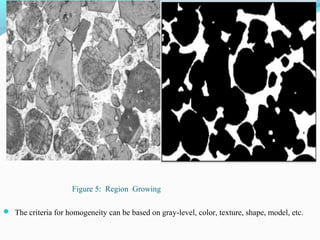
This document presents information on face detection techniques. It discusses image segmentation as a preprocessing step for face detection. Some common segmentation methods are thresholding, edge-based segmentation, and region-based segmentation. Face detection can be classified as implicit/pattern-based or explicit/knowledge-based. Implicit methods use techniques like templates, PCA, LDA, and neural networks, while explicit methods exploit cues like color, motion, and facial features. One method discussed is human skin color-based face detection, which filters for skin-colored regions and finds facial parts within those regions. Advantages include speed and independence from training data, while disadvantages include sensitivity to lighting and accessories.















![References
[B1]: Digital Image Processing, by Rafael Gonzalez, Richard Woods
[B2]: Image Processing, Analysis, and Machine Vision, by Milan Sonka, Vaclav Hlavac,
Roger Boyle
[B3]: A Guide to MATLAB, by Brian R. Hunt, Ronald L. Lips man, Jonathan M. Rosenberg
Web-sites:
[W1]: www.civs.stat.ucla.edu
[W2]: www.cs.cf.ac.uk
[W3]: www.icaen.uiowa.edu
[A] Wiskott, et al. (1997) “Face recognization by elastic bunch graph matching. IEEE Trans.
Patt. Anal. Mach. Intel. 19, 775-779.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/facedetectionppt-170501081302/85/Face-detection-ppt-21-320.jpg)

