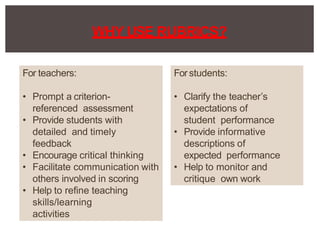
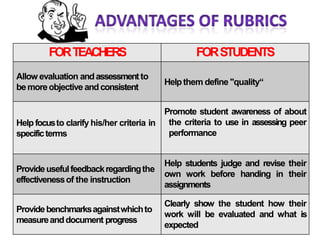
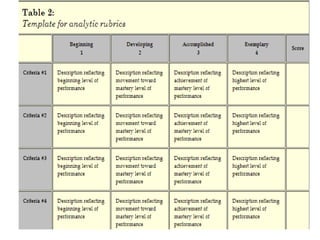
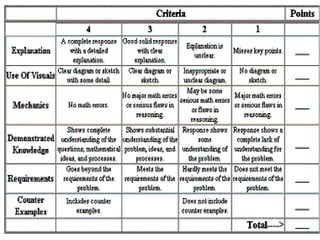
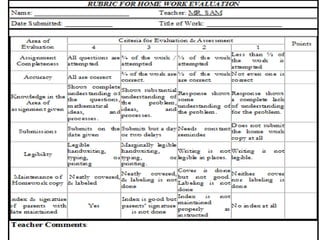
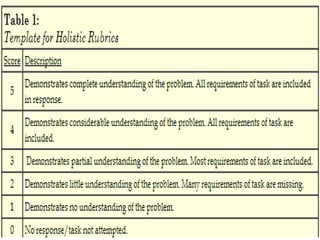
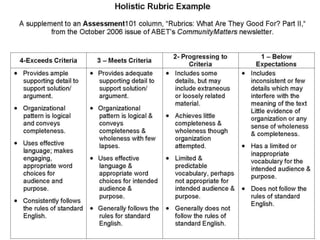
The document discusses rubrics, which are guides that list specific criteria for grading academic work. It explains that rubrics can be analytic, evaluating each criterion separately, or holistic, assigning one overall score. Analytic rubrics provide detailed feedback but take more time, while holistic rubrics are faster to use. The document advises teachers on how to create and implement rubrics to provide transparent assessments and help students understand expectations.