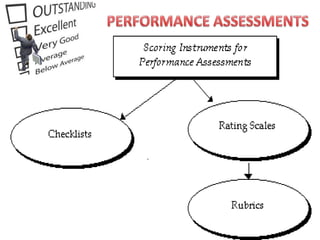
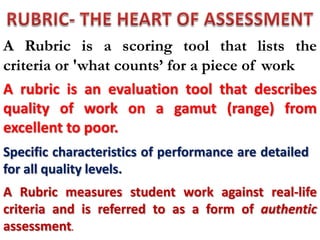
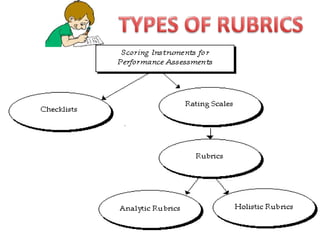
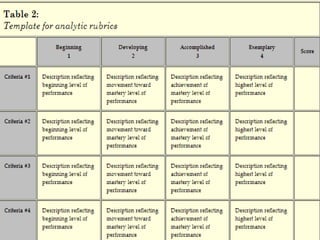
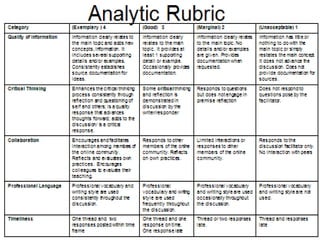
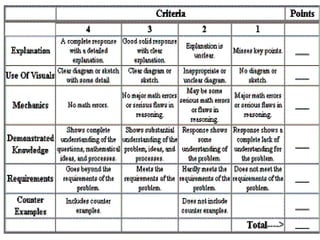
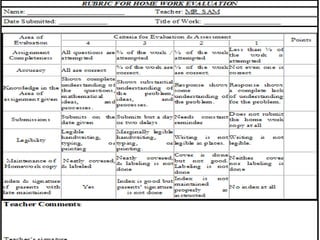
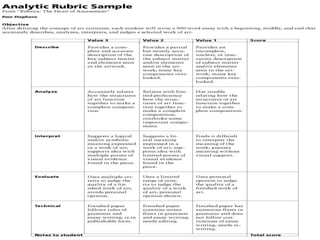
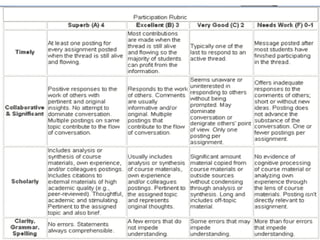
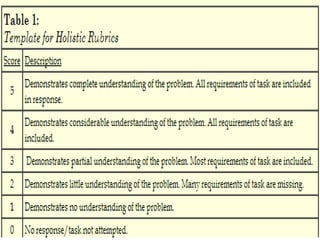
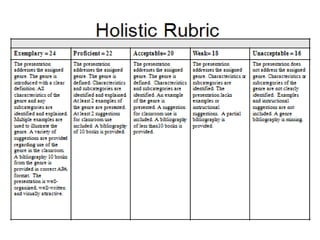
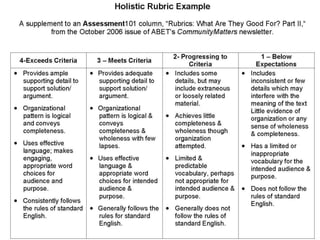
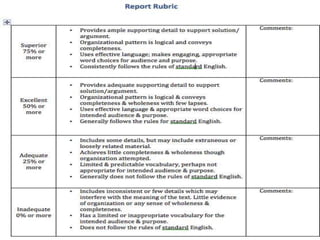
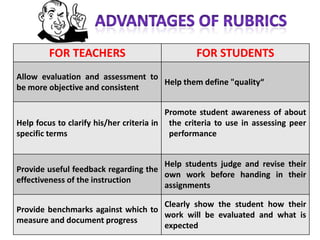
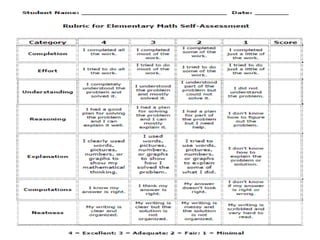
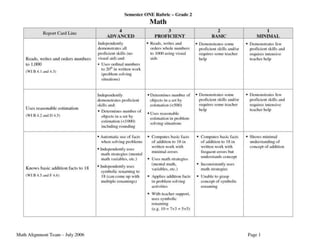
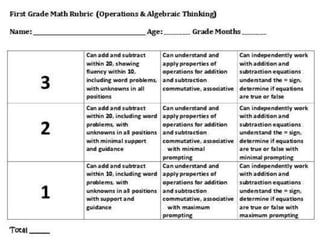
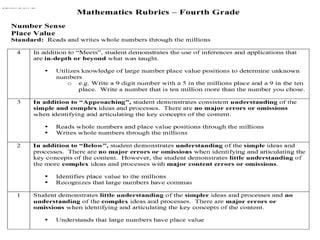
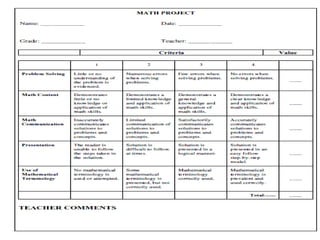
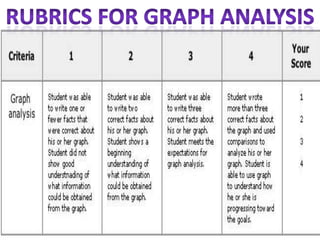
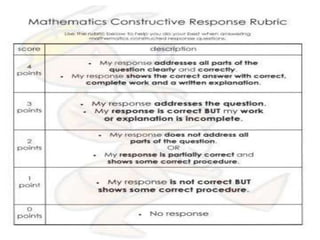
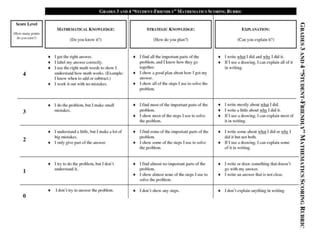
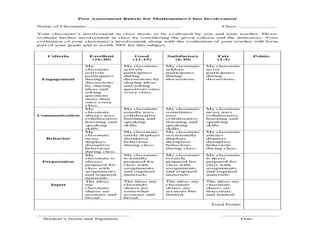
The document discusses the use of rubrics as scoring tools that outline specific criteria for evaluating student work, ranging from excellent to poor. It highlights the differences between analytic rubrics, which assess performance across multiple criteria individually, and holistic rubrics, which provide a single score based on an overall judgment. Additionally, the document notes the advantages and disadvantages of each type of rubric, emphasizing their role in promoting objective assessment and providing feedback for improvement.