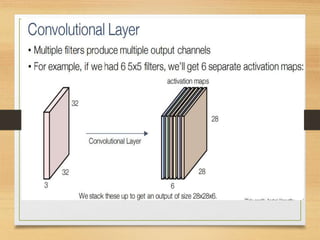
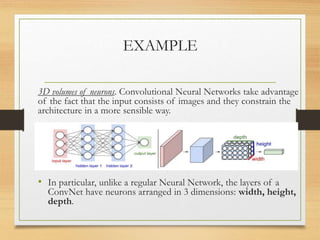
This document presents an overview of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), emphasizing their structure and functionality in analyzing visual imagery. It describes the key components of CNNs, including convolutional, pooling, and fully connected layers, and explains how these layers operate on input data. Additionally, it illustrates how CNNs process image inputs through a 3D arrangement of neurons and conclude with an example related to the CIFAR-10 dataset.