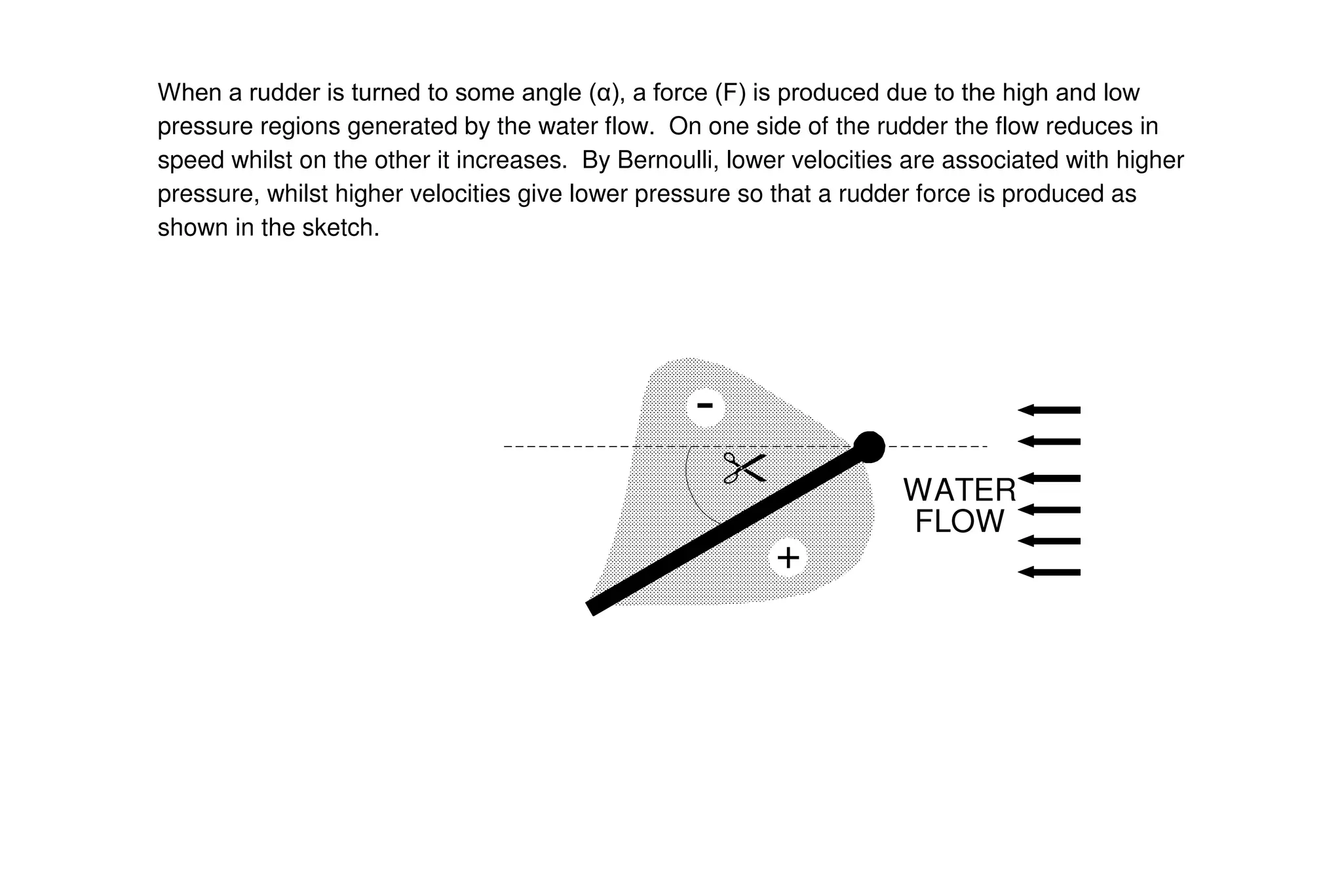
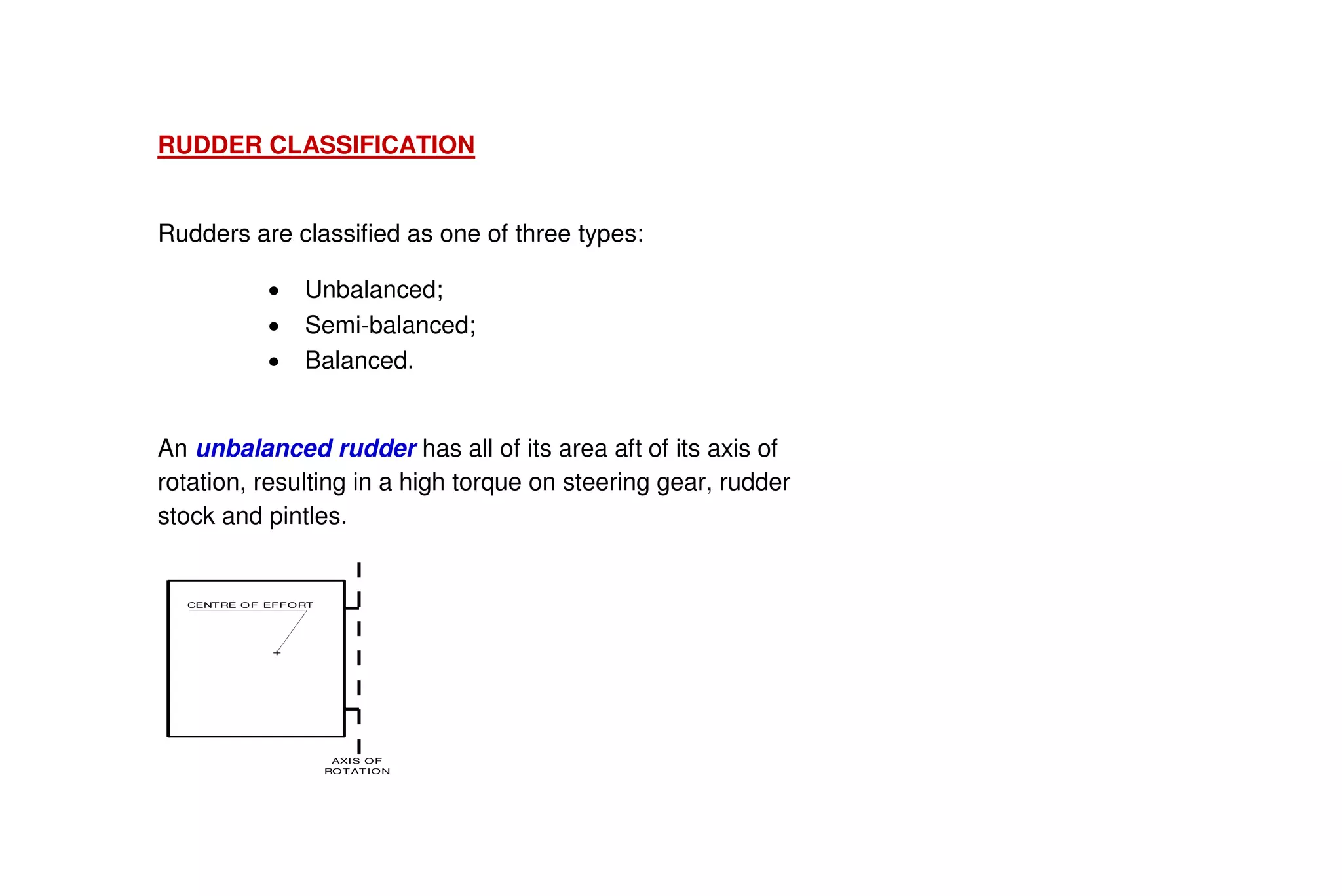
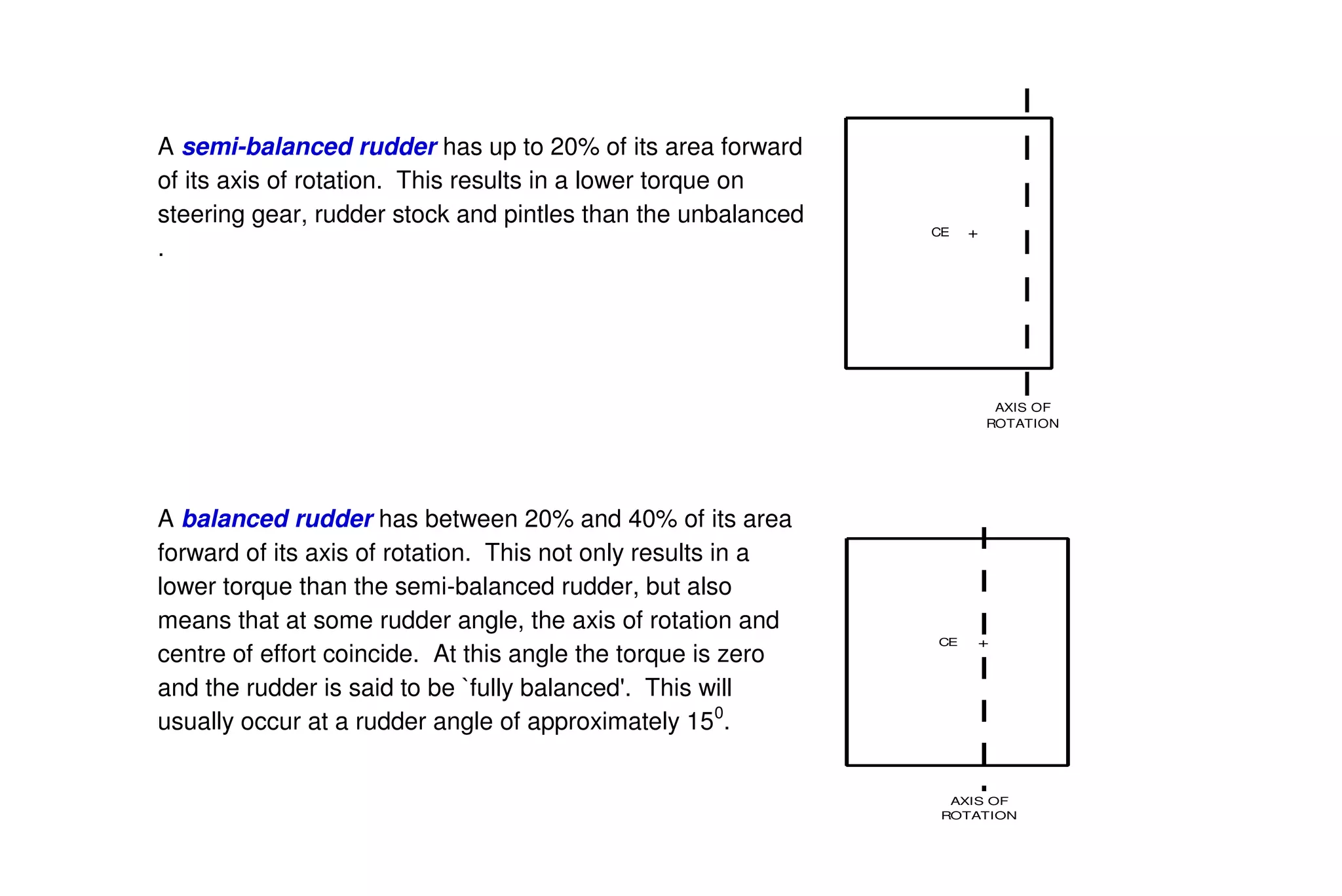
