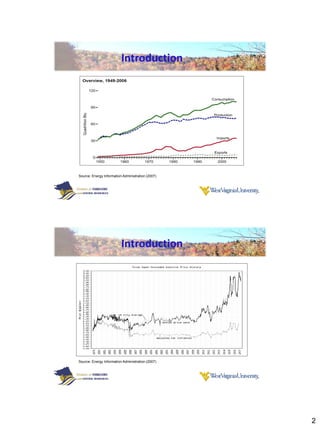
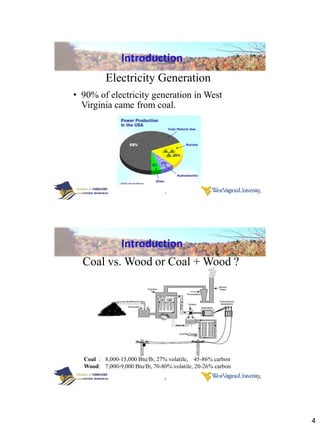
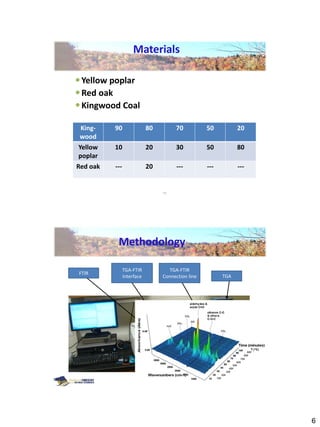
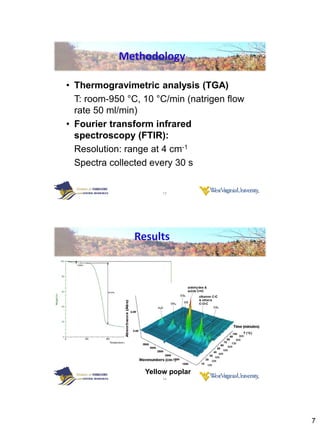
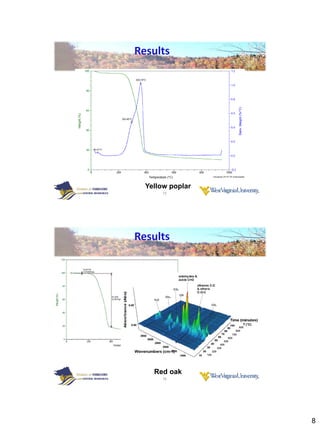
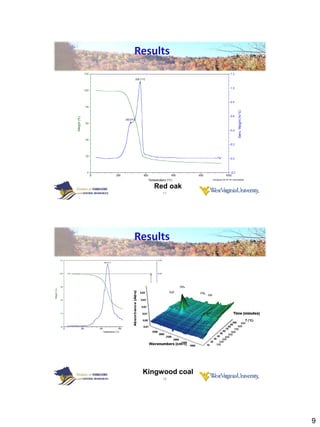
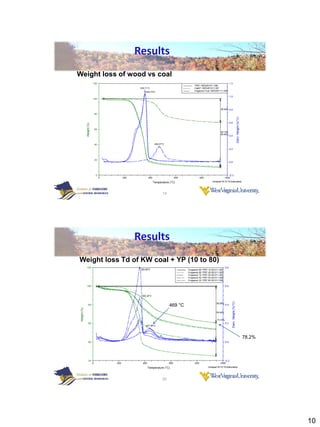
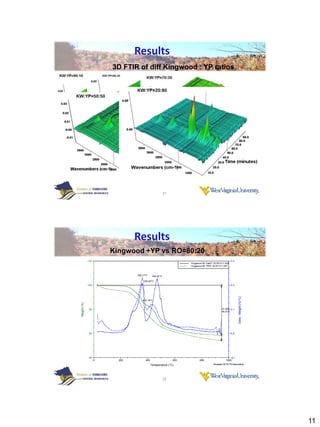
Thermogravimetric analysis with Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (TGA-FTIR) was used to analyze the pyrolysis and gasification of woody biomass, coal, and their mixtures. Yellow poplar, red oak, and Kingwood coal were tested individually and in various mixtures. The results showed that biomass decomposes at lower temperatures than coal, releasing gaseous products like CO2, CH4, CO, and H2O. Adding biomass to coal was found to enhance and stimulate the pyrolysis and gasification processes of coal. The study provides insight into how different biomass materials may influence the thermal decomposition of coal.