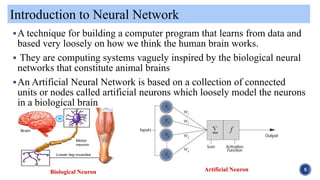
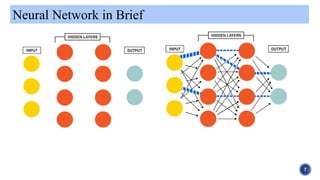
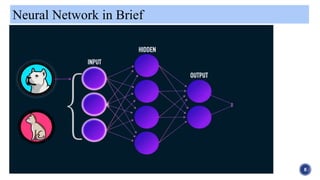
The document provides an overview of artificial neural networks, beginning with their historical development by pioneers like McCulloch and Pitts in 1943. It explains the concept of neural plasticity and how artificial neural networks operate through interconnected nodes that learn from data, highlighting applications such as pattern recognition, time series prediction, and anomaly detection. Additionally, it includes references for further reading on the topic.