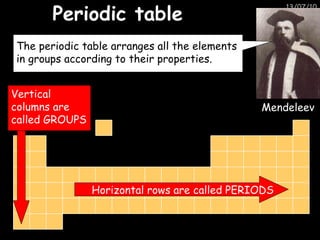
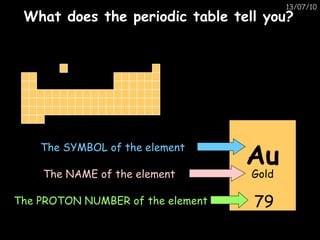
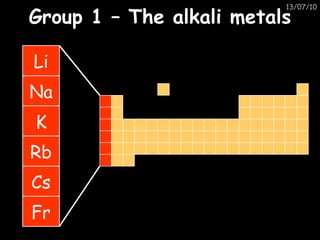
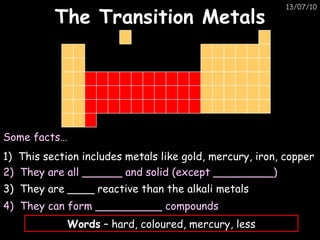
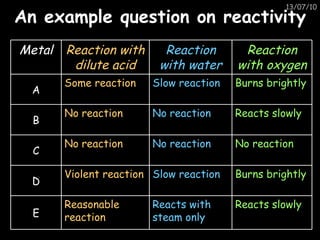
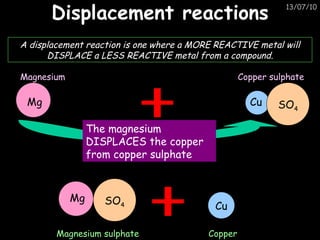
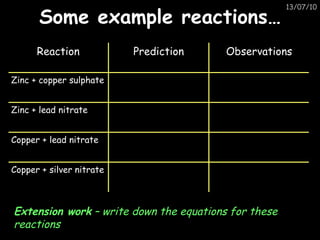
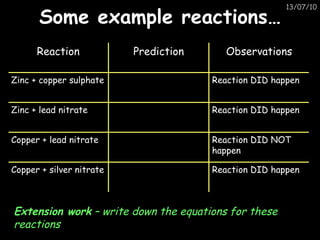
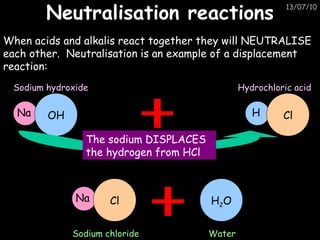
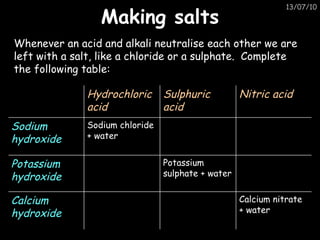
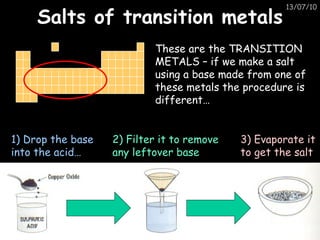
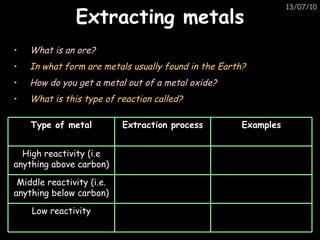
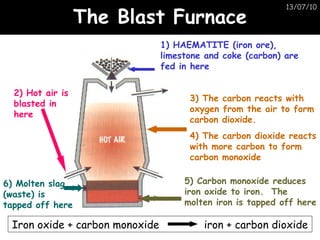
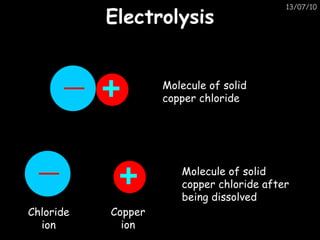
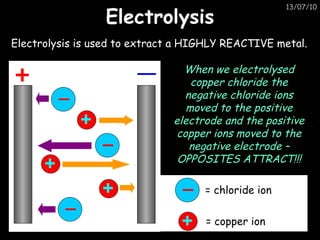
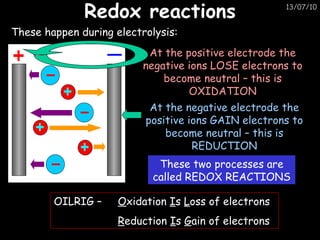
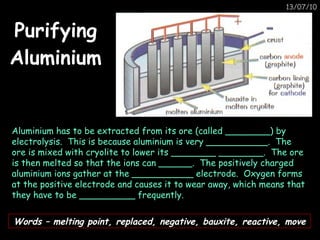
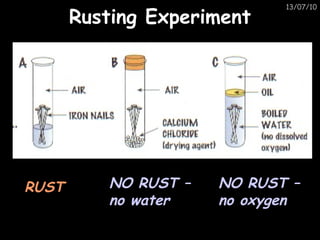
The periodic table arranges elements in horizontal rows called periods and vertical columns called groups. It provides the symbol, name, and proton number of each element. Group 1 elements are alkali metals that react with oxygen and water. Transition metals are hard, colored solids that form complex compounds and are less reactive than alkali metals. The reactivity series lists metals in order of reactivity from most to least reactive. Displacement reactions occur when a more reactive metal displaces a less reactive one from a compound.