This document discusses the properties of alkaline earth metals, specifically beryllium, magnesium, calcium, strontium, and barium. It covers their occurrence in nature, physical properties like melting points and flame tests, and similarities between beryllium and magnesium, including their tendency to form covalent compounds and hydrides.

![The Alkaline Earth Metals
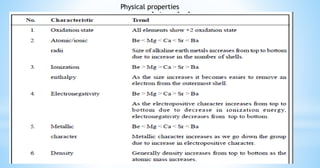
IIA [ns2] group elements are called alkaline earth
metals.
Mg -second most abundant metallic element in the sea,
and carnallite (KCl.MgCl2.6H2O) in earth crust.
Ca- occurs as calcium carbonate (marble, chalk etc) and
with magnesium as dolomite (CaCO3.MgCO3).
Sr and Ba - rare and are found as carbonates and
sulphates.
Be- rare and is found as beryl (Be3Al2(SiO3)6).
Occurrence](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/beryllium-200923112923/85/Alkaline-earth-metals-2-320.jpg)
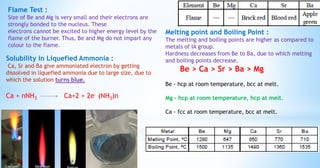






![Both Be and Al form polymeric covalent hydrides
while hydrides of other alkaline earth are ionic.
BeCl2 and AlCl3 both have a bridged polymeric
structure.
Be and Al both form fluoro complex ions [BeF4]2-
and [AlF6]3- in solution state whereas other
members of 2nd group do not form such
complexes.
Both forms hydrated ions in aqueous solution](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/beryllium-200923112923/85/Alkaline-earth-metals-11-320.jpg)
