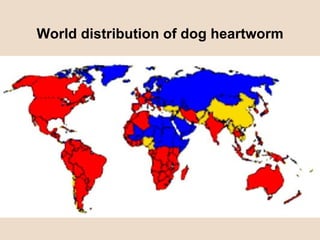
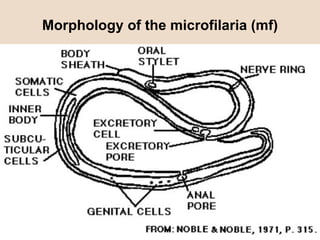
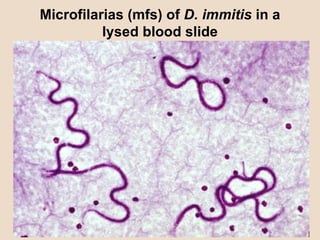
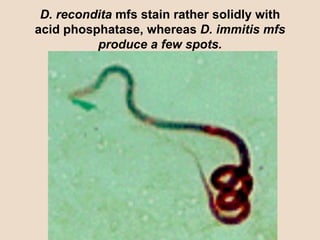
Dog heartworm disease is caused by the nematode Dirofilaria immitis infecting dogs and other canids through mosquito vectors. It causes blockages in major blood vessels leading to reduced blood flow and damage to organs like the lungs, liver and kidneys. Common symptoms include coughing, difficulty breathing, weakness and rapid pulse. Diagnosis is through blood tests detecting microfilariae or antibodies. Treatment aims to eliminate adult worms and microfilariae while limiting complications from dying worms through limited exercise and monitoring for issues like disseminated intravascular coagulation.