1) The document summarizes state-of-the-art topics in computer vision, including recognition, reconstruction, deep learning theory, and trends moving forward.
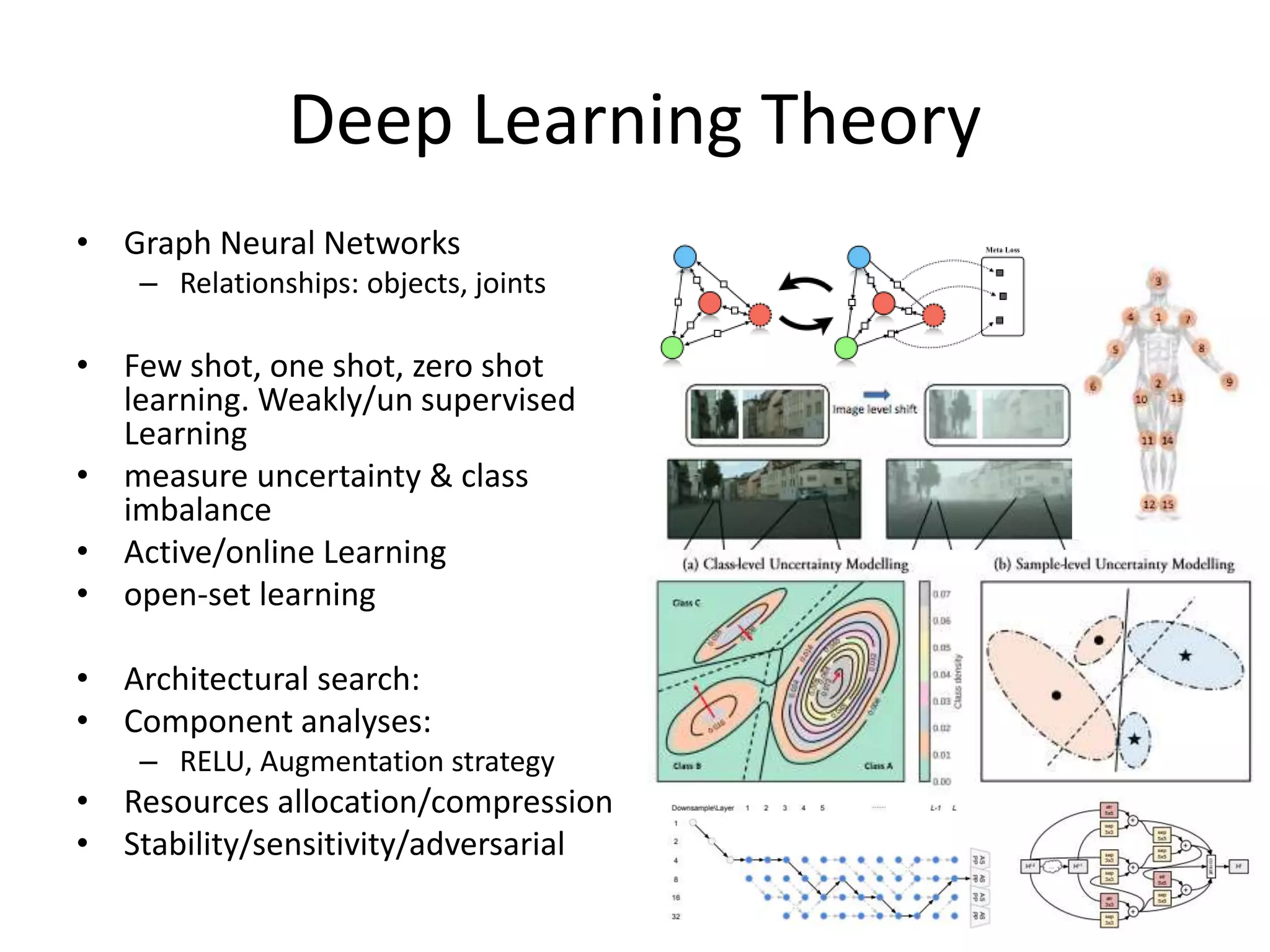
2) Contemporary computer vision topics discussed include graph neural networks, few-shot learning, active learning, architectural search, and measuring uncertainty.
3) Overarching trends include larger datasets dictating research activities and smaller manually annotated datasets catching up in performance through techniques like few and no shot training.











![Deep Learning Theory
• Graph Convolutional Networks [https://arxiv.org/pdf/1609.02907.pdf]
– http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_CVPR_2019/papers/Kim_Edge-Labeling_Graph_Neural_Network_for_Few-
Shot_Learning_CVPR_2019_paper.pdf
• Few shot, one shot, zero shot learning. Weakly/un
supervised Learning
– http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_CVPR_2019/papers/Wang_Few-Shot_Adaptive_Faster_R-CNN_CVPR_2019_paper.pdf
• Active Learning
• measure uncertainty & class imbalance
– http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_CVPR_2019/papers/Khan_Striking_the_Right_Balance_With_Uncertainty_CVPR_2019_paper.pdf
• Online learning, open-set
• Architectural search:– http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_CVPR_2019/papers/Liu_Auto-DeepLab_Hierarchical_Neural_Architecture_Search_for_Semantic_Image_Segmentation_CVPR_2019_paper.pdf
• Component analyses:
– RELU, Augmentation strategy
– http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_CVPR_2019/papers/Cubuk_AutoAugment_Learning_Augmentation_Strategies_From_Data_CVPR_2019_paper.pdf
• Resources allocation/compression:– http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_CVPR_2019/papers/Qiao_Neural_Rejuvenation_Improving_Deep_Network_Training_by_Enhancing_Computational_Resource_CVPR_2019_paper.pdf
• Stability/sensitivity/adversarial](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dataconla2019presentation-190901003646/75/Data-Con-LA-2019-State-of-the-Art-of-Innovation-in-Computer-Vision-by-Christian-Siagian-16-2048.jpg)