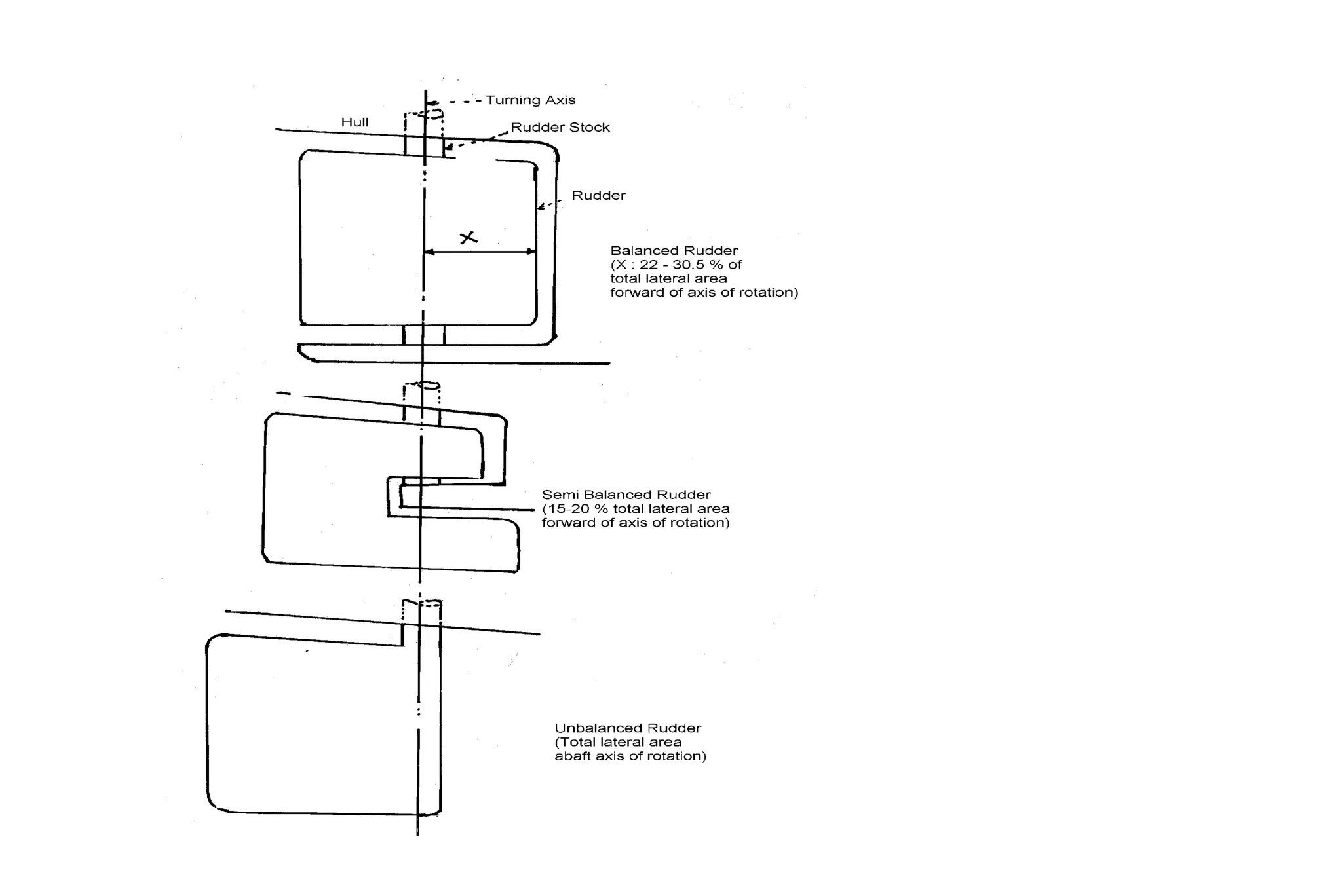
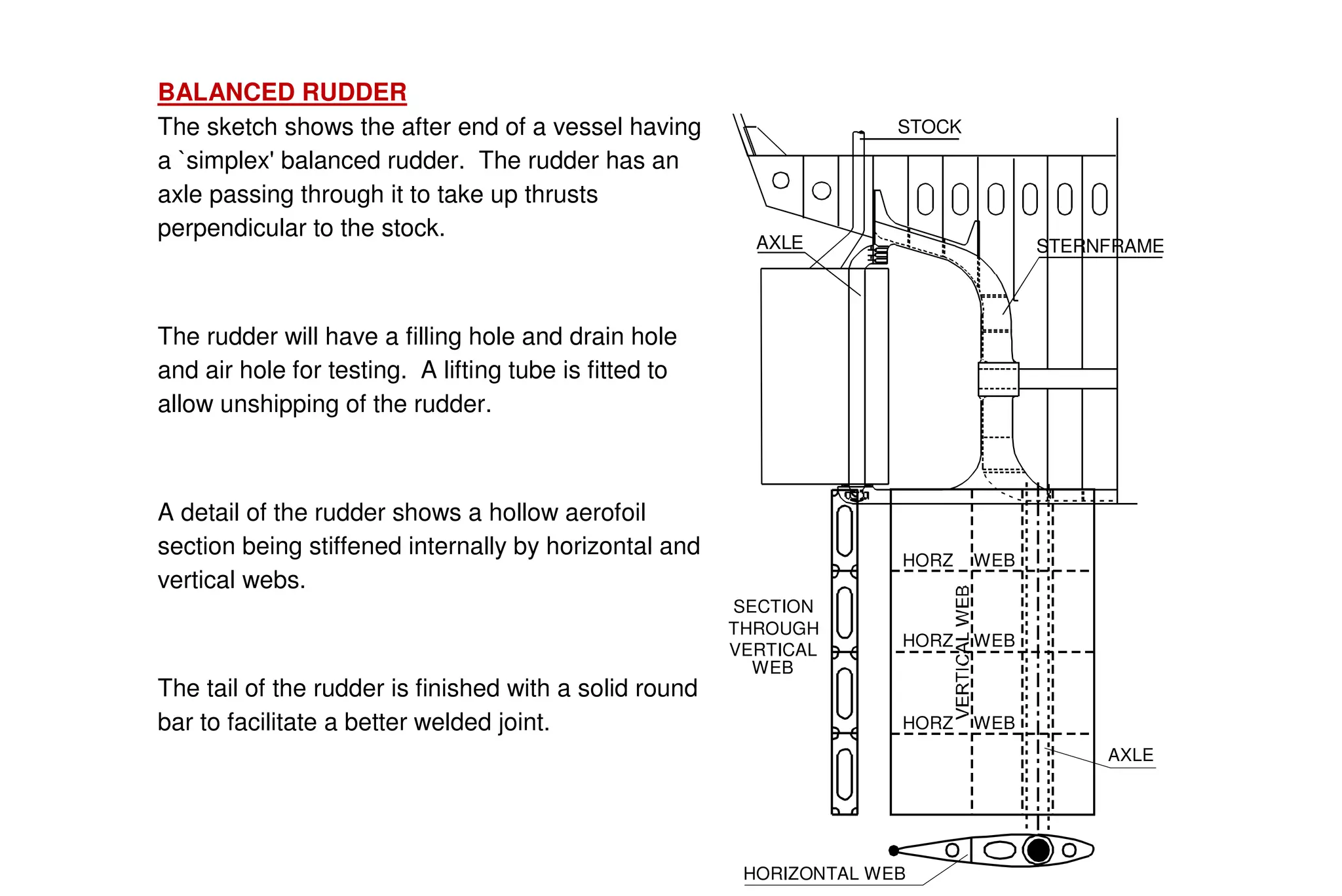
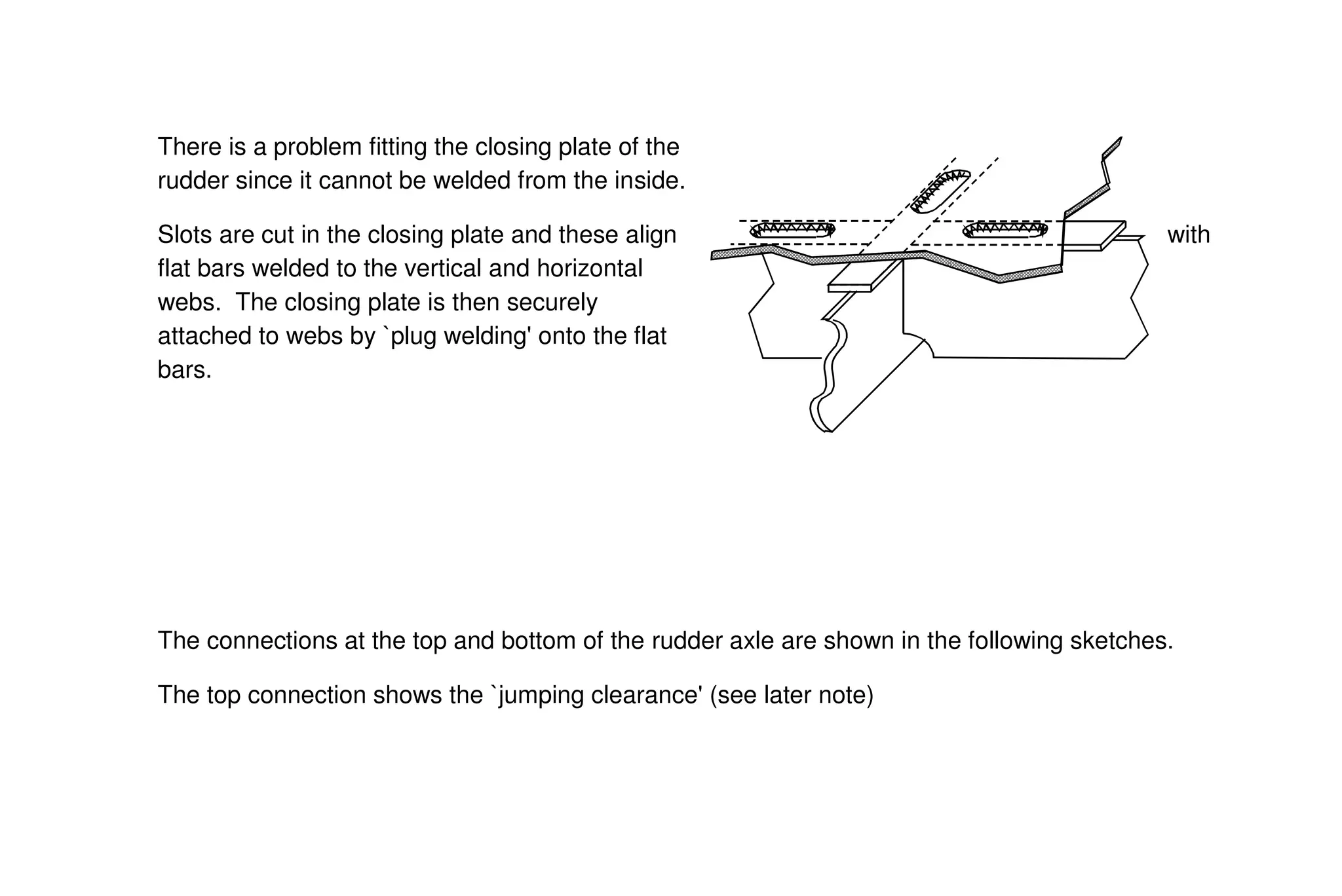
