipitation reaction will occur.
3. Practical experiments are described to mix solutions of substances like lead nitrate and barium chloride and observe any precipitates that form based on the solubility rules. Word equations are also written for precipitation