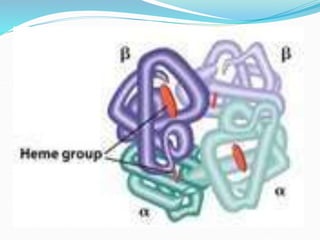
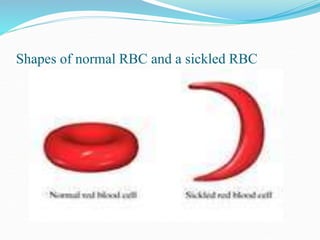
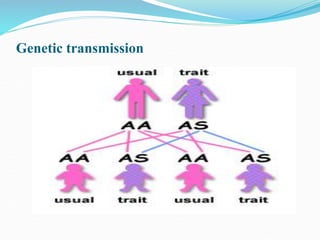
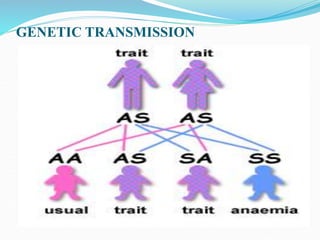
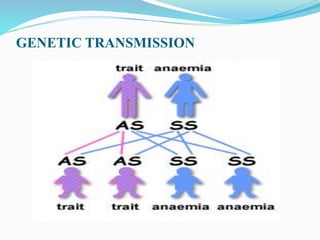
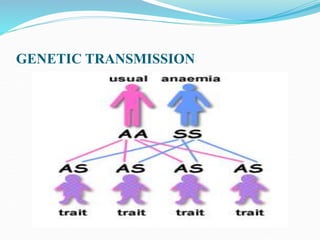
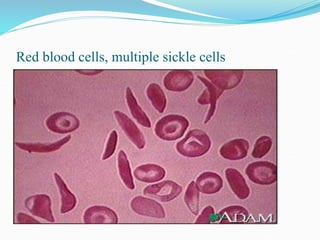
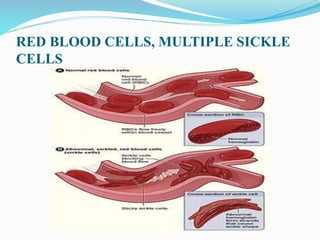
Sickle cell disease is a genetic blood disorder that affects millions worldwide, particularly those of African, Mediterranean, Middle Eastern, and Indian descent. It is caused by a mutation in the beta-globin gene that causes red blood cells to take on a rigid, sickle shape. These sickled cells can block blood vessels and damage tissues, causing pain crises, organ damage, strokes, and early death. Treatments aim to relieve pain, prevent infections that can trigger crises, and reduce complications through medications, transfusions, hydration, and lifestyle management.