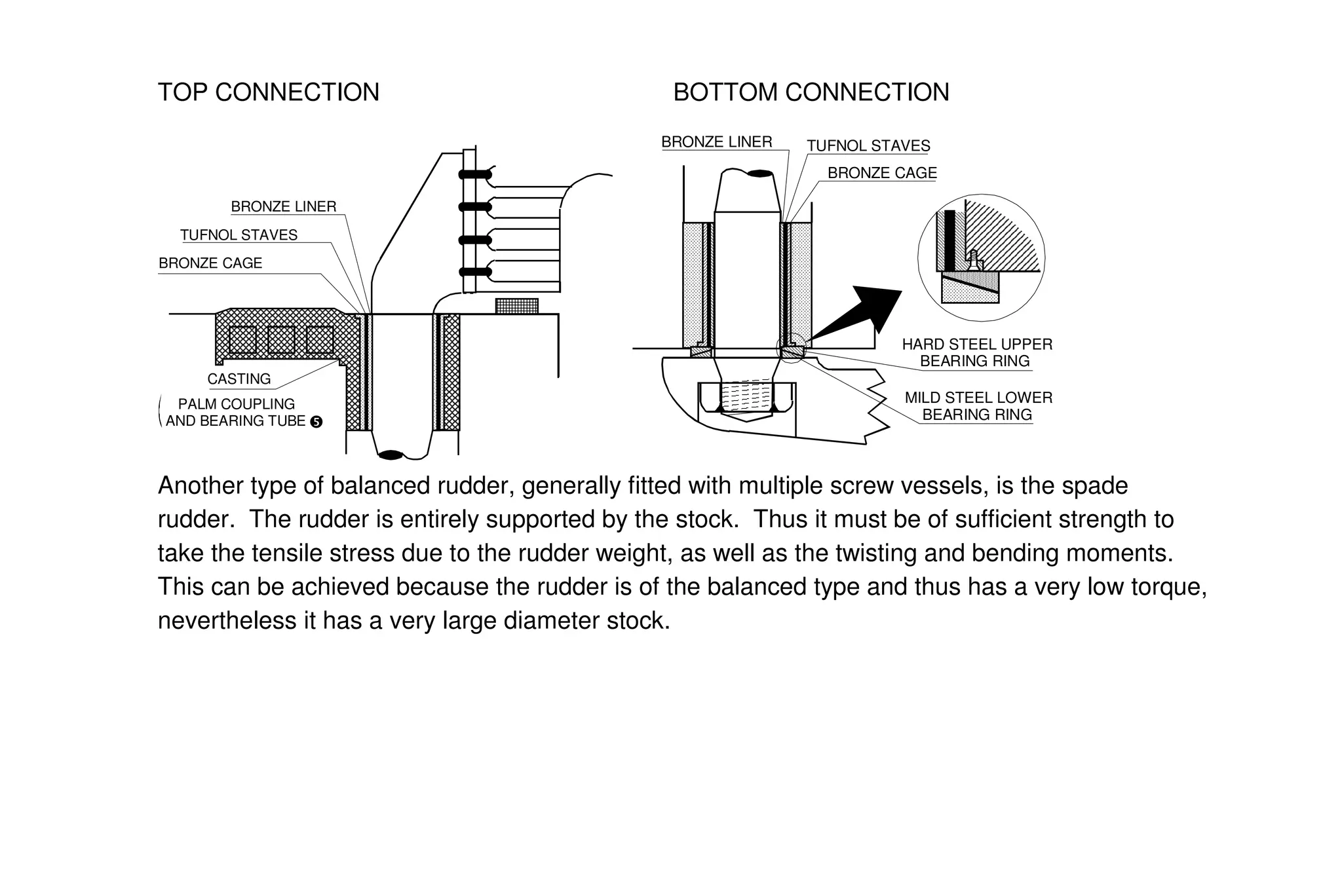
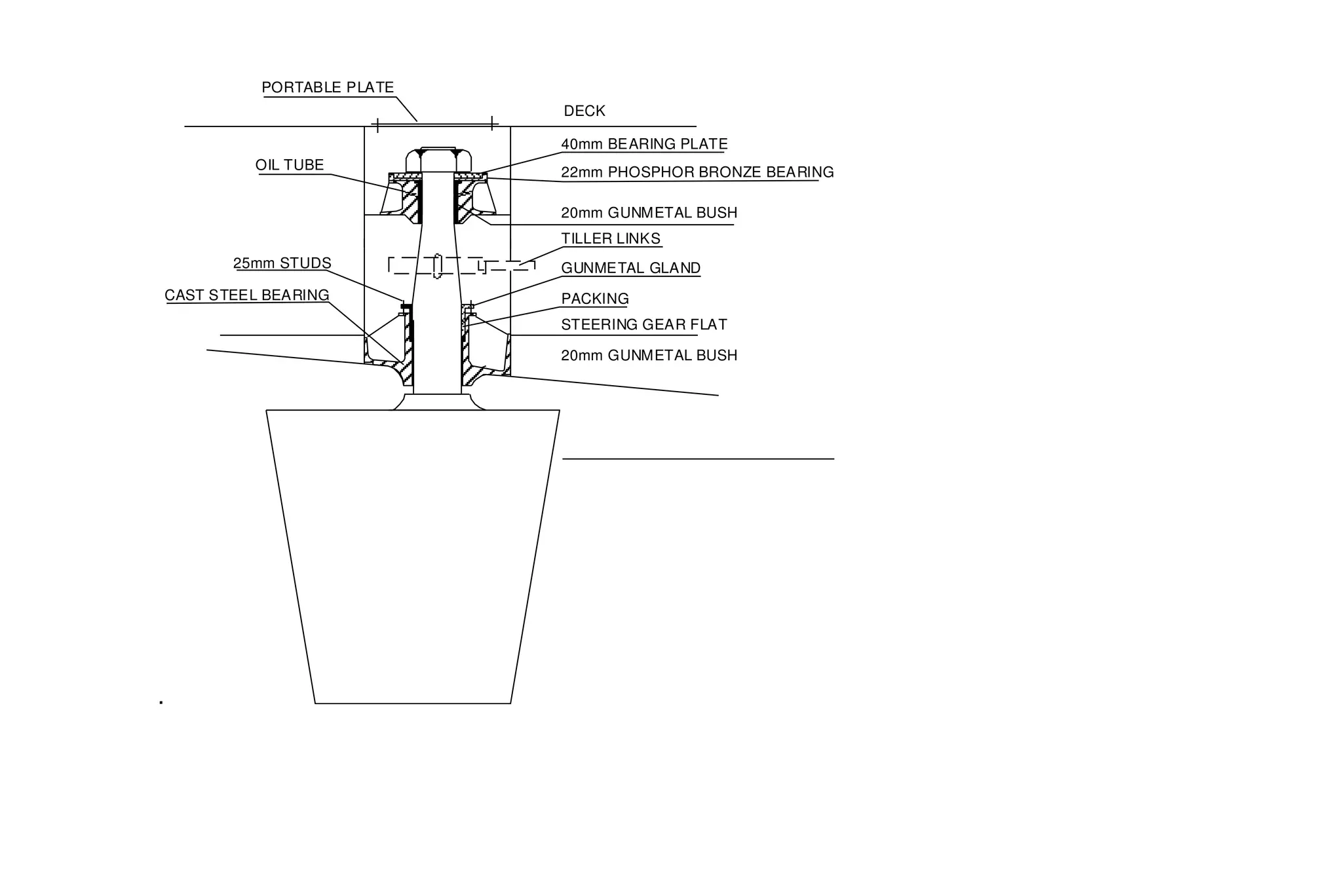
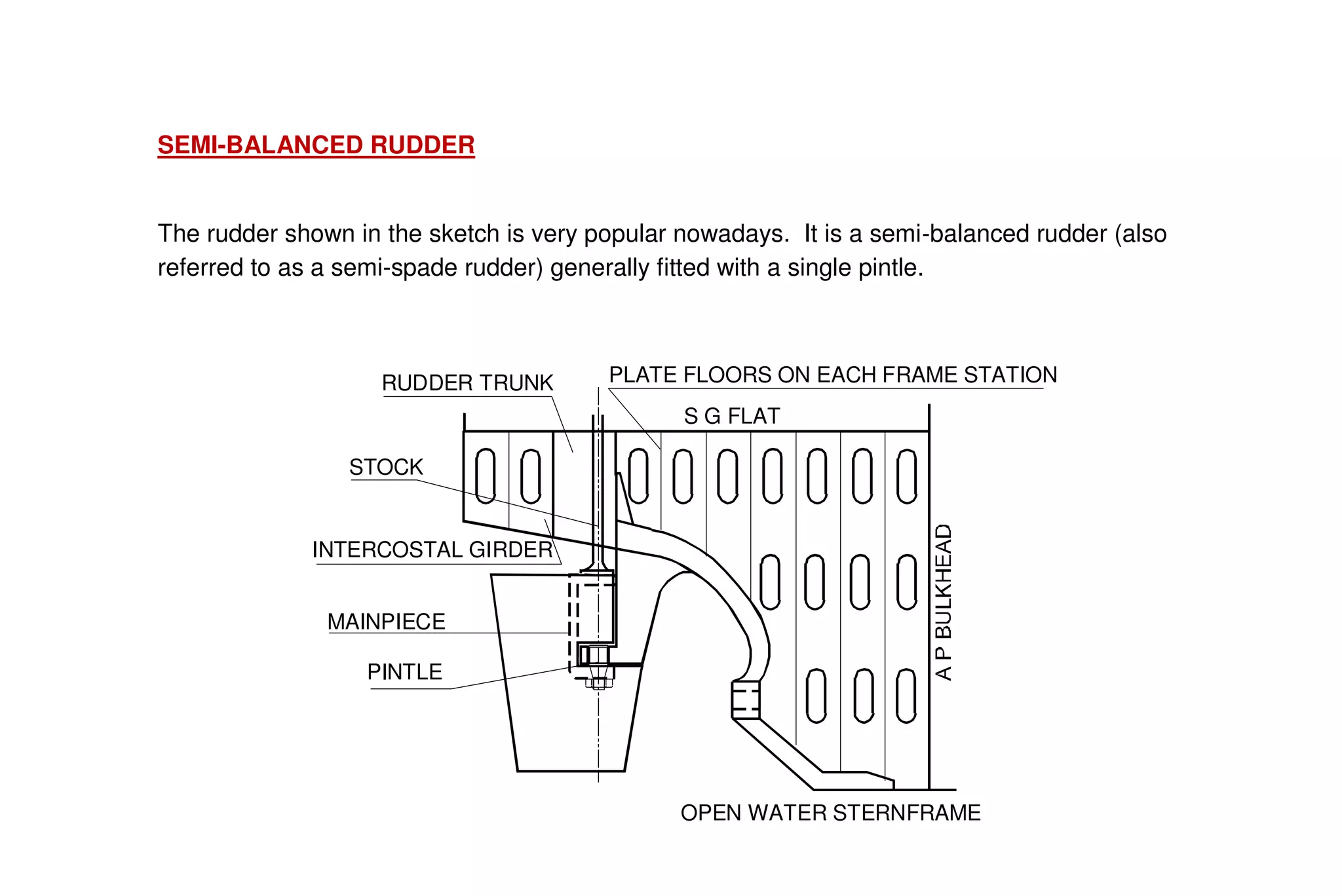
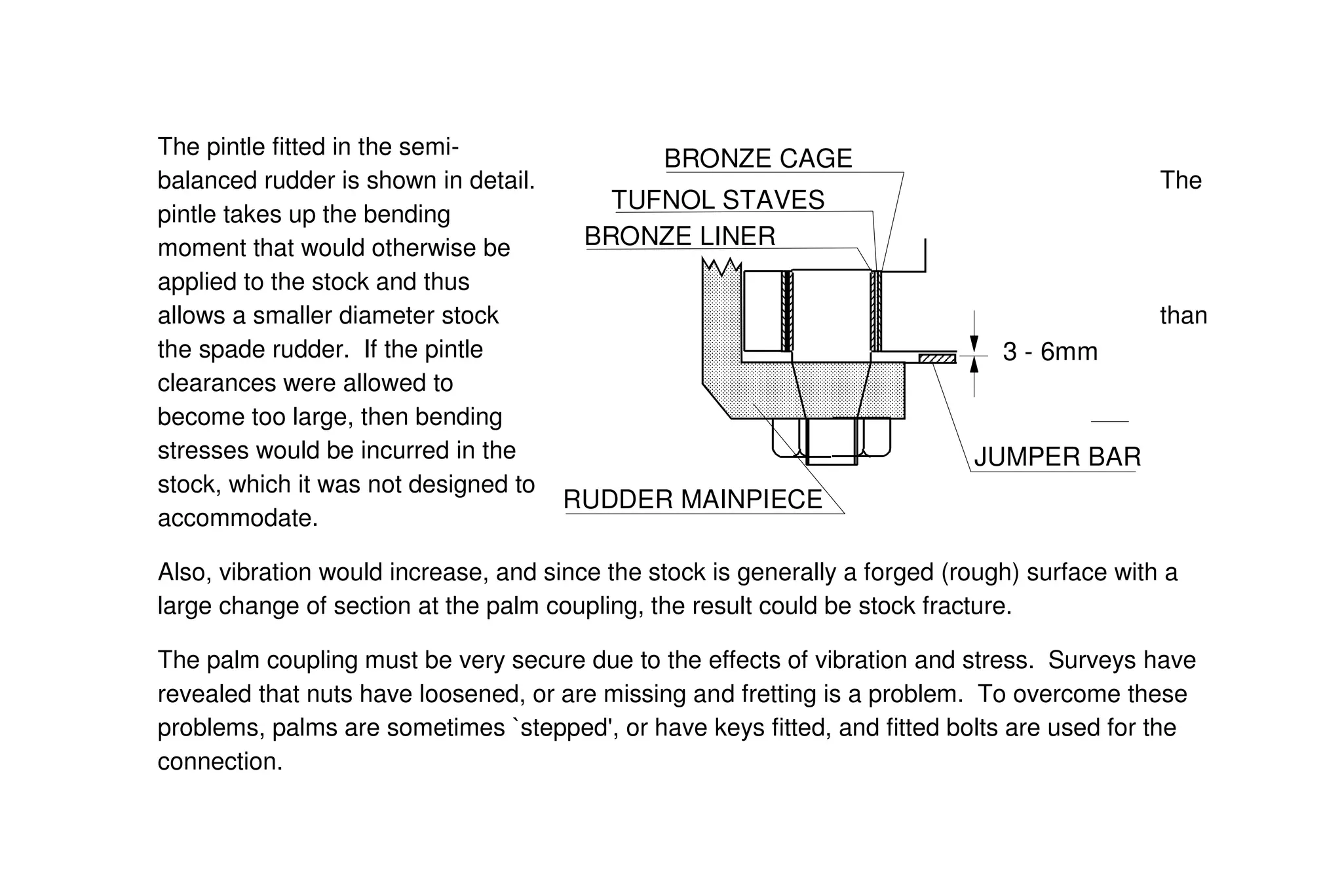
