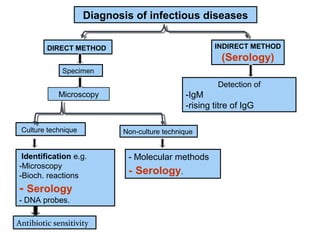
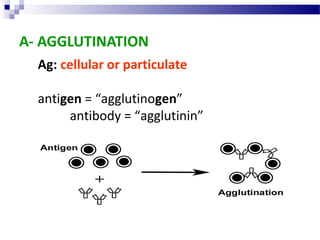
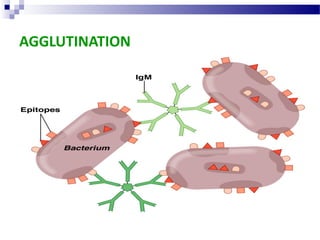
This document discusses various direct and indirect methods used for the diagnosis of infectious diseases. Direct methods involve detecting the pathogen itself through microscopy, culture techniques, or molecular methods on a specimen. Indirect methods involve detecting the immune response to the pathogen through serology techniques like detecting IgM or rising titers of IgG antibodies. It then discusses various antigen-antibody reactions that can be used for serological diagnosis, including agglutination, precipitation, complement fixation, viral neutralization, immunofluorescence, ELISA, and radioimmunoassay.