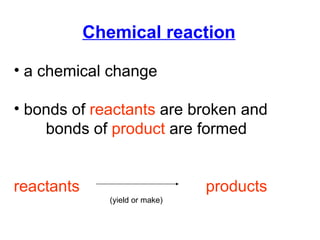
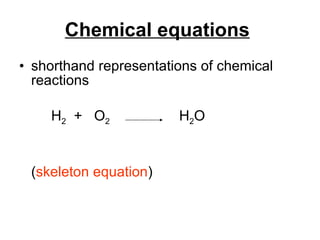
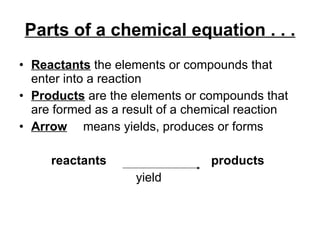
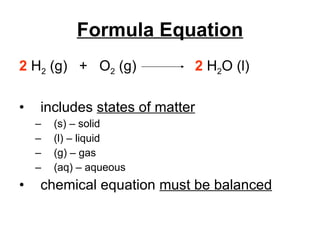
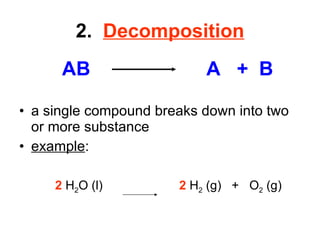
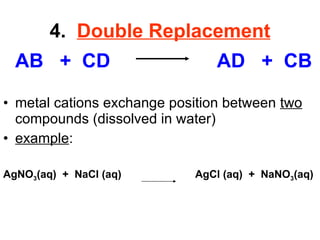
The document discusses chemical reactions and equations. It defines chemical reactions as chemical changes where bonds in reactants break and products form. It also lists several types of chemical reactions including synthesis, decomposition, single replacement, and combustion. The document emphasizes the importance of balancing chemical equations so that mass is conserved in reactions according to the law of conservation of mass.