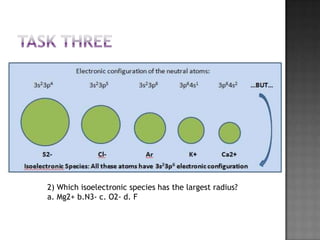
This document contains questions and activities about periodic trends, including:
- Comparing the ionic radii and electronic configurations of Li+ and Be2+
- Explaining why Na has a higher melting point than Cs
- Discussing why ionic compounds don't have bond angles
- Describing the periodic table in terms of proton number, periods, groups, and chemical properties
- Explaining trends in ionization energy using knowledge of effective nuclear charge and electron shells