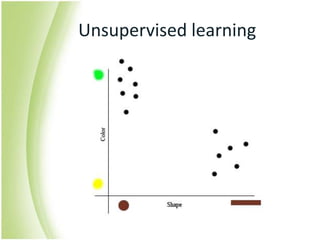
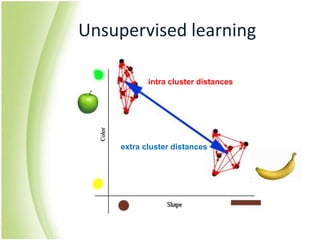
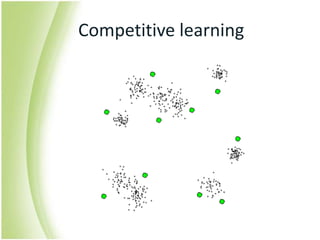
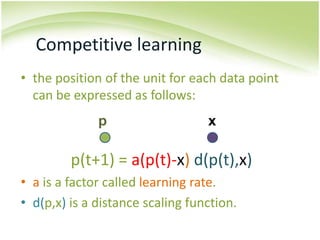
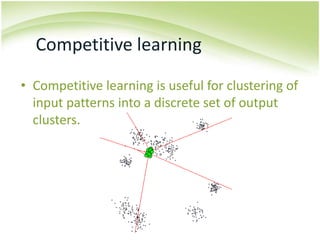
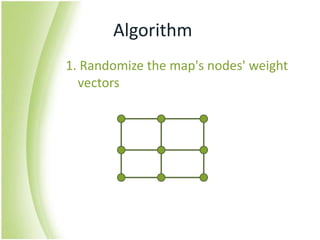
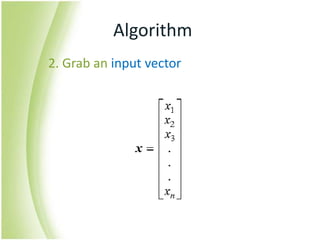
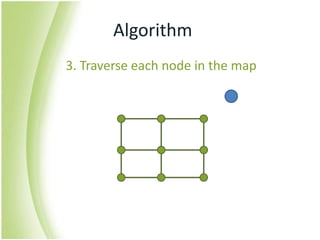
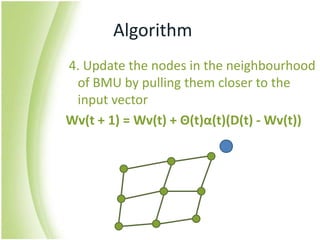
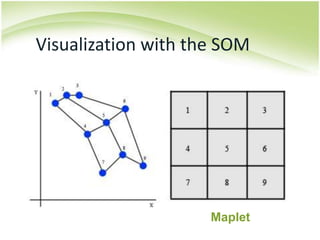
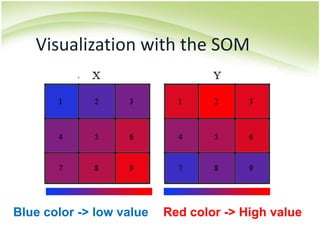
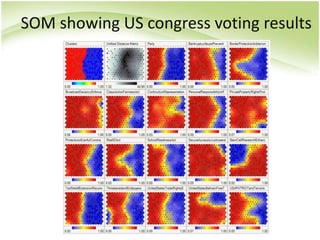
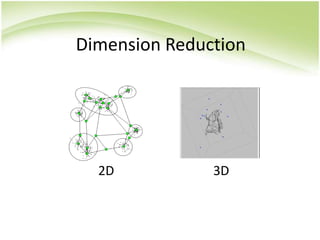
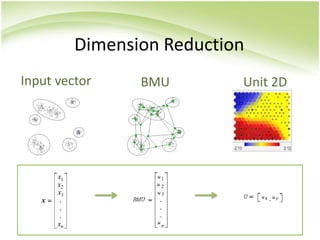
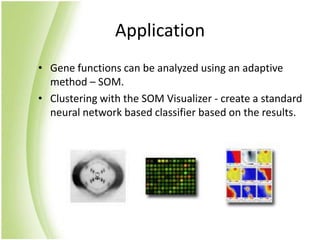
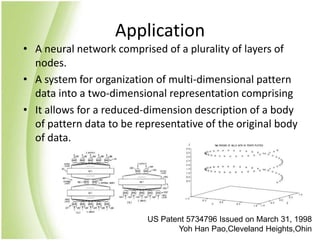
The document provides an overview of self-organizing maps (SOM). It defines SOM as an unsupervised learning technique that reduces the dimensions of data through the use of self-organizing neural networks. SOM is based on competitive learning where the closest neural network unit to the input vector (the best matching unit or BMU) is identified and adjusted along with neighboring units. The algorithm involves initializing weight vectors, presenting input vectors, identifying the BMU, and updating weights of the BMU and neighboring units. SOM can be used for applications like dimensionality reduction, clustering, and visualization.