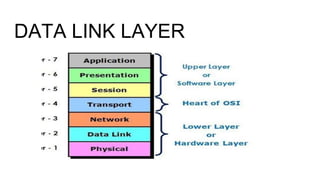
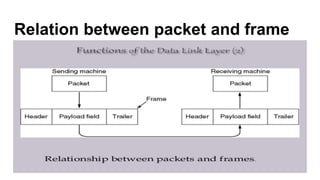
The data link layer provides services like error detection and correction to the network layer. It deals with issues like framing, flow control, and error handling when transmitting data frames between devices. Flow control mechanisms like stop-and-wait and sliding window are used to regulate frame transmission rates to prevent the receiver from being overwhelmed. Stop-and-wait allows sending one frame at a time while sliding window allows sending a fixed number of frames before needing an acknowledgment, improving efficiency over stop-and-wait. The data link layer frames network layer packets for transmission and handles issues like framing the data, detecting and correcting errors, and implementing flow control.