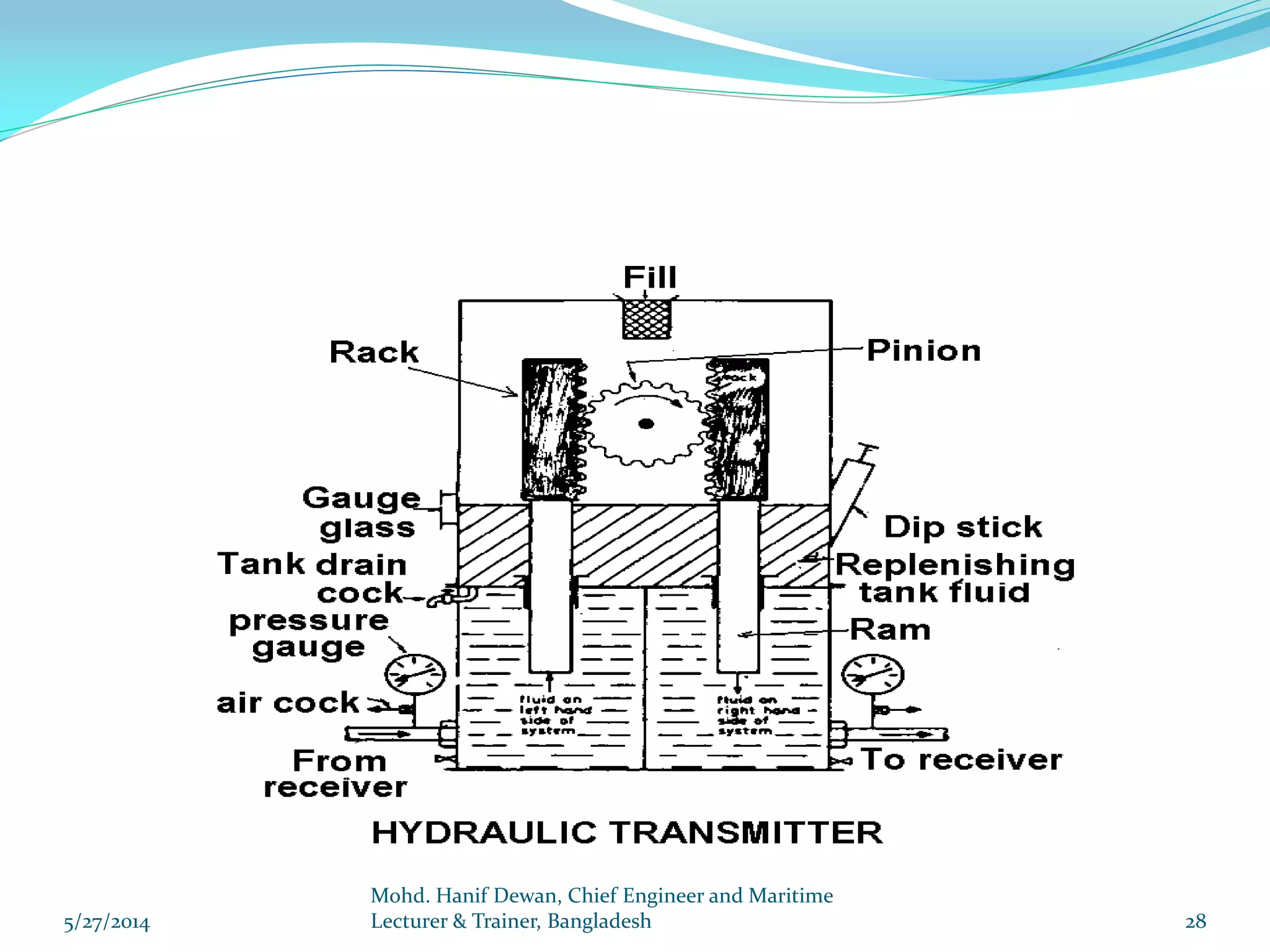
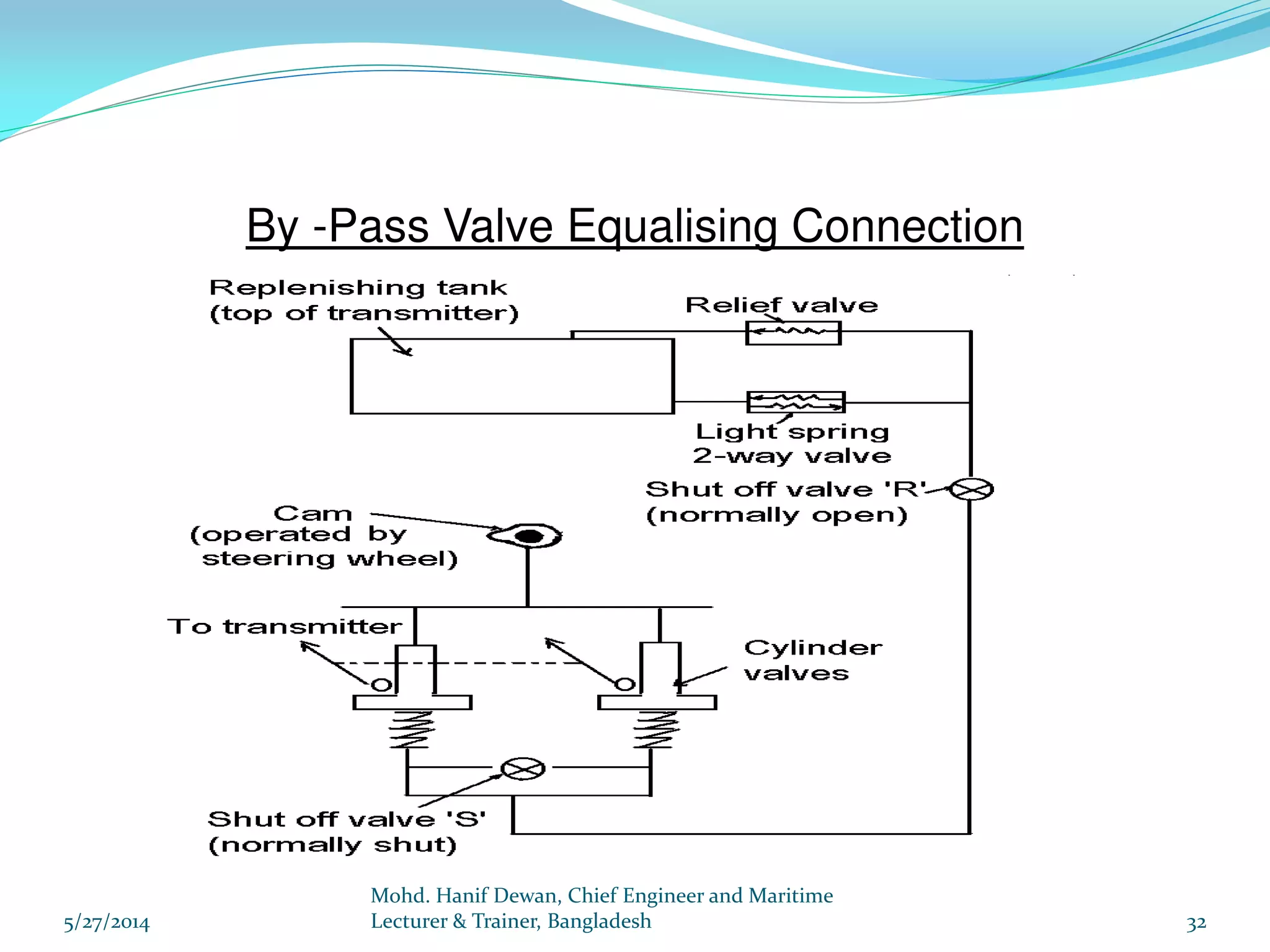
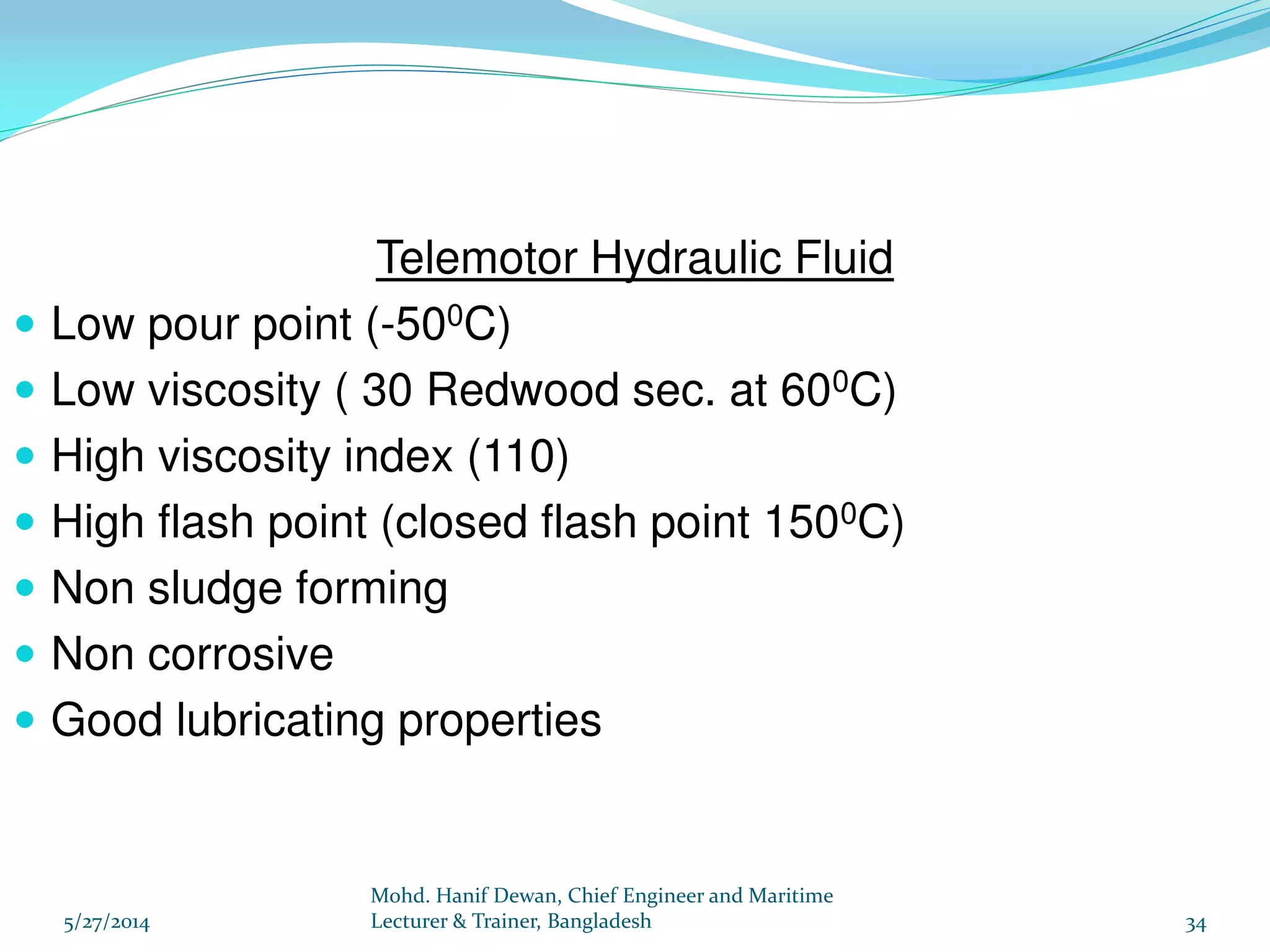
