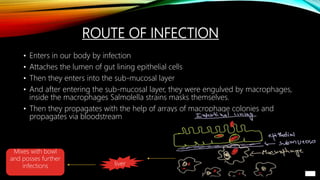
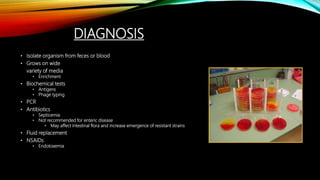
Salmonellosis is an infectious disease caused by Salmonella bacteria, which are rod-shaped, gram-negative bacteria. The disease is characterized by diarrhea, fever, abdominal cramps, and vomiting. Symptoms usually appear 12 to 72 hours after ingesting contaminated food or water and can last up to a week. Salmonella bacteria are commonly transmitted through contaminated foods like poultry, eggs, and produce. At risk groups include the young, elderly, and immunocompromised. While most cases resolve without treatment, antibiotics may be prescribed for severe or prolonged cases. Proper hygiene and sanitation are important for preventing transmission.