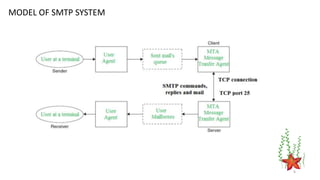
This document discusses SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol). It defines SMTP as an application layer protocol used to transfer email between servers. It describes the basic model of SMTP including the roles of user agents (UA), mail transfer agents (MTA), and how emails are transferred between MTAs across the network. It also lists some common SMTP commands used in the transfer process such as HELO, MAIL, RCPT, and DATA.