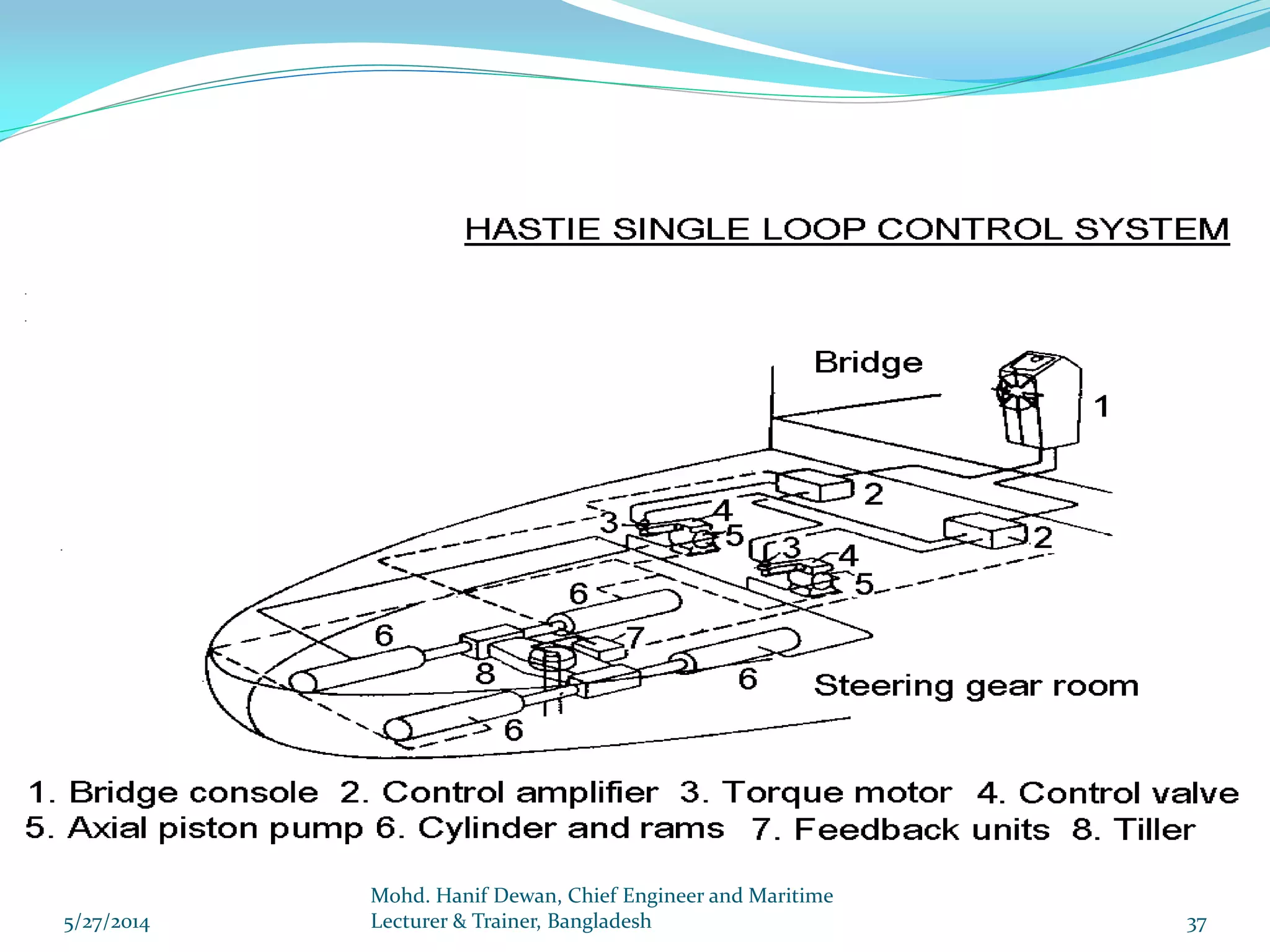
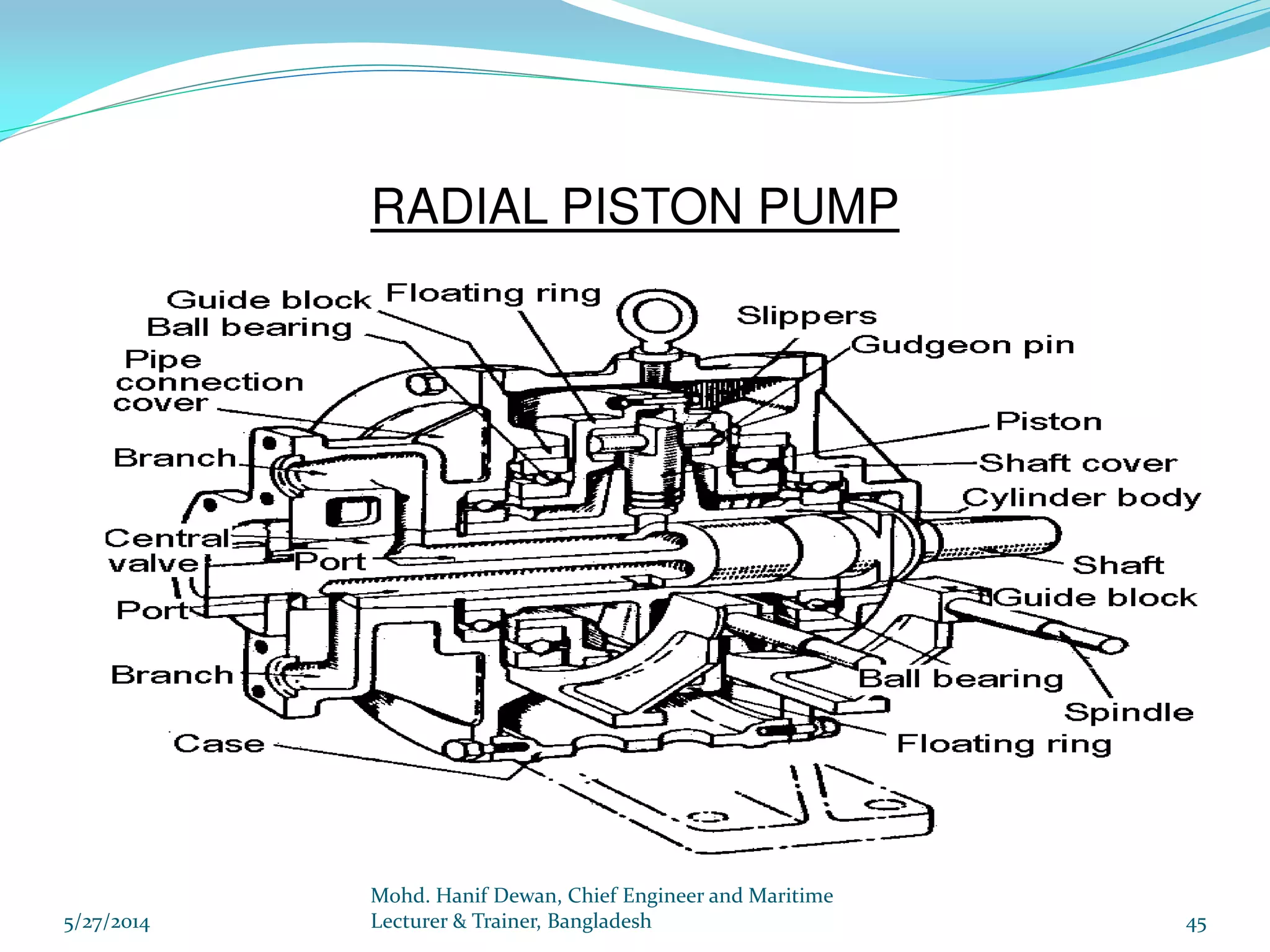
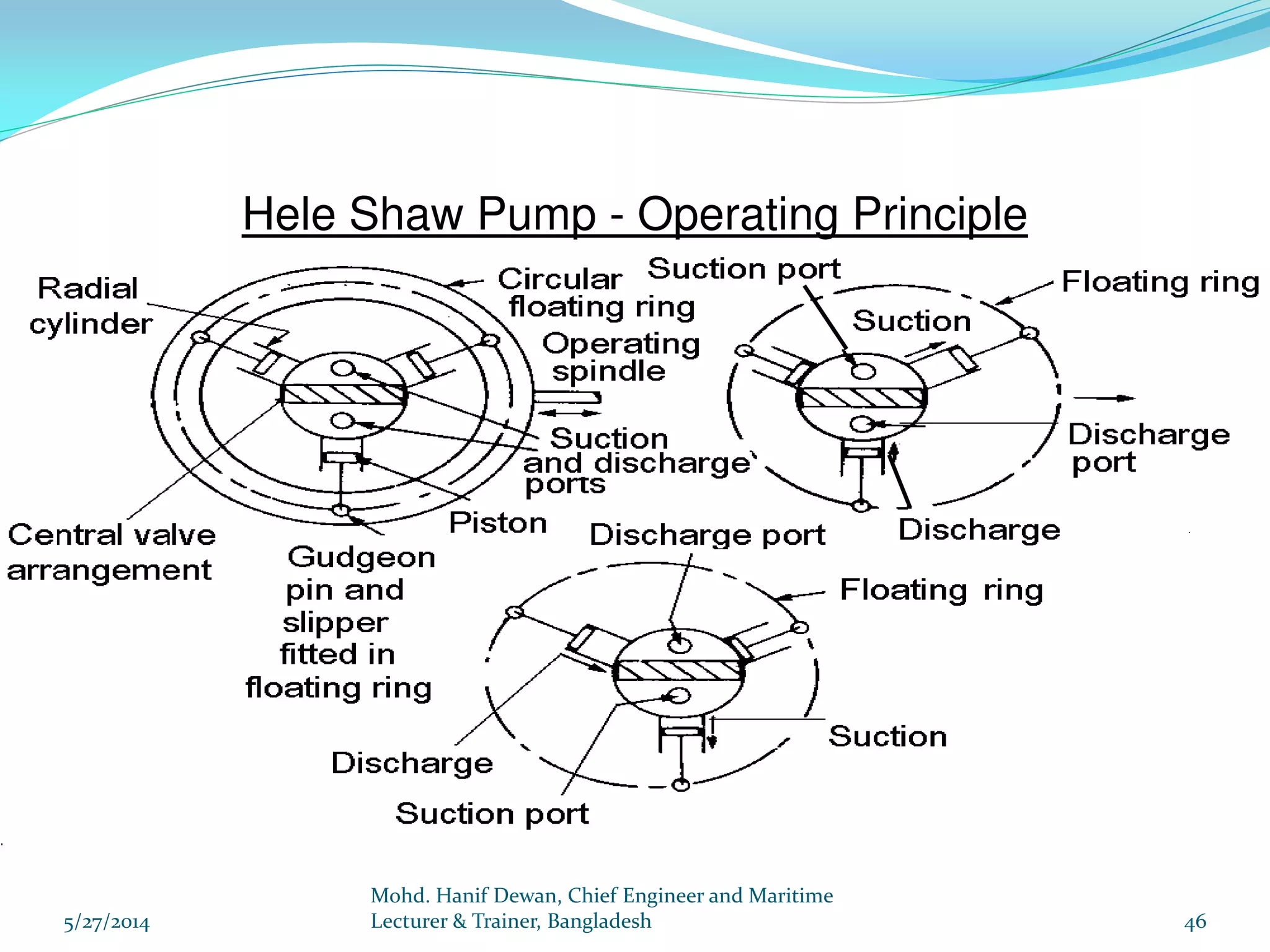
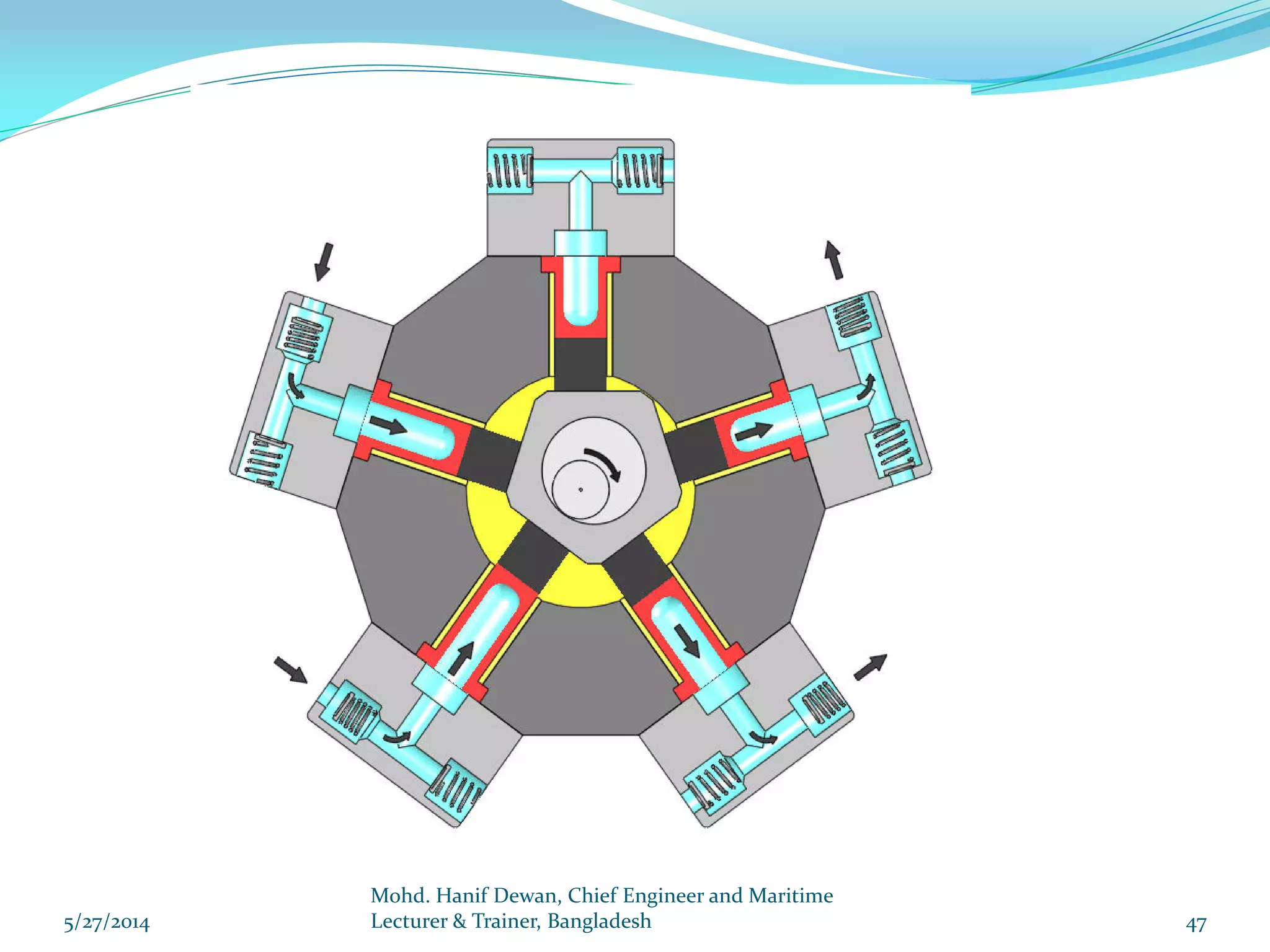
El documento detalla los requisitos de los sistemas de dirección marina según el reglamento SOLAS, destacando la necesidad de equipos de dirección principales y auxiliares, así como la operación y control de estos sistemas. Se especifican las pruebas y mantenimientos necesarios para garantizar su funcionamiento seguro, incluyendo simulaciones de fallos y la implementación de alarmas visuales y auditivas. Se enfatiza además la importancia de realizar ejercicios de emergencia y registrar todos los procedimientos en un libro de bitácora.