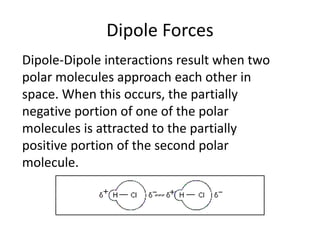
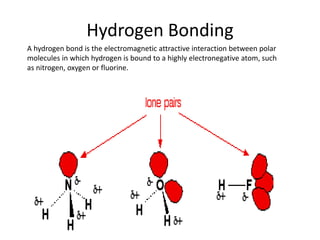
This document provides instructions for an experiment on intermolecular forces. Students are asked to draw the structures of water, carbon dioxide, and ammonia including bond angles and lone pairs. They must describe van der Waals, dipole, and hydrogen bonding forces and relate these intermolecular forces to physical properties. The document further explains these different intermolecular forces and provides context for why the experiment is being done to examine solubility based on intermolecular forces. It concludes with a short quiz and assigning homework on bonding.