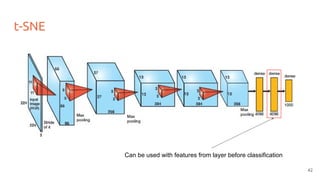
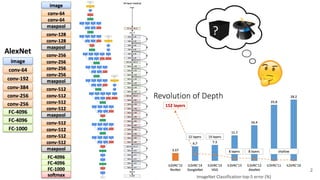
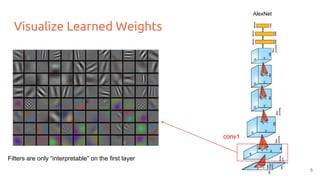
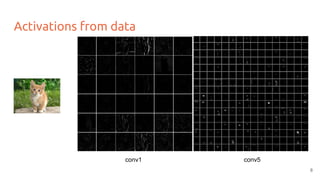
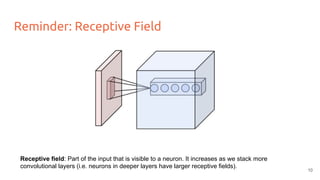
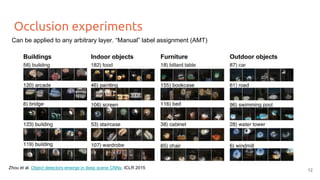
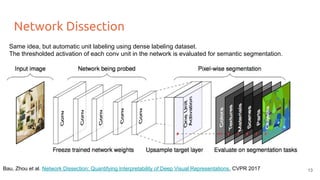
The document discusses various techniques for visualizing deep learning models, focusing on learned weights, activations, and methods such as gradient-based visualization and optimization approaches. It highlights methods like DeepDream and neural style transfer, explaining the process of extracting image features at different layers and applying these techniques for interpreting network behaviors. Additionally, it includes references to key papers and tools used in the field of deep learning visualization.
![[course site]
Visualization
#DLUPC
Amaia Salvador
amaia.salvador@upc.edu
PhD Candidate
Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlcv2017d1l6visualization-170621134756/85/Visualization-of-Deep-Learning-Models-D1L6-2017-UPC-Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-1-320.jpg)








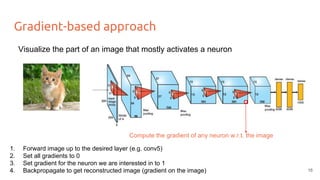



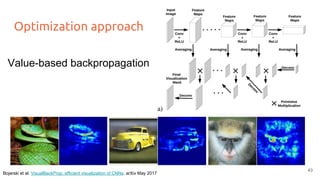
![Optimization approach
Simonyan et al. Deep Inside Convolutional Networks: Visualising Image Classification Models and Saliency Maps, 2014
Obtain the image that maximizes a class score (or a neuron activation)
1. Forward random image
2. Set the gradient of the scores vector to be [0,0,0…,1,...,0,0]
3. Backprop to get gradient on the image
4. Update image (small step in the gradient direction)
5. Repeat
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlcv2017d1l6visualization-170621134756/85/Visualization-of-Deep-Learning-Models-D1L6-2017-UPC-Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-20-320.jpg)



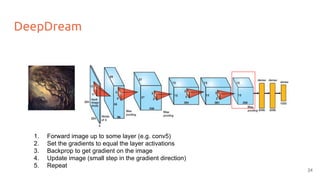





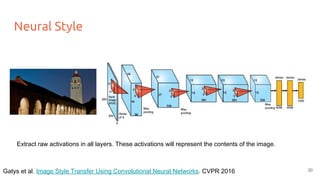
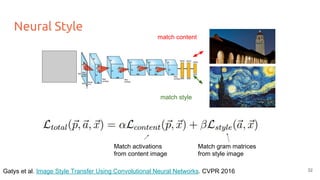
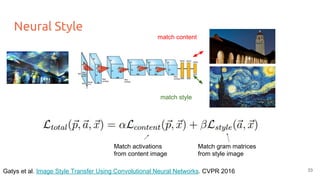
![Neural Style
V =
● Activations are also extracted from the style image for all layers.
● Instead of the raw activations, gram matrices (G) are computed at each layer to represent the style.
E.g. at conv5 [13x13x256], reshape to:
169
256
...
G = VT
V
The Gram matrix G gives the
correlations between filter responses.
31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlcv2017d1l6visualization-170621134756/85/Visualization-of-Deep-Learning-Models-D1L6-2017-UPC-Deep-Learning-for-Computer-Vision-31-320.jpg)