Embed presentation
Downloaded 225 times


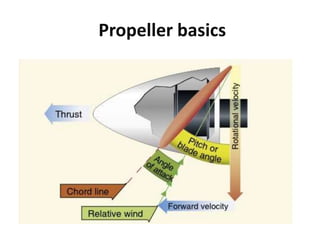
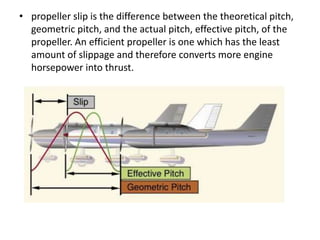


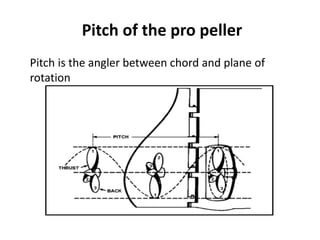









The document provides an overview of propellers, including: 1) A propeller converts rotational power from an engine into thrust by generating an aerodynamic lift force through its rotating blades, similar to how an airplane wing passes through air. Additional factors like trailing vortices and compressibility also affect propeller performance. 2) Propeller types include fixed pitch, variable pitch, constant RPM, feathering, and reverse pitch propellers. Variable pitch propellers can adjust their blade angle to maintain a constant RPM despite changing loads. Feathering propellers angle their blades parallel to airflow to reduce drag. 3) Other topics briefly covered include propeller slippage, pitch, push vs pull configurations, and















