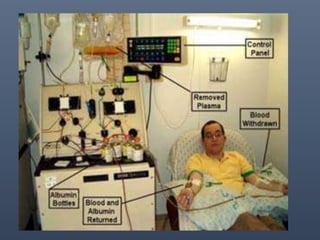
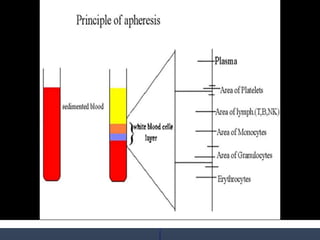
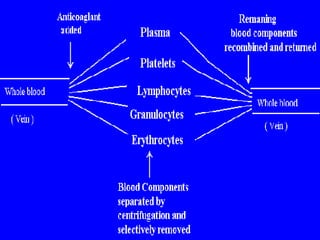
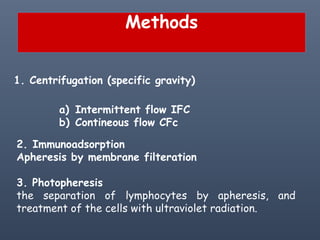
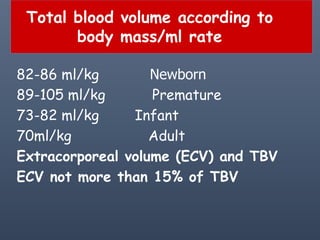
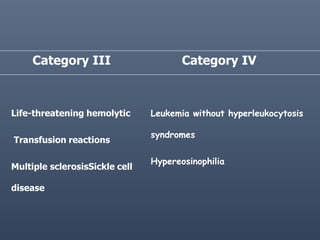
Apheresis is a medical technology where blood is passed through an apparatus that separates out one constituent and returns the remainder to circulation. It works by centrifugation separating components by specific gravity. It can be used to collect blood components from donors or perform therapeutic procedures. Therapeutic apheresis includes plasma exchange and cytapheresis to treat conditions like thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura or remove toxins. Guidelines categorize conditions based on evidence for apheresis with category I being primary therapy and category IV not responding. Potential adverse effects include citrate toxicity, infections, or depletion of components, so careful monitoring is important.