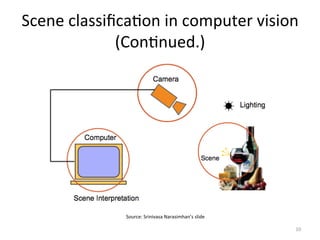
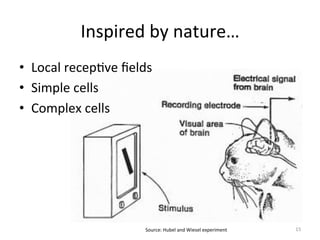
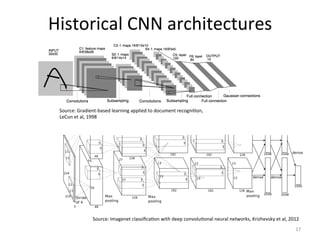
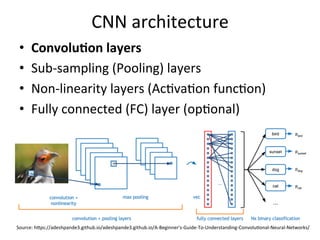
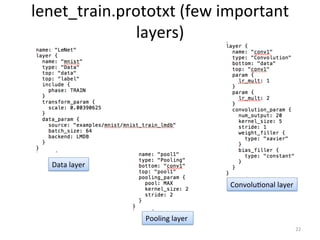
The document discusses scene classification using convolutional neural networks (CNNs). It begins with an outline of the topic, then provides background on computer vision as an AI problem and the importance and challenges of scene classification. It introduces CNNs as a deep learning technique for visual pattern recognition, describing their hierarchical organization and components like convolution and pooling layers. The document also discusses traditional machine learning approaches versus deep learning for scene classification and frameworks like Caffe that can be used to implement CNNs.