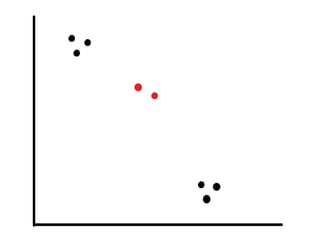
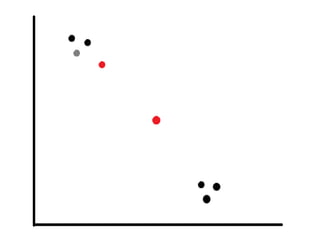
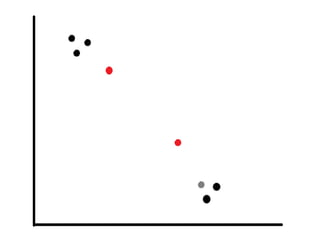
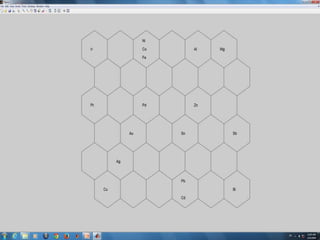
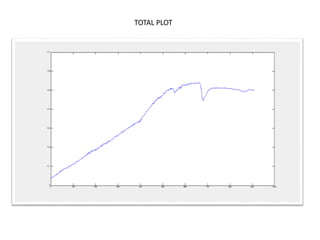
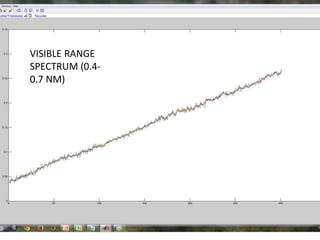
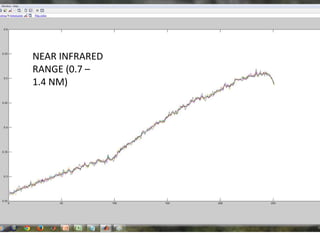
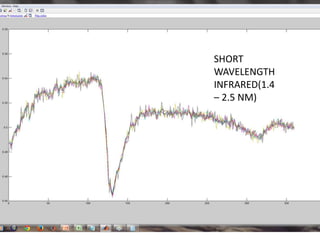
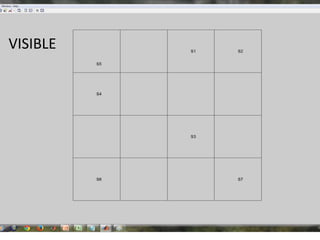
This document discusses self-organizing maps (SOM), an unsupervised machine learning technique that projects high-dimensional data into a low-dimensional space. SOM creates a map that clusters similar data items together and separates dissimilar items. It is useful for data mining, data analysis, and pattern recognition. The document provides examples of using SOM to cluster metallic elements based on their physical properties and cluster different soil types based on their spectral properties with increasing noise.