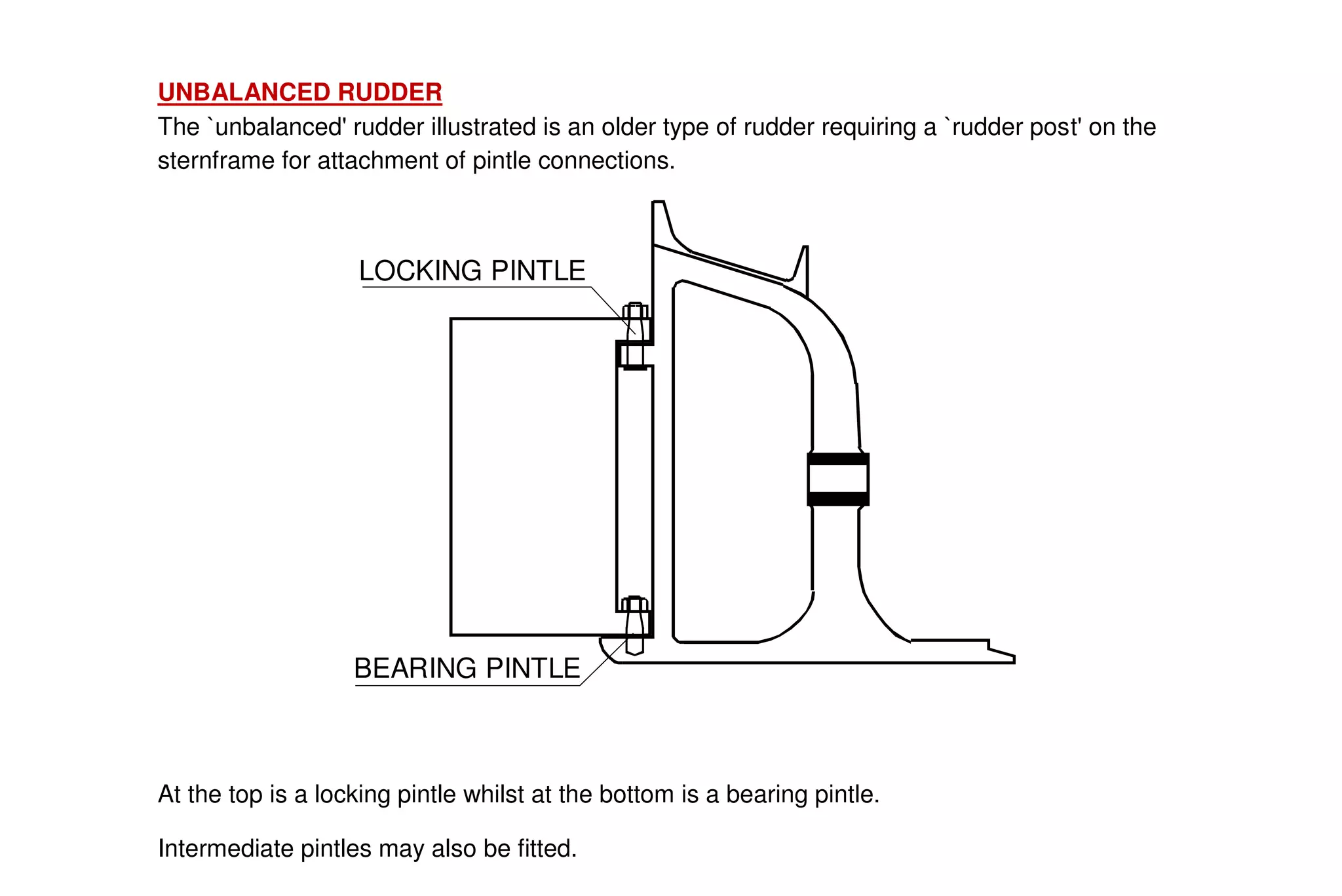
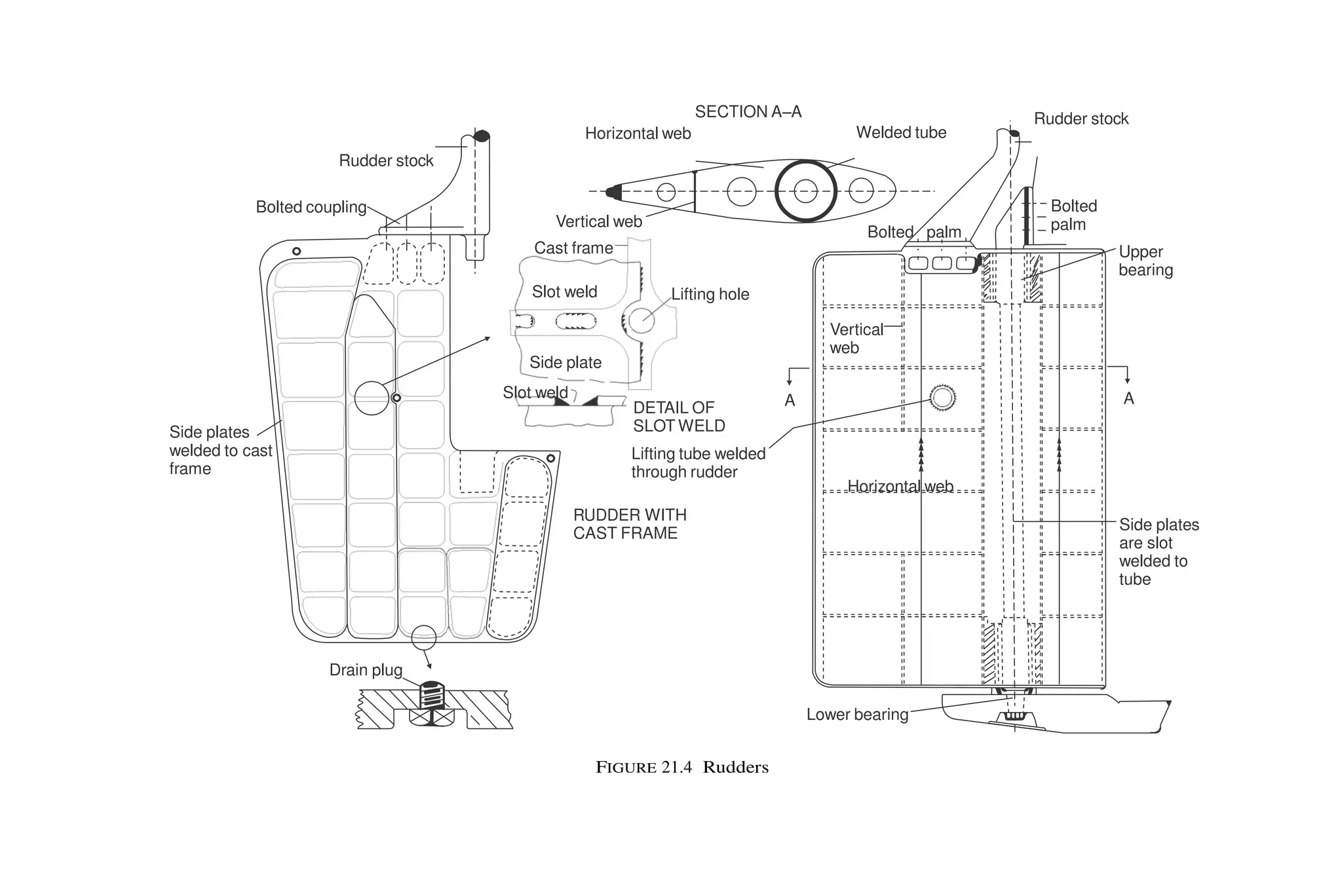
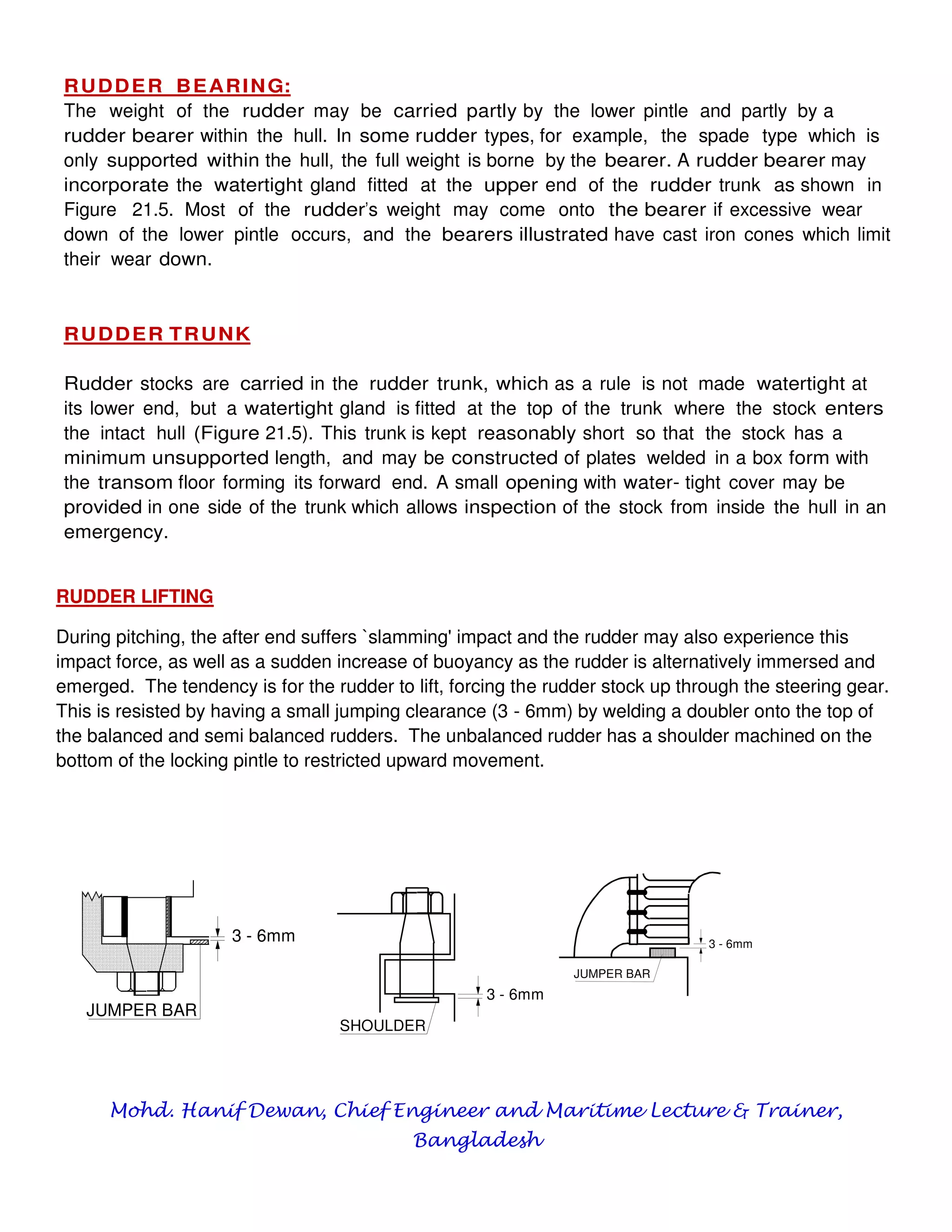
This document summarizes key aspects of rudder theory and design. It discusses how rudders generate force through pressure differences on each side, and how this force has both lift and drag components. It describes different types of rudders based on the position of the center of effort relative to the axis of rotation, including balanced, semi-balanced, and unbalanced rudders. It also discusses rudder construction materials, pintle bearings, and considerations for rudder stock sizing based on the type of rudder.