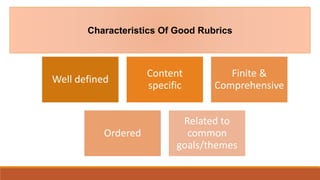
The document discusses rubrics as essential educational tools used for grading and evaluating student work based on specific criteria. It outlines the steps to design effective rubrics, including defining performance skills, listing assessment traits, and establishing gradations of mastery. It also contrasts holistic and analytic rubrics, explaining their advantages and disadvantages in assessment